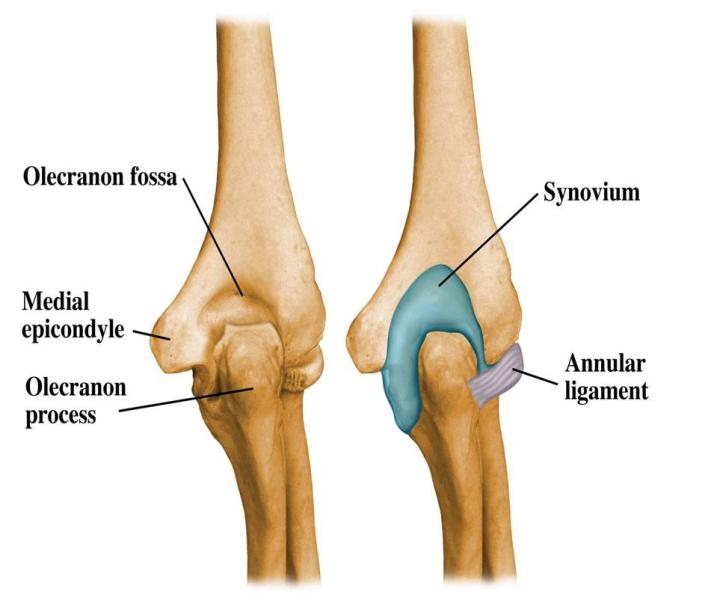
Elbow Joint
Elbow Joint The elbow joint serves as a pivotal connection between the upper arm bone (humerus) and the two forearm bones, the radius and ulna. This crucial joint facilitates a wide range of movements essential for everyday activities, including bending (flexion) and straightening (extension) of the arm, as well as rotational movements of the forearm…