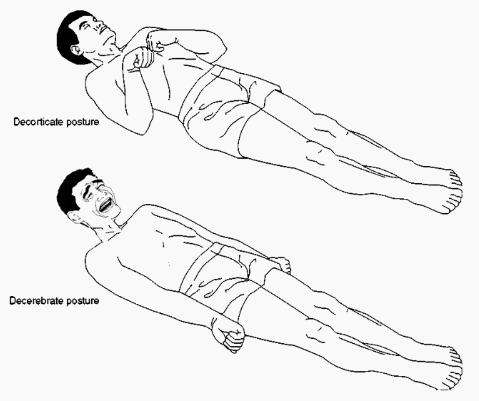
Decerebrate posture vs Decorticate posture:
Decerebrate posture vs Decorticate posture is a mostly an abnormal posture in which Body a typical rigid state mostly related severe damage to Brain related condition symptoms and treatment are vary depends upon cause, symptoms and Diagnosis of the condition.
There may be Decorticate posture in one side of the Body and the decerebrate posture on other side of the Body in severe Brain related injury or condition. Decorticate posture and Decerebrate posture Both are severe brain related condition require medical emergency, However comparatively Decerebrate posture is more severe condition.
If Decordticate posture worsens or untreated may leads to Decerebrate posture.
In This article we inform you how to differentiate between Decerebrate posture vs Decorticate posture and which posture is worse as compared to other.
Table of Contents
What is Decerebrate posture?
Decerebrate posture is caused by damage to the cerebral cortex but the clinical manifestations depend on the site of the lesion. Causes of decerebrate postures include seizures, tumors, vascular lesions, and trauma. Spontaneous nystagmus or eye deviation is also seen in decerebrate postures. This type of posturing usually indicates that there has been severe damage to the brain.
Decerebrate posture is a rare type of posture seen in people who have injuries to their brainstem and is a rare medical condition, in which the upper extremities are held outstretched and internally rotated. In this position, the arms are pronated with the forearms held vertically, the toes being pointed downward, and the head and neck being arched backward. The legs are also extended and pronated.The patient is rigid, with the teeth clenched. This kind of posturing seen mostly in severe midbrain lesions.
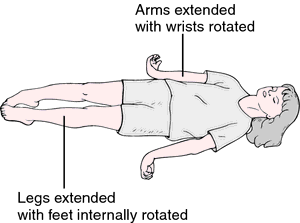
Decerebrate posture can occur on one side or both sides, or in just the arms or limbs. It is also seen with another type of abnormal posture called decorticate posture . A person who have decorticate posture on one side of the body while at the opposite side decerebrate posture in few severe cases.
Opisthotonos may occur in severe cases of decerebrate posture where a severe muscle spasm of the neck and back are seen. The Nobel Laurette Charles Sherrington first time described decerebrate posturing in 1898 after transecting the brainstems of live monkeys and cats.
Decerebrate posturing are considered pathological posturing responses to usually unpleasant stimuli from an external or internal, in which stereotypical body movements of the trunk and limb are seen.
What is Decorticate posture?
Decorticate posture is an abnormal posture in which a patient’s Body is in rigid-stiff with both arms flexed over the chest, while fingers clenched , wrist flexed, and both legs are in extended full-straight. The arms are bent in toward the body and the wrists and fingers are bent and held on the chest. This type of posturing is a sign of severe damage in the brain.
People who have this condition should require emergency medical treatment. It may occur on one or both sides of the body.
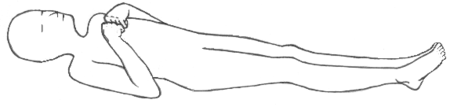
It is an abnormal posture characterized by body is in rigid state with arms flexed, fingers clenched and wrist flexed positioned while lower extremities are extended occurs mainly due to brain related condition.
Decorticate posturing is a type of pathological state in which patient is unable to control body movement and its require immediate medical treatment. It is often an indication of certain types of severe Brain or spinal cord injury.
Decerebrate posture vs Decorticate posture comparison:
Following are the few difference points Between Decerebrate posture vs Decorticate posture.
| Name | Decorticate Posture | Decerebrate posture |
| Body Position | a patient’s Body is in rigid-stiff with both arms flexed over the chest, while fingers clenched , wrist flexed, and both legs are in extended full-straight. | The upper extremities are held outstretched and internally rotated. |
| The arms are bent in toward the body and the wrists and fingers are bent and held on the chest. | In this position, the arms are pronated with the forearms held vertically, the toes being pointed downward, and the head and neck being arched backward. | |
| The legs are also extended and pronated.The patient is rigid, with the teeth clenched. | ||
| Causes | Traumatic brain injury (TBI) Bleeding in the brain Certain types of Brain cancer mainly Brain tumor Stroke overdose of Drugs side effects that affects the Brain (poisoning, infection, or liver failure) Increased pressure in the brain Infection, such as Reye’s syndrome, malaria, or Meningitis, encephalitis. Brain injury from lack of oxygen Seizures Coma | Haemorrhage in the brain from any cause Brain tumour Brain Abscess Hemorrhagic Stroke Brain affected mainly due to side effect of drugs, poisoning or fungal , Bacterial infection Head- brain injury Brain injury due to liver failure Increased pressure in the brain from any cause such as Hydrocephalus Low blood sugar (hypoglycaemia) Brain tumour Infections, such as meningitis Intracerebral hemorrhage. Reye syndrome ( liver function and brain damage related problems that mostly affects children) Brain injury from lack of oxygen Cerebral malaria Lead poisoning |
| Symptoms | A severe muscle spasticity in flexor group of upper limb muscles and extensor group of lower limb muscles | A severe muscle spasm of the neck and back may occur in severe cases of decerebrate posture(Opisthotonos posture). |
| In Decorticate posture, movement pattern are adduction and internal rotation of shoulder, flexion at the elbows with pronation of the forearm, wrist are flexed and flexion of the fingers. The both hands are placed over the chest. | In Decerebrate posturing movement pattern are adduction and internal rotation of the shoulder, extension at the elbows with pronation of the forearm, and flexion of the fingers and the lower limbs movement pattern are Hip extended and internally rotated with the knee also extended and Ankle are plantar flexed while Toes are typically abducted and hyperextended. | |
| Patient is mostly unconscious or semi-unconscious state with unable to control body movement | The patient is in rigid state with the teeth clenched. | |
| There may paralysis of one side of Body or it may cerebral palsy in severe cases. | The decerebrate posture can be seen on just one side of the body or on both sides, and it may be only in the arms and may be both arms and legs in severe trauma. | |
| Severe Rigidity or Spasticity | Decerebrate posturing responses to usually unpleasant stimuli from an external or internal where exetends arms and leg movements of the trunk and extremities are typically indicative of significant brain or spinal injury. | |
| Prognosis | This abnormal posture could indicate severe brain damage of nervous system injury and sometimes permanent brain damage. | Normally people showing decerebrate posture are in a coma and have poor prognoses, with risks for cardiac arrhythmia or arrest and respiratory failure. It is more severe case of Decorticate posture. |
| Damage to which part of The Body | Mostly area of the midbrain, which is located between the brain and spinal cord. The midbrain controls motor movement. | large bilateral forebrain lesions with progression caudally into the diencephalon and midbrain. posterior fossa lesion compressing the midbrain or rostral pons. the level between the superior and inferior colliculi within the midbrain (being at or below the level of the red nucleus) |
| Other Name | Decorticate response, decorticate rigidity, flexor posturing, or, colloquially, mummy baby. | Opisthotonos posture |
Which posturing is worse Decorticate or decerebrate?
The Decorticate posture is still a life-threatening sign of severe brain damage while Decerebrate posture is a sign of more severe damage of the Brain at the rubrospinal tract, and so, the red nucleus is also involved, showing a lesion lower in the brainstem.
What is the main difference between Decorticate and decerebrate rigidity?
In decerebrate posture, in which the arms extending at the sides of the body, while in the decorticate posture the arms are flexed over the chest with wrist and finger are flexed. There may be Decerebrate posture in one side of the body while decordticate posture in the opposite side of the Body.
FAQ
Which is better Decorticate or decerebrate?
The main principles of the Rood approach are normalization of tone, gradual developmental sequence, purposeful movement restoration, and repetition or practice.
What is Rood’s approach used for?
The Rood Approach used for the treatment of central nervous system disorders developed by Margaret Rood in the 1950s provides the origin for many of the facilitation and inhibition techniques.