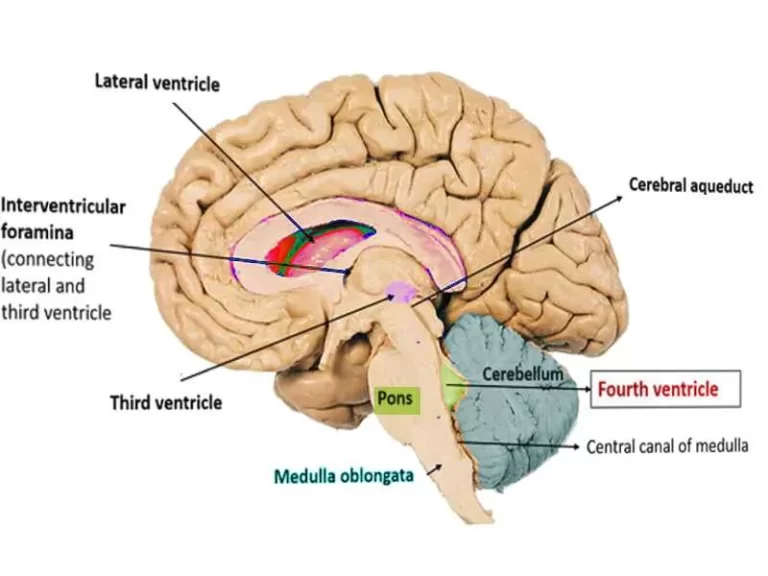
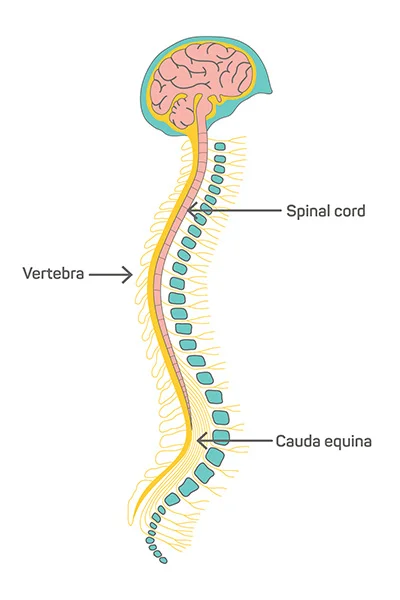
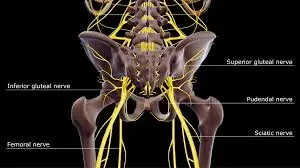
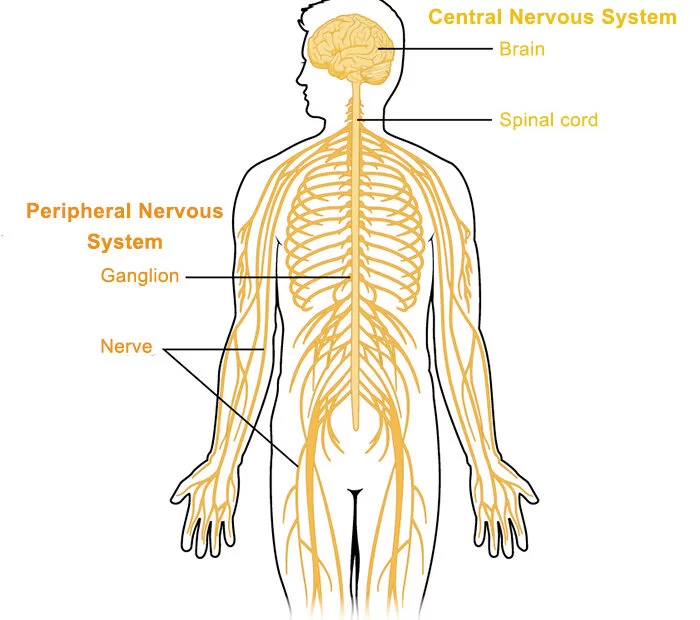
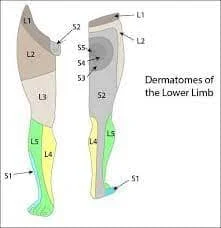
Nerve Tissue Composition
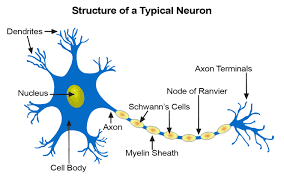
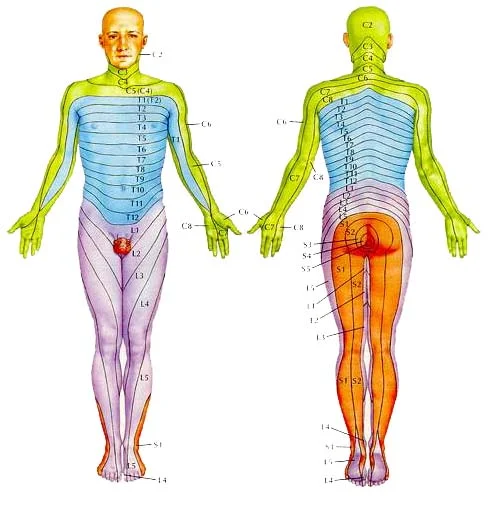
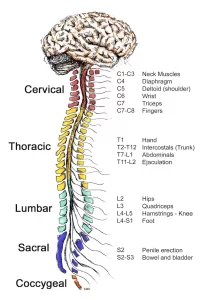
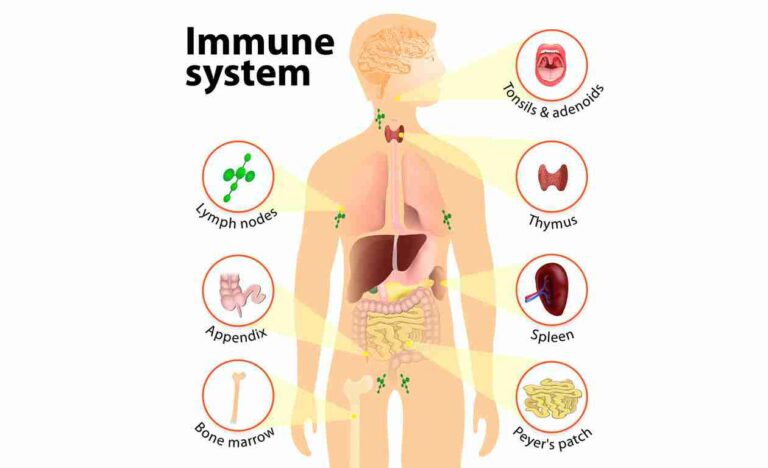
Nerve tissue is a fundamental component of the nervous system, responsible for transmitting signals throughout the body. Comprising of specialized cells called neurons, nerve tissue is characterized by its unique structure and function. What is a Nerve Tissue Composition? Within the neurological system, neurons are cells that send messages to other neurons, muscles, or gland…