List Of Neurological Conditions Related To Physiotherapy Only
List Of Neurological Condition Related To Physiotherapy Only :
(1) Cerebral palsy
(2) Reflex sympathetic dystrophy
(3) Amyotrophic lateral sclerosis
(4) Multiple sclerosis
(5) Stroke
(6) Trigeminal neuralgia
(7) Guillain barre syndrom
(8) Hemilegia
(9) Quadriplegia
(10) Paraplegia
(11) Facial palsy
(12) Epilepsy
(13) Parkinsons disease
(14) Aneurysms
(15) Muscle dystrophy
(16) Hydrocephalus
(17) Attention Deficit hyperactivity disorder(ADHD)
(18) Agnosia
(19) Aphasia
(20) Apraxia
(21) Arnold-chiari malformation
(22) Spina bifida
(23) Ataxia
(24) Beckers myotonia
(25) Brachial plexus injuries
(26) Brown sequard syndrome
(27) Carpal tunnel syndrome
(28) causalgia
(29) Cushings syndrome
(30) Dandy walker syndrome
(31) Dementia
(32) Dystonia
(33) Encephalopathy
(34) Erb’s palsy
(35) Foot drop
(36) Herpes zoster
(37) Muscular dystrophy
(38) Myasthenia gravis
(39) Peripheral neuropathy
(40) Polymyositis
(41) Reflex sympathetic syndrome
(42) Tabes dorsalis
(1) Cerebral palsy :
loss or impairment of motor function, Cerebral Palsy is actually caused by brain damage. The brain damage is caused by brain injury or abnormal development of the brain that occurs while a child’s brain is still developing — before birth, during birth, or immediately after birth.Cerebral Palsy affects body movement, muscle control, muscle coordination, muscle tone, reflex, posture and balance. It can also impact fine motor skills, gross motor skills and oral motor functioning.
Physiotherapy :
Common Treatment Varies According To Condition :
Passive Stretching
Manual Stretching
Weight Bearing
Splinting
Serial Casting
Static Weight-bearing Exercises
Muscle Strengthening Exercises
Functional Exercises
Body Weight Supported Treadmill Training
Electrical Stimulation
Hippo-therapy
(2) Reflex sympathetic dystrophy :
Reflex Sympathetic Dystrophy syndrome (RSD) is a complex multi-symptom pain syndrome affecting a limb or limbs that can affect any one of any age. It usually occurs following tissue damage to the limb, but it can also be triggered by visceral diseases, central nervous system lesions or from unknown causes.
Physiotherapy :
- The most important element of treating RSD syndrome is restoring normal movement to the affected part.
- TENS (Trans cutaneous Electrical Nerve Stimulation)
- Infrared thermography
- Comorbidity such as depression, sleep disturbance and anxiety
- Aquatic therapy allows activities to be performed with decreased weight bearing on the lower extremities.
- Mirror therapy
- Desensitization
- Gradual weight bearing
- Stretching.
(3) Amyotrophic lateral sclerosis :
Amyotrophic lateral sclerosis is a type of motor neuron disease. It refers to a group of progressive, neurological diseases that cause dysfunction in the nerves that control muscle movement.
physiotherapy :
- Physical therapy can help people with amyotrophic lateral sclerosis (ALS) learn to adjust to their physical disabilities.
- Improving function, evaluating each patient’s joint range of motion, strength and general mobility skills.
- Stretching exercises
- Range of motion exercises (ROM)
- Strengthening exercises
(4) Multiple sclerosis :
Multiple sclerosis is a chronic disease that attacks the central nervous system. It affects the brain, spinal cord, and optic nerves. Multiple sclerosis affects the central nervous system.
Diagnosis usually happens between the ages of 20 and 50 years.
physiotherapy :
- PT for MS involves exercises to strengthen your muscles and improve your gait (how you walk) and your balance and coordination.
- It also involves stretches to help you maintain mobility and prevent muscle spasms.
- PT can also include training on how to use mobility aids like a cane, walker, or wheelchair.
- improve strength
- improve mood and well-being.
(5) Stroke :
A stroke, sometimes called a “brain attack,” occurs when blood flow to an area in the brain is cut off. The brain cells, deprived of the oxygen and glucose needed to survive, die. If a stroke is not caught early, permanent brain damage or death can result.
There are two types of stroke : (1) Ischemic stroke
(2) Hemorrhagic stroke
physiotherapy :
- acute care – prevention of recurrent events, mobilization, and screening.
- Rehab care – Setting rehab goals
- Manage motor deficiency
- Prevent and treat complications
(6) Trigeminal neuralgia :
Trigeminal neuralgia is a chronic pain condition that affects the trigeminal nerve, which carries sensation from your face to your brain.may initially experience short, mild attacks. trigeminal neuralgia can progress and cause longer, more-frequent bouts of searing pain.
physiotherapy :
- Pain Relief – Both acupuncture and TENS are exciting great controversy at the present time.
- Dorsal column stimulation, Treatments include the use of electro-physical agents and acupuncture to relieve pain during acute onset. Manual therapy,exercise therapy for TemporomandibularJoint (TMJ) as well as self-massage for facial muscles can also help to restore patients’ functions.
- Interferential therapy (IFT) is another electro- physicalmodality commonly used for pain management in clinical situations.
(7) Parkinsons disease :
Parkinson’s disease affects the nerve cells in the brain that produce dopamine. Parkinson’s disease symptoms include muscle rigidity, tremors, and changes in speech and gait. After diagnosis, treatments can help relieve symptoms, but there is no cure.
physiotherapy :
- Reduces stiffness, improves mobility, posture, balance and gait, Aerobic exercise.
- posture, trunk rotation and normal rhythmic, symmetric movements are the best. Riding a stationary bicycle without doing other activities, Weight lifting
- Treadmill walking at a slow speed.Activities in a standing position strengthen legs
- Pushing up to rise on the toes
- Modified squats
- Repetitively rising and sitting from a chair
- Wearing ankle and wrist weights around the house or out on a walk.
(8) Aneurysms :
An excessive localized swelling of the wall of an artery.“An aneurysm is some sort of bulging of a blood vessel within the body.
The thick walls of the arteries are meant to hold up under normal blood pressure, but when the walls weaken or become damaged, an aneurysm can develop.
physiotherapy :
- The aims of the physiotherapy program were to avoid complications of bed rest, improve postural control and functional activity, and provide post-discharge education for patients and their families.Physiotherapy focused on muscle control, quality of movement, weight bearing and trunk stability.
(9) Guillain barre syndrom :
Gullian-Barré syndrome is a rare but serious autoimmune disorder in which the immune system attacks healthy nerve cells in your peripheral nervous system. This leads to weakness, numbness, and tingling. It can eventually cause paralysis.
physiotherapy :
- passive limb movements to maintain joint ranges of movement and muscle flexibility whilst they are immobilized in bed.
- Later, as the patient begins to recover limb control, physiotherapy is vital in assisting the restoration of muscle strength, limb control, balance and coordination.
- Neuro-physiotherapy rehabilitation aims to increase muscle strength, maintain joint ranges of movement, restore mobility and balance, and re-train the normal movement patterns that are necessary for normal function and independence.
(10) Paraplegia :
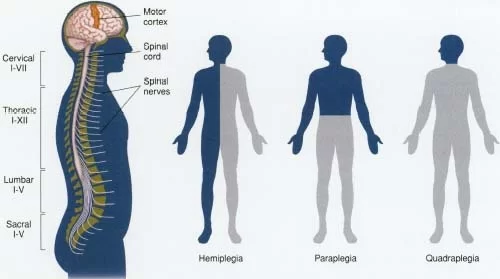
partial or complete paralysis of the lower half of the body with involvement of both legs that is usually due to injury or disease of the spinal cord in the thoracic or lumbar region.
physiotherapy :
- passive movement
- full ROM movement for mobility
- in spastic patient stretching
- balance training
- sitting activity
- bed activity
- education about condition of the patient.
(11) Hemiplegia :
Total or partial paralysis of one side of the body that results from disease of or injury to the motor centers of the brain. usually suffered brain damage, often from a wound or blood clot.
Physiotherapy :
- Positioning, Early Mobilization,
- Balance- trunk exercise training improve trunk performance and dynamic sitting balance.
- Gait & Mobility- improving walking and includes exercise.
- gradual weight bearing on affected side.
- active- passive movement, strengthening exercise.
- over-ground walking, circuit classes and treadmill training with and without body weight support.
- Orthotics – Prevention or Correction of Deformity
- Electrical Stimulation
- Mirror Therapy
- Cardio respiratory Training
- Stretch.
(12) Quadriplegia :
one affected with partial or complete paralysis of both the arms and legs especially as a result of spinal cord injury or disease in the region of the neck.
physiotherapy :
- The goal is to help a patient manage pain,
- improve circulation, prevent or reduce muscle atrophy, contractures, and weakness,
- and improve their overall health and wellness.
- This is done by helping to retrain your brain and body in an attempt to regain some or all lost mobility.
- This type of traditional therapy involves a lot of hands-on therapy, exercises, and stretching maneuvers to facilitate movement.
- Muscle stretching,
- Massage therapy,
- Joint manipulation,
- Acupuncture, and
- Neurodynamic exercises.
(13) Facial palsy :
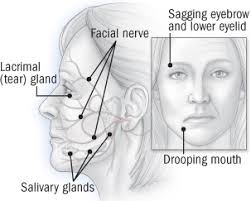
Facial muscle also called Bell’s palsy where – paralysis is a loss of facial movement due to nerve damage.
Your facial muscles may appear to droop or become weak. It can happen on one or both sides of the face.
Common causes of facial paralysis include: infection or inflammation of the facial nerve.
physiotherapy :
- Massage to keep the muscles mobile and healthy.
- Relaxation of your facial nerve and muscles.
- Exercises to reduce involuntary, unwanted movements.
- Education about how the facial nerve works and how it recovers plays a very important part in the therapy.
- facial expression movement
- Electrical stimulation.
(14) Epilepsy :
A neurological disorder marked by sudden recurrent episodes of sensory disturbance, loss of consciousness, or convulsions, associated with abnormal electrical activity in the brain.
physiotherapy :
- Improving the quality of movement and physical performance,
- Physiotherapists improve sensory awareness, balance and coordination, strength and mobility, increasing the range and sphere of movement.
(15) Muscle dystrophy :
One of a group of genetic diseases characterized by progressive weakness and degeneration of the skeletal or voluntary muscles which control movement. The muscles of the heart and some other involuntary muscles are also affected in some forms of muscular dystrophy, and a few forms involve other organs as well.
progressive weakening and wasting of the muscles.
physiotherapy :
- Physiotherapy helps slow the depression of range of motion.
- Muscle strength
- Activity daily living
- Work to improve gait pattern/ posture
- Stretching – can be a combination of active and passive stretches
- Cope up with muscle extensible and muscle contracture.
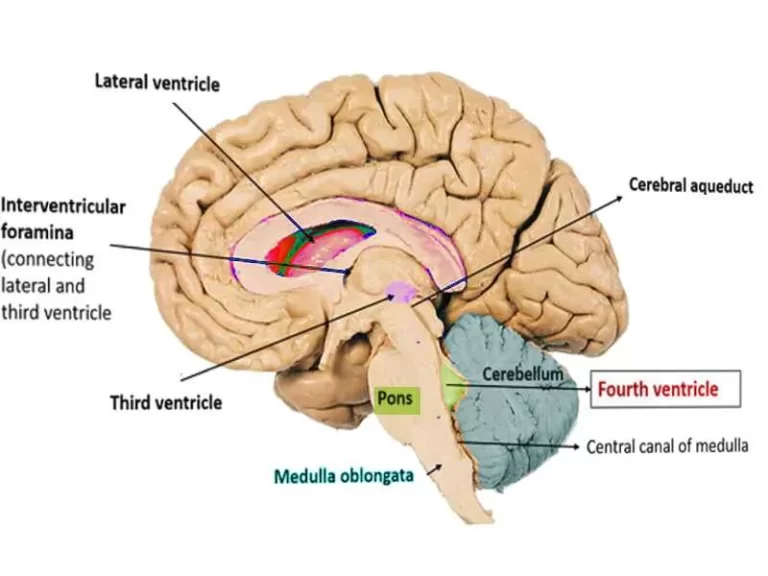
(16) Hydrocephalus :

Hydrocephalus is the buildup of fluid in the cavities (ventricles) deep within the brain. The excess fluid increases the size of the ventricles and puts pressure on the brain.
Hydrocephalus is a condition in which excess cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) builds up within the ventricles (fluid-containing cavities) of the brain and may increase pressure within the head.
physiotherapy :
- Provide gait training (walking exercises) to improve the co-ordination and way your child moves.
- Strengthening exercises can help decrease muscle wastage and improve their functional abilities such as crawling, walking or climbing stairs.
- Stretching can help lengthen your child’s muscles.
(17) Attention Deficit hyperactivity disorder(ADHD) :
Attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder (ADHD) is a brain disorder marked by an ongoing pattern of inattention and/or hyperactivity-impulsivity that interferes with functioning or development.
Physiotherapy :
Aerobic exercise : Aerobic exercise creates new pathways in your brain.
Martial arts: Experts say the more complex your exercise is, the better for your brain.
Focus and concentration
Balance
Timing
Memory
Consequences of actions
Fine motor skills
Gymnastics
Yoga
Rock climbing
Strength training :
Lunges
Squats
Pushups
Pull-ups
Weightlifting
(18) Agnosia :
loss or diminution of the ability to recognize familiar objects or stimuli usually as a result of brain damage.
physiotherapy :
- Physicians may recommend that people with agnosia get sensory information through other senses, that others explain objects verbally to people with agnosia, or that people with agnosia institute organizational strategies to cope with their symptoms.
- Relaxation technique is more important to maintain the position and posture.To reduce hyper-activeness use sedative otherwise due to hyper-activeness rigidity will increase and result will be dislocation/fracture/injury of some joints/bones or muscle/ligament injury. To avoid torticollis maintain the position of neck and do the proper exercise and stretching.
(19) Aphasia :
Aphasia is an impairment of language, affecting the production or comprehension of speech and the ability to read or write.
Aphasia is always due to injury to the brain-most commonly from a stroke, particularly in older individuals.
physiotherapy :
- treatment for aphasia is usually speech and language therapy.
- This treatment is carried out by a speech and language therapist (SLT).
- Most people with aphasia need many hours of speech and language
(20) Apraxia :
Apraxia is a motor disorder caused by damage to the brain (specifically the posterior parietal cortex) in which the individual has difficulty with motor planning to perform tasks or movements when asked, provided that the request or command is understood and the individual is willing to perform the task.
physiotherapy :
- Improve the person’s functional abilities where possible.
- Teaching the person compensatory strategies such as verbalizing the steps of the task and carrying them out at the same time or
- writing down the steps of the task.
- Sensory stimulation
- Gait training
(21) Arnold-chiari malformation :
Chiari malformations are structural defects in the cerebellum. That’s the part of the brain that controls balance.
Spina bifida is the incomplete development of the spinal cord and/or its protective covering. Type II is also known as “classic” Chiari malformation or Arnold-Chiari malformation. In type II Chiari malformation, both the cerebellum and the brain stem extend into the foramen magnum.
physiotherapy :
- Vestibular Rehabilitation is indicated when patients have vestibular problems
- Conservative physiotherapy soft tissue techniques may be of benefit for cervical pain
- Soft tissue techniques may be of benefit for headaches.
(22) Spina bifida :
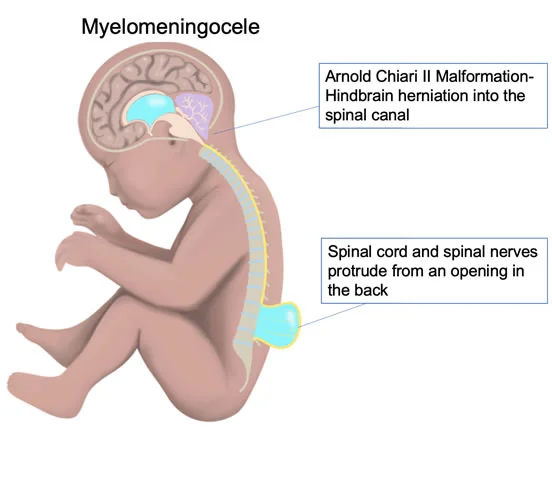
Spina bifida is a birth defect where there is incomplete closing of the backbone and membranes around the spinal cord. There are three main types: spina bifida occulta, meningocele, and myelomeningocele. The most common location is the lower back, but in rare cases it may be the middle back or neck.
physiotherapy :
properly prescribe exercise training sub-maximal and maximal testing is necessary.
treadmill speed and 6 minute walk distance are the best ways.
reduce pain
correct deformity
(23) Ataxia :
- Ataxia is a degenerative disease of the nervous system. Many symptoms of Ataxia can mimic those of being drunk – slurred speech, stumbling, falling, and in coordination. Ataxia describes a lack of muscle control or coordination of voluntary movements, such as walking or picking up objects.
physiotherapy :
- focused on balance, gait, and muscle strengthening, can improve SARA score and gait speed.
- including coordination training
- improves gait ability
- Trunk stabilization and loco-motor training in cerebellar ataxia can improve the balance score
- improves posture.
(24) Becker’s myotonia :
Myotonia congenital is an inherited myopathy, a disease that causes problems with the tone and contraction of skeletal muscles. It doesn’t cause muscle atrophy (shrinkage); instead, it sometimes can cause muscle enlargement and increased muscle strength.
physiotherapy :
- Reducing the occurrence spasm
- Encourage normal movement patterns
- Advise and work with you to reduce your risk of falling
- walking and moving into and out of sitting and lying positions.
- Activities to improve your smooth completion of everyday tasks and manage prolonged muscle contractions.
(25) Brachial plexus injuries :
- Paralysis of the arm due to an injury to the brachial plexus. The brachial plexus is a network of spinal nerves that originates in the back of the neck, extends through the axilla (armpit), and gives rise to nerves in the upper limb (arm). The brachial plexus is formed by the union of portions of the fifth through eighth cervical nerves and the first thoracic nerve, all of which come from the spinal cord.
physiotherapy :
- electrotherapy
- electrical stimulation
- PNF technique
- Neck Stretching
- Shoulder Shrugs
- Shoulder Abduction
- Isometric Exercises
(26) Brown sequard syndrome :
Ipsilateral paresis and proprioception disorder with contra-lateral pain and temperature disturbances, resulting from hemisection of the spinal cord. Brown-Séquard syndrome is an incomplete spinal cord lesion characterized by a clinical picture reflecting hemisection injury of the spinal cord, often in the cervical cord region.
physiotherapy :
- Maintaining strength in neurologically intact muscles
- Maintaining range of motion in joints
- Preventing skin break down by proper positioning and weight shifting
- Improving respiratory function by positioning and breathing exercise
- Providing emotional and education support.
(27) Carpal tunnel syndrome :
Carpal tunnel syndrome is a common condition that causes pain, numbness, and tingling in the hand and arm. The condition occurs when one of the major nerves to the hand — the median nerve — is squeezed or compressed as it travels through the wrist.
physiotherapy :
- Bracing or splinting
- Nerve gliding exercises
- Wrist bend
- Wrist stretch with weight
- Hand squeeze
- Gripping, Repetition and Micro-vibration.
(28) causalgia :
a constant, usually burning pain that results from injury to a peripheral nerve and is often considered a type of complex regional pain .
physiotherapy :
- pain reduction
- ice application
- active-passive exercise
- stretching
- strengthening
(29) Cushings syndrome :
Cushing’s syndrome is caused by either excessive cortisol-like medication such as prednisone or a tumor that either produces or results in the production of excessive cortisol by the adrenal glands. Cases due to a pituitary adenoma are known as Cushing’s disease.
Physiotherapy :
- Physical Therapy can provide relief for structural, muscular, and neural problems. Pituitary abnormalities can cause an array of symptoms and impairments.
- Cushing’s patients are often faced with muscle weakness, especially in their hips and shoulders.
- Physical therapy can combat weakness and increase muscle tone in necessary areas to help reduce muscle fatigue.
(30) Dandy walker syndrome :
Dandy–Walker syndrome (DWS) is a rare group of congenital human brain malformations. There are three sub types which affect multiple organs to varying degrees, but the fundamental abnormalities involve the cerebellum which controls muscle coordination.
physiotherapy :
- Maintaining strength in neurologically intact muscles
- Maintaining range of motion in joints
- Preventing skin break down by proper positioning and weight shifting
- Improving respiratory function by positioning and breathing exercise
- Providing emotional and education support.
(31) Dementia :
Dementia is not a specific disease. It’s an overall term that describes a group of symptoms associated with a decline in memory or other thinking skills severe enough to reduce a person’s ability to perform everyday activities. Alzheimer’s disease accounts for 60 to 80 percent of cases.
physiotherapy:
- It helps in improving physical function mobility, balance,coordination and strength
- range of movement, swelling, pain and increased risk of falling
- improves independence with ADL’s and quality of life.
(32) Dystonia :
Dystonia is a movement disorder in which a person’s muscles contract uncontrollably. The contraction causes the affected body part to twist involuntarily, resulting in repetitive movements or abnormal postures. Dystonia can affect one muscle, a muscle group, or the entire body.
physiotherapy :
- physiotherapy is to correct the postures and movements affected by dystonia through a set of targeted exercises.
- Regain movement in stiff joints.
- Improve nerve glide (encouraging nerves to glide ‘normally’ during movement).
- Strengthen weakened muscles.
- Regain normal length in tightened muscles.
- Improve postural symmetry/alignment.
- Improve balance.
- Develop a self-management strategy to aid reduction and management of symptoms.
(33)Encephalopathy :
Encephalopathy is a general term that means brain disease, damage, or malfunction. The major symptom of encephalopathy is an altered mental state. The causes of encephalopathy are numerous and varied; they include infections, anorexia, metabolic problems, toxins, drugs, physiologic changes, trauma, and other causes.
physiotherapy :
Range of motion (ROM) exercises for maintaining the mobility of joints and soft tissues and preventing contractures
Progressive resistance exercises for building muscle strength
Exercises for strengthening knee extensor muscles improve crouching and stride length
Postural and motor control exercises help kids control their posture and hold themselves upright.
(34) Erb’s palsy :
paralysis of the arm caused by injury to the upper group of the arm’s main nerves, specifically the severing of the upper trunk C5–C6 nerves. These form part of the brachial plexus, comprising the ventral rami of spinal nerves C5–C8 and thoracic nerve T1.
physiotherapy :
- include gentle massage, strength exercises, range of motion exercises, stimulation exercises, and gentle stretching.
- Another aspect of physical therapy is the use of splints, braces, and tape to promote proper alignment of joints and to train the infant’s arm, wrist, shoulder, and hand to move in the correct ways that promote healing.
(35) Foot drop :
Foot drop is a gait abnormality in which the dropping of the forefoot happens due to weakness, irritation or damage to the common fibular nerve including the sciatic nerve, or paralysis of the muscles in the anterior portion of the lower leg. It is usually a symptom of a greater problem, not a disease in itself.
physiotherapy :
- Towel Stretch. Sit on the floor with both legs straight out in front of you. …
- Toe to Heel Rocks. Stand in front of a table, chair, wall, or another sturdy object you can hold onto for support. …
- Marble Pickup.
- Ankle Dorsi flexion.
- Plantar Flexion.
- Ball Lift.
- Stretching and range of motion exercises.
(36) Herpes zoster :
zoster infection that results when varicella-zoster virus reactivates from its latent state in a posterior dorsal root ganglion.
Herpes zoster inflames the sensory root ganglia, the skin of the associated dermatome, and sometimes the posterior and anterior horns of the gray matter, meninges, and dorsal and ventral roots.
physiotherapy :
- TENS may be used to treat acute pain and reduce the healing time of the rash associated with herpes zoster.
- TENS therapy generally involves placing two electrodes on the dermatome affected by herpes zoster for 30 minutes five times per weeks for a period of time up to three weeks.
- If the facial nerve is affected by herpes zoster and peripheral facial palsy results, facial exercises have been found to be effective.
- Mirror therapy, mime therapy, facial muscular re-education, and Kabat’s exercises were found to be effective means of facial rehabilitation techniques.
(37) Muscular dystrophy :
MD is a group of muscle diseases that results in increasing weakening and breakdown of skeletal muscles over time. The disorders differ in which muscles are primarily affected, the degree of weakness, how fast they worsen, and when symptoms begin.
physiotherapy :
- Physiotherapy helps slow the depression of range of motion.
- Muscle strength
- Activity daily living
- Work to improve gait pattern/ posture
- Stretching – can be a combination of active and passive stretches
- Cope up with muscle extensibility and muscle contracture.
(38) Myasthenia gravis :
Myasthenia gravis is a chronic autoimmune neuromuscular disease that causes weakness in the skeletal muscles, which are responsible for breathing and moving parts of the body, including the arms and legs. The name myasthenia gravis, which is Latin and Greek in origin, means “grave, or serious, muscle weakness”.
physiotherapy :
- Build and maintain your muscular strength
- Utilize warm up effects to reduce the impact of Myasthenia Gravis
- Develop strategies for effective management of your condition specific to your individual needs
- Decrease your risk of falling
- Enhance your ability to function daily.
- Muscle strengthening
- Joint flexibility / range
- Completion of functional tasks and maintenance of independence
- Balance
- Smoothness and coordination of activities.
(39) Peripheral neuropathy :
Peripheral neuropathy refers to the conditions that result when nerves that carry messages to and from the brain and spinal cord from and to the rest of the body are damaged or diseased. The peripheral nerves make up an intricate network that connects the brain and spinal cord to the muscles, skin, and internal organs.
physiotherapy :
- Strengthening exercises for peripheral neuropathy moderately improve muscle strength in people with PN.
- Aerobic Exercise
- Flexibility Exercise
- Strength Training Exercise
- Balance Exercise.
- Maintaining and improve functions via a range of motion – passive range of motion exercises consist of progressive stretching and self-stretches
- Strengthening muscles – this includes exercising against increasing resistance, use of weights, and isometric exercise
- Balance training provides stability and prevents falls
- Physical therapists can also recommend braces and/or splints to enhance balance and posture
- Splinting is often used in the treatment of compression mono neuropathies, such as carpal tunnel syndrome.
(40) Poliomyelitis :
A condition marked by inflammation and degeneration of skeletal muscle throughout the body.
Having this condition can make it difficult to climb stairs, rise from a seated position, lift objects or reach overhead.
physiotherapy :
- Preservation of muscle function
- Avoidance of disuse atrophy
- Light resistance (be cautious with eccentric activity) Strengthening of distal musculature, which has the greater potential for strength gains, can contribute greatly to an overall improvement in performance with ADL’s
- Open chain exercises utilize less energy than closed chain, but closed chain exercises yield the greatest outcomes with functional mobility.
- Energy conservation is key (avoid high resistance open chain or aggressive closed chain exercises (Ex: plyometrics))
- Cycle ergo meter
- Walking
- Contracture prevention
- Patient education
- A loss of muscle mass results in weakness and fatigue, which may result in the adoption of a sedentary lifestyle. It is very important that patients remain active to avoid disuse atrophy and further muscle weakness.
(41) Reflex sympathetic syndrome :
Reflex sympathetic dystrophy (RSD), is a clinical syndrome of variable course and unknown cause characterized by pain, swelling, and vasomotor dysfunction of an extremity. This condition is often the result of trauma or surgery.
physiotherapy :
- To reduce pain: Ice packs may be used to reduce pain; avoid extremes of temperature. Do not use ice packs if there is cold sensitivity.
- Avoid painful movements: These may stimulate the sympathetic nerves & worsen the pain.
- To reduce swelling/edema:
Cold packs
Elevate the part. Avoid keeping the part in a dependent position.
Massage
Compression garments - Go for walks: Walking can help release Endorphins (Happy Hormones) which are shown to not only elevate mood but also reduce pain. Avoid walks in case of RSD of the Foot.
(42) Tabes dorsalis :
Tabes dorsalis is a complication of untreated syphilis that involves muscle weakness and abnormal sensations.
Tabes dorsalis is a form of neurosyphilis, which is a complication of late-stage syphilis infection. Syphilis is a bacterial infection that is spread sexually.
physiotherapy :
- Strengthening of muscles.
- Use of assistive aids to improve mobility.
- Balance retraining.
- Frankel’s Exercise.


One Comment