Annular Ligament
Table of Contents
Introduction
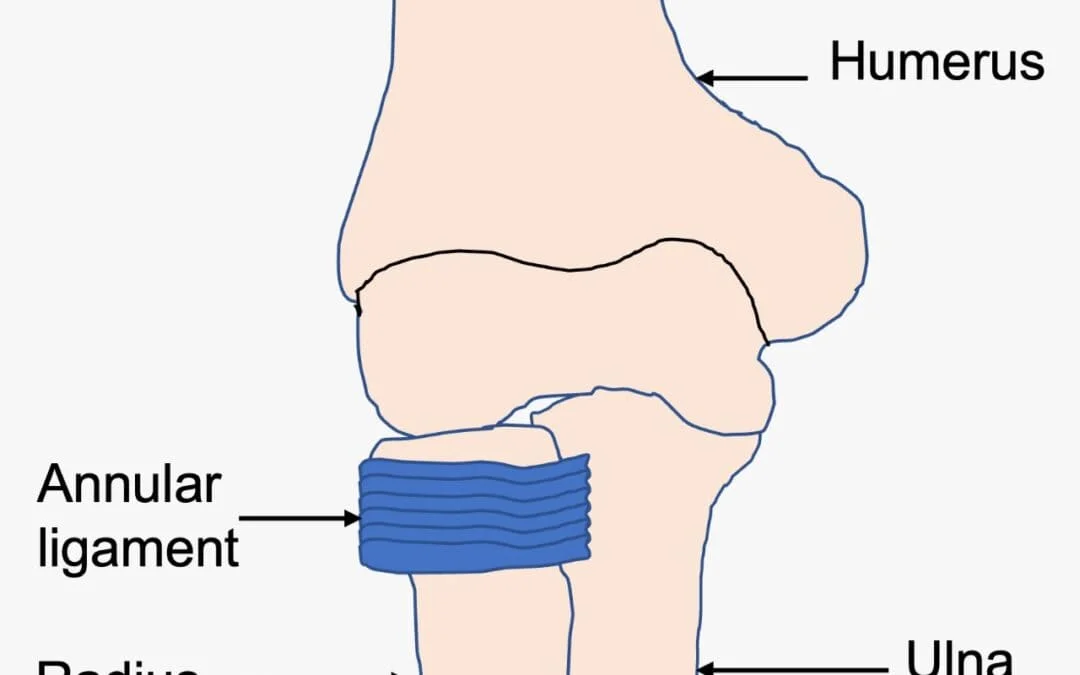
The Annular Ligament is a fibrous band that encircles and stabilizes the head of the radius bone in the elbow joint. It is located around the radial notch of the ulna bone and helps to hold the radius bone in place during movements of the forearm.
The annular ligament is composed of dense connective tissue and is attached to the ulna bone on one end and the radius bone on the other end. It plays an important role in maintaining the stability of the elbow joint and allowing for smooth movements of the forearm. Dysfunction or injury to the annular ligament can result in pain, instability, and limited range of motion in the elbow joint.
Structure of the Annular Ligament
The annular ligament is a fibrous band that encircles the head of the radius bone in the elbow joint. It is a circular structure that is attached to the ulna bone on one end and the radius bone on the other end. The ligament is composed of dense connective tissue, which gives it strength and stability.
The annular ligament is located around the radial notch of the ulna bone, which is a depression on the lateral side of the ulna. The head of the radius bone fits into this notch, forming the proximal radioulnar joint. The annular ligament wraps around the head of the radius bone, holding it in place and allowing it to rotate during movements of the forearm.
The annular ligament has two parts: a proximal part and a distal part. The proximal part is thicker and stronger than the distal part and is attached to the ulna bone. The distal part is thinner and more flexible than the proximal part and is attached to the radius bone.
The annular ligament is reinforced by several structures that help to stabilize the elbow joint. These structures include the quadrate ligament, which attaches the annular ligament to the ulna bone, and the oblique cord, which connects the annular ligament to the radius bone.
The annular ligament plays an essential role in maintaining the stability of the elbow joint and allowing for smooth movements of the forearm. During pronation and supination, the annular ligament allows the head of the radius bone to rotate within the radial notch of the ulna bone. Dysfunction or injury to the annular ligament can result in pain, instability, and limited range of motion in the elbow joint.
Attachments of the Annular Ligament
It is attached to the ulna bone on one end and the radius bone on the other end. The attachment of the annular ligament to the ulna bone is through the quadrate ligament, which is a thickened band of connective tissue that runs from the medial border of the ulna bone to the annular ligament. The quadrate ligament reinforces the annular ligament, providing additional stability to the elbow joint.
The attachment of the annular ligament to the radius bone is through the oblique cord, which is a thin band of connective tissue that runs from the lateral aspect of the ulna bone to the annular ligament. The oblique cord reinforces the distal part of the annular ligament, allowing it to maintain its flexibility and allow for smooth movements of the forearm.
The attachment of the annular ligament to the radius bone is also through a bony ridge called the supinator crest, which is located on the lateral aspect of the radius bone. The annular ligament wraps around the head of the radius bone and attaches to this bony ridge, holding it in place and allowing it to rotate during movements of the forearm.
In general, the attachment of the annular ligament to both the ulna and radius bones provides stability to the elbow joint and allows for smooth movements of the forearm. Dysfunction or injury to any of these attachments can result in pain, instability, and limited range of motion in the elbow joint.
Functions of the Annular Ligament
The annular ligament plays a crucial role in the stability and movement of the elbow joint.
These major functions are:
- Stabilization: The annular ligament helps to keep the head of the radius bone in place within the elbow joint. This is important because the radius bone rotates around the ulna bone during movements of the forearm. Without the annular ligament, the head of the radius bone could slip out of place, leading to instability and pain.
- Flexibility: Although the annular ligament provides stability, it also needs to be flexible enough to allow for smooth movements of the forearm. The oblique cord and supinator crest attachments help to reinforce the annular ligament while still allowing it to flex and rotate as needed.
- Protection: The annular ligament helps to protect the joint from excessive wear and tear. By keeping the head of the radius bone in place, it prevents it from rubbing against other bones or soft tissues in the joint.
- Transmission of forces: During activities that involve gripping or twisting, forces are transmitted through the elbow joint. The annular ligament helps to distribute these forces evenly throughout the joint, reducing the risk of injury.
So in general, the annular ligament is a vital structure in the elbow joint that provides stability, flexibility, protection, and force transmission. Dysfunction or injury to this ligament can lead to pain, instability, and limited range of motion in the elbow joint.
Injuries of the Annular Ligament
Annular ligament injuries can occur due to a variety of activities that put stress on the elbow joint. Some common causes of annular ligament injuries include:
- Repetitive motions: Activities that involve repetitive motions of the elbow joint, such as throwing a baseball or playing tennis, can put a lot of stress on the annular ligament and surrounding tissues. Over time, this can lead to wear and tear on the ligament and increase the risk of injury.
- Trauma: Trauma to the elbow joint, such as a fall or direct blow to the arm, can cause damage to the annular ligament. This type of injury is more common in contact sports or activities that involve high impact.
- Overuse: Overuse of the elbow joint, such as excessive weightlifting or typing, can also lead to annular ligament injuries. This is because these activities put constant strain on the ligament, which can cause it to become inflamed or torn over time.
- Improper technique: Using improper technique when performing certain activities, such as lifting weights or playing sports, can also increase the risk of annular ligament injuries. This is because an incorrect form can put additional stress on the elbow joint and surrounding tissues.
So in the end, it is important to take steps to prevent annular ligament injuries by using proper technique during activities, taking breaks to rest and stretch the elbow joint, and seeking medical attention if any pain or discomfort occurs.
Symptoms of the Annular Ligament Injury
Symptoms of annular ligament injuries can vary depending on the severity of the injury, but some common symptoms include:
- Elbow Pain: Pain in the elbow joint is one of the most common symptoms of an annular ligament injury. The pain may be sharp or dull and may be felt during activities that put stress on the elbow joint.
- Swelling: Swelling around the elbow joint is another common symptom of an annular ligament injury. The swelling may be mild or severe and may be accompanied by redness or warmth in the affected area.
- Stiffness: Stiffness in the elbow joint is another symptom of an annular ligament injury. The stiffness may be mild or severe and may make it difficult to move the arm or perform certain activities.
- Weakness: Weakness in the affected arm is another symptom of an annular ligament injury. This may be due to pain or damage to the ligament, which can make it challenging to use the arm usually.
- Clicking or popping: Clicking or popping sounds in the elbow joint is another symptom of an annular ligament injury. This may be due to a tear or other damage to the ligament, which can cause the joint to move abnormally.
So in the end, if you feel any of these symptoms, it is important to take medical attention to determine the cause and receive appropriate treatment.
Diagnosis
The diagnosis of an annular ligament injury typically involves a physical examination and imaging tests. During the physical exam, the doctor will examine the affected arm and elbow joint, looking for signs of swelling, stiffness, and pain. They may also move the arm and elbow joint in different directions to check for weakness or instability.
Imaging tests such as X-rays, MRI, or ultrasound may also be used to diagnose an annular ligament injury. X-rays can help rule out other conditions such as fractures or dislocations, while MRI or ultrasound can show the extent of the damage to the ligament.
In some conditions, the doctor may also perform an arthroscopy, which involves inserting a small camera into the joint to examine the annular ligament and surrounding structures. This can help provide a more detailed diagnosis and determine the best course of treatment.
So in general, a thorough physical examination and imaging tests are typically used to diagnose an annular ligament injury and determine the appropriate treatment plan.
Treatment of the Annular Ligament Injury
Treatment of the annular ligament can be done in two ways;
conservative treatment
physiotherapy treatment
Conservative treatment
Conservative treatment of an annular ligament injury typically involves rest, ice, compression, and elevation (RICE). This can help in reducing pain and swelling in the injured area.
Resting the affected arm and avoiding activities that aggravate the injury can help prevent further damage to the annular ligament. Ice packs or cold compresses can be applied to the area for 15-20 minutes at a time, several times a day, to reduce swelling and inflammation.
Compression with a bandage or brace can also help reduce swelling and provide support to the affected area. Elevation of the arm over the heart level can also help in reducing swelling and promoting healing.
Pain medications such as acetaminophen or nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) may also be recommended to help in managing pain and inflammation.
Physical therapy may also be recommended to help improve the range of motion, strength, and flexibility in the affected arm. This may involve exercises to stretch and strengthen the muscles surrounding the elbow joint, as well as manual therapy techniques such as massage or joint mobilization.
In some conditions, a splint or brace may be recommended to immobilize the affected arm and allow the annular ligament to heal. This may be necessary if conservative treatment does not provide adequate relief or if there is a risk of further injury.
So in the end, conservative treatment of an annular ligament injury focuses on reducing pain and inflammation, promoting healing, and restoring function to the affected arm.
Physiotherapy treatment
Physiotherapy treatment for an annular ligament injury typically involves a combination of exercises, manual therapy techniques, and other modalities to help reduce pain and inflammation, improve range of motion, and restore function to the affected arm.
Initially, the physiotherapist will conduct a thorough assessment of the injury to determine the extent of the damage and develop an individualized treatment plan. This may include:
Rest and immobilization: In the acute phase of the injury, the physiotherapist may recommend resting the affected arm and immobilizing it with a splint or brace to allow the annular ligament to heal.
Ice therapy: The application of ice packs or cold compresses to the injured area can help in reducing pain and swelling.
Manual therapy: Manual therapy techniques such as massage, joint mobilization, and stretching can help improve the range of motion and reduce muscle tension around the elbow joint.
Strengthening exercises: Strengthening exercises for the muscles surrounding the elbow joint can help improve stability and prevent further injury.
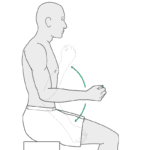
Range of motion exercises: Range of motion exercises can help improve flexibility and mobility in the affected arm.
Ultrasound therapy: Ultrasound therapy uses high-frequency sound waves in order to promote healing and reduce pain and inflammation in the injured area.
Electrical stimulation: Electrical stimulation can be used to reduce pain and improve muscle strength and function.
The physiotherapist will monitor progress throughout the treatment process and adjust the treatment plan as needed to ensure optimal results. With proper physiotherapy treatment, most patients with an annular ligament injury can expect to experience significant improvement in pain, function, and quality of life.
Risk factors of the annular ligament
The annular ligament is a band of tissue that surrounds the head of the radius bone in the forearm, helping to keep it in place within the elbow joint. While it is a strong and resilient structure, there are several risk factors that can increase the likelihood of an annular ligament injury, including:
- Overuse: Repetitive motions of the forearm and elbow, such as those involved in sports like tennis or golf, can put excessive strain on the annular ligament and lead to injury.
- Trauma: Direct trauma to the elbow joint, such as a fall or impact, can cause the annular ligament to stretch or tear.
- Age: As we age, our tissues become less elastic and more prone to injury. Older adults may be more susceptible to annular ligament injuries.
- Genetics: Some individuals may be born with weaker or more fragile ligaments, making them more prone to injury.
- Poor posture: Poor posture can put increased stress on the elbow joint and its surrounding structures, including the annular ligament.
- Improper technique: Using improper technique during sports or other physical activities can increase the risk of injury to the annular ligament and other structures in the elbow joint.
- Medical conditions: Certain medical conditions, such as rheumatoid arthritis or osteoarthritis, can weaken the annular ligament and make it more susceptible to injury.
- Poor nutrition: A diet lacking essential nutrients like protein and vitamin C can weaken the body’s tissues and increase the risk of injury to the annular ligament and other structures in the elbow joint.
It is very crucial to be aware of these risk factors and take steps to minimize them in order to reduce the likelihood of an annular ligament injury. This may include maintaining good posture, using proper technique during physical activities, and ensuring a balanced and nutritious diet.
How to prevent injuries of the Annular Ligament?
Preventing annular ligament injuries involves a combination of lifestyle changes, proper technique during physical activities, and medical management of underlying conditions. Here are some tips for preventing annular ligament injuries:
- Maintain good posture: Poor posture can put increased stress on the elbow joint and its surrounding structures, including the annular ligament. To prevent injury, maintain proper posture while sitting, standing, and performing physical activities.
- Use proper technique during physical activities: Using improper technique during sports or other physical activities can increase the risk of injury to the annular ligament and other structures in the elbow joint. To prevent injury, learn the proper technique and form for your chosen activity and use it consistently.
- Stretch before physical activity: Stretching before physical activity can help warm up your muscles and prevent injury. Focus on stretching your forearm, wrist, and elbow muscles to prepare them for activity.
- Strengthen your forearm muscles: Strong forearm muscles can help support the elbow joint and reduce the risk of injury to the annular ligament. Involve exercises that focus your forearm muscles in your workout routine.
- Wear appropriate protective gear: If you participate in high-risk activities like contact sports or rock climbing, wearing appropriate protective gear like elbow pads can help prevent injury.
- Manage underlying medical conditions: Certain medical conditions, such as rheumatoid arthritis or osteoarthritis, can weaken the annular ligament and make it more susceptible to injury. Work with your healthcare provider to manage any underlying conditions that may increase your risk of injury.
- Maintain a balanced and nutritious diet: A diet lacking essential nutrients like protein and vitamin C can weaken the body’s tissues and increase the risk of injury to the annular ligament and other structures in the elbow joint. To prevent injury, maintain a balanced and nutritious diet that includes plenty of lean protein, fruits, vegetables, and whole grains.
By incorporating these tips into your lifestyle, you can reduce your risk of annular ligament injuries and other elbow joint injuries. If you do experience pain or discomfort in your elbow, take medical attention promptly to prevent further injury and promote healing.
FAQ
The annular ligament is a band of fibrous tissue that wraps around and holds the head of the radius bone in place within the elbow joint.
The annular ligament is located in the elbow joint, specifically around the head of the radius bone.
The annular ligament helps to stabilize the head of the radius bone within the elbow joint, allowing for smooth movement of the forearm.
Common injuries or conditions associated with the annular ligament include annular ligament tears, radial head subluxation (partial dislocation), and chronic instability of the elbow joint.
Injuries or conditions of the annular ligament are typically diagnosed through physical examination, imaging studies (such as X-rays or MRI), and sometimes arthroscopy. Treatment may include rest, immobilization, physical therapy, or surgery relay on the effect of the injury.
Preventative measures to avoid injuries of the annular ligament include maintaining strong forearm muscles through exercise, avoiding repetitive motions that strain the elbow joint, and wearing protective gear during activities that pose a risk for elbow injury.