Stroke: Physiotherapy Rehabilitation
Stroke From Physiotherapy Point Of View
A stroke is a medical condition in which poor blood flow or High Blood Pressure to the brain results in cell death in the Area Of the Brain.
Mainly Two Types: One is ischemic Stroke, due to lack of blood flow or Blockage Of the Artery Mainly Occurs in the Old Age, & 2nd is hemorrhagic Stroke, due to High Blood Pressure which Occurs Young/Middle Age.
This May Result in parts of the brain Mostly the Motor Area Not functioning properly Which is Mostly Seen in Paralysis on One Side Of The Body. Which May Be the Left Side Of The Right Side Of The Body. Common Signs/symptoms of a stroke may include an inability to move One Side Of the Body (Paralysis Of One Side ), Difficulty in understanding or speaking, dizziness, or loss of vision to one side. Signs/symptoms often appear soon after the stroke has occurred. If symptoms last less than one or two hours it is known as a transient ischemic attack (TIA) or mini-stroke( Temporary Stroke ). A hemorrhagic stroke may also be associated with a severe headache. The symptoms of a stroke can be permanent. Long-term complications may include pneumonia or loss of bladder/bowel control.
The main risk factor for stroke is high blood pressure. Other risk factors include tobacco smoking, obesity, high blood cholesterol, Diabetes mellitus, a previous History Of TIA, and atrial fibrillation. An ischemic stroke is typically caused by blockage of a blood vessel, though there are also less common causes. A hemorrhagic stroke is caused by either bleeding directly into the brain or into the space between the brain’s membranes. Bleeding may occur due to a ruptured brain aneurysm.
Diagnosis is typically based on a physical exam and supported by medical imaging such as a CT scan or MRI scan. A CT scan can rule out bleeding, but may not necessarily rule out ischemia, which early on typically does not show up on a CT scan. Other tests such as an electrocardiogram (ECG) and blood tests are done to determine risk factors and rule out other possible causes. Low blood sugar may cause similar symptoms.
Prevention includes decreasing risk factors, as well as possibly aspirin, statins, surgery to open up the arteries to the brain in those with problematic narrowing, and warfarin in those with atrial fibrillation. A stroke or TIA often requires emergency care. An ischemic stroke, if detected within three to four and half hours, may be treatable with a medication that can break down the clot. Aspirin should be used. Some hemorrhagic strokes benefit from surgery Like Craniotomy.
Treatment to try to recover lost function is called Post-stroke rehabilitation and ideally takes place in a stroke unit, Like Physiotherapy, Nursing Care, and Speech Therapy, however, these Perfect Combination units of doctors are not available in much of the world.
In 2013 approximately 70lakh people had an ischemic stroke and 34 lakh people had a hemorrhagic stroke. In 2015 there were about 4 crore 24 lakh people who had previously had a stroke and were still alive. Between 1990 and 2010 the number of strokes which occurred each year decreased by approximately 10% in the developed world and increased by 10% in the developing world. In 2015, stroke was the second most frequent cause of death after coronary artery disease, accounting for 63 lakh deaths (11% of the total). About 30 lakh deaths resulted from ischemic stroke while 33 lakh deaths resulted from hemorrhagic stroke. Overall, two-thirds of strokes occurred in those over 65 years old.
Table of Contents
Type Of Stroke
Ischemic Stroke: A blood vessel carrying blood to the brain is blocked by a blood clot (ischemic) is one type of stroke. Most Common Stroke And More Common in Old Age.
Hemorrhagic Stroke: A brain aneurysm burst or a weakened blood vessel leak (hemorrhagic) is one of two types of stroke. While the least common of the two types of stroke it most often results in death.
Signs/Symptoms
Paralysis or numbness of the face, arm/leg: Weakness, Numbness, Or Unable to Use One Side Of The Body. Mostly One Side Of the Face, Upper Limb, Lower Limb, and Trunk Are Not Working Properly With Difficulty In sitting or standing Balance.
Headache: Severe Headache is the Most Common Symptom And Increasing At Night Mostly Seen in Hemorrhagic Stroke.
Difficulty in Speech: Speech Problems are Mostly Seen In Both kinds of Stroke, Altered speech or Complete Loss Of Speech Also Called Dysphasia.
Loss Of Vision on One Side. : Left or Right Side Of The Vision Loss Also Called Dysmetria.
Loss Of Balance: Difficulty in Sitting Position Or Standing Position.
Incoordination: Coordinated Movement Is Difficult and mostly Seen If the Cerebellar Area is Affected Also Called Cerebellar ataxia Syndrome.
Memory Loss: Temporary Memory Loss is More Common.
Psychological Symptom Also Seen.
vertigo and or disequilibrium.
Cause Of Stroke
Cause Varies According to ischemic or Hemorrhagic or TIA.
Cause Of Ischemic Stroke:
Mostly 80 percent of strokes are ischemic strokes. Ischemic strokes occur when the arteries to your brain become narrowed or blocked, causing severely reduced blood flow (ischemia).
Thrombotic stroke: A thrombotic stroke occurs when a blood clot (thrombus) forms in one of the arteries that supply blood to your brain.
Embolic stroke: An embolic stroke occurs when a blood clot is swept through your bloodstream to lodge in narrower brain arteries. This type of blood clot is called an embolus.
Cause Of Hemorrhagic stroke:
Hemorrhagic stroke occurs when a blood vessel in your brain leaks or ruptures. Brain hemorrhages can result from:
Uncontrolled high blood pressure (hypertension)
Over-treatment with anticoagulants (blood thinners)
Weak spots in your blood vessel walls (aneurysms)
Risk factors
Lifestyle And Diet And Other Diseases Affect Or Increase Risk Of Stroke.
Most Common Are:
Other factors associated with a higher risk of stroke include:
Lifestyle risk factors:
- Being overweight or obese
- Physical inactivity
- Heavy or binge drinking
- Use of illicit drugs such as cocaine and methamphetamines
- Medical risk factors
- Blood pressure readings higher than 120/80 millimeters of mercury (mm Hg)
- Cigarette smoking or exposure to secondhand smoke
- High cholesterol
- Diabetes
- Obstructive sleep apnea
- Cardiovascular disease, including heart failure, heart defects, heart infection or abnormal heart rhythm
- Personal or family history of stroke, heart attack, or transient ischemic attack.
Age —People age 55 or older have a higher risk of stroke than younger people.
Race — African Americans have a higher risk of stroke than people of other races.
Sex — Men have a higher risk of stroke than women. Women are usually older when they have strokes, and they’re more likely to die of strokes than men.
Hormones — use of birth control pills or hormone therapies that include estrogen, as well as increased estrogen levels from pregnancy and childbirth.
Diagnosis
Stroke is Diagnosed through several Methods: a Neurological examination like Manual Examination, Other Imagin methods like CT Scan, MRI, Blood Examination, And Reports.
Physical examination: Taking History and neurological tests like Physical Check Of Limbs.Checking of Speech, Movement Of Limb, Balance Of Sitting And Standing, Walking.
Imaging: Like CT Scan, MRI, ultrasound/doppler study of the carotid arteries Blockage.
Blood Reports And Blood Pressure Monitoring To Rule Out Diabetes And Blood Pressure.
Medical Treatment
Treatment Varies According To Type Like Ischemic Or Hemorrhagic.
Regulating Blood Pressure, Diabetes Proper Management, And Thrombolytic Medicine Mostly Use in ischemic Stroke.
Blood Pressure Monitoring is Important in Hemorrhagic Stroke.
Surgical Treatment Like Craniotomy is the Most Common Surgery in Hemorrhagic Stroke.
Rehabilitation And Physiotherapy Treatment :
Physiotherapy Treatment is Important in Rehabilitation Purpose For Restoration Of Movement And Giving Patients a New Life.
The Physiotherapist First assesses the patient’s Movement And Balance, And Other Related Symptoms Like Spasticity And Other Related Symptoms, Breathing Patterns, And Related Other Symptoms.
Physiotherapy Indications are Mainly Prevent Complication, Restoration Of Movement, and Preventing Deformity With Early Rehabilitation.
Development Motor/Sensory is Primary Importance With Technique With Approach.
Chest Physiotherapy, Breathing Exercise According To Condition.
Physiotherapy Approach Like Rood’s Approach, Bobath’s Approach
For Facial Palsy: Facial Palsy Mostly Upper Motor Neurone Type Palsy Seen Mostly in Lower Facial Muscle Affected. So Active Assisted Exercise Of That Affected Muscle is Essential.
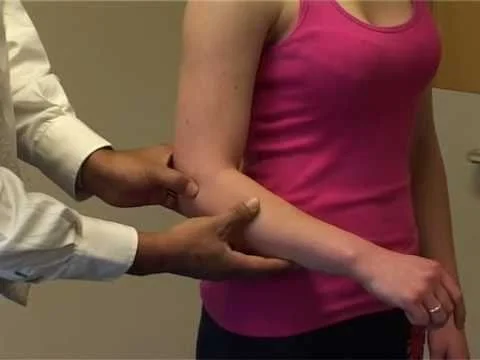
Upper Limb Treatment: Restoration Of All Movement From Shoulder Girdle To Shoulder Joint, Elbow Movement, Wrist Joint Movement, and Fine Movement Of Fingers Require Restoration Movement Via Various Method Neurological Techniques such as Rood’s approach, PNF Technique, and Other Methods.
Trunk And Lower Limb: Back Flexion is Too Important in Early Achieve of Sitting position From the Supine Position. Lower Limb Movement Of Hip Joint, Knee Joint, And Ankle Joint Movement.
Balance: Siting Balance And Standing Balance And Balance Require During Walking is Too Important For Gait And Early Rehabilitation.
In Co-ordination: Frankle’s Co-Ordination Exercise in This Condition.
Pain Control Ice And Medicine.
Balance: Siting Balance And Standing Balance And Balance Require During Walking is Too Important For Gait And Early Rehabilitation.
In Co-ordination: Frankle’s Co-Ordination Exercise in This Condition.
Pain Control Ice And Medicine.
Deformity: Splinting And Positioning Are Useful To Avoid Deformity Like Foot Drop And Other Deformity.
Speech Therapy: Speech Therapist Helps To Restore Speech.
Psychological Support is Also required because Depression And Other symptoms may Be Sometimes Associated.
Occupational Therapy: Helps Patient How To To Back To Working Position.
Preventive Measure
History Of TIA Or Time Stroke Have a High Risk Of Stroke, So Preventive Measure is Important.
Mostly Lifestyle Changes, Diet, Regular Exercise, Regular Checking Blood pressure, Diabetes, And Follow-Up Physicians/Doctors/Neurophysicials Are Too Important.
A healthy diet can reduce your risk of acquiring medical conditions such as hypertension (high blood pressure), diabetes, high lipid levels (high cholesterol), coronary artery disease, and obesity. All of these conditions can increase your chance of having a stroke. Your genetics, history of prior stroke, age, sex, current weight, distribution of body fat, eating habits, and fitness level also influence your risk.
Factors that Affect/Responsible To High Blood pressure:
Obesity
Lack of exercise, Sedentary lifestyle
Over Stress Like Business Stress Due To Debt Or Family Stress
Smoking/Alcohol/Other Habits Like Drugs Or Medicine That Affect Brain
Low intake of some minerals, such as calcium and potassium, Vitamin
High intake of sodium (salt), Sugar, and Fat.
To Minimize your risk of stroke, the following Tips are Helpful:
- Eat a variety of foods With a Mix Of Colour Of Fruit, Leafy Vegetable And Seasonal Foods.
- Maintain a healthy weight by balancing the calories you eat with physical activity.
- Active Lifestyle Or Morning Exercise Also Maintain Body Weight and Lower Cholesterol Fat.
- Reduce Overtime to Relieve Work Stress, Family Vacation At Regular Interval also Lower Stress.
- Never Retire From Work, Do Part-time Or Minimum Some kind Of Physical And Mental Activity
- Choose more whole grains, vegetables, and fruits.
- Choose foods low in saturated fat and cholesterol.
- Choose foods with moderate/low amounts of added sugar.
- Choose foods with moderate/low amounts of salt (sodium).
- If you drink alcoholic beverages, consult your physician and do so in moderation.
- Practical tips for getting started on a healthier diet and lifestyle.
Be realistic: Make one or two small changes every month and stick to them, such as including a fruit and/or vegetable with each meal.
Be adventurous: Expand your tastes and try a greater variety of foods.
Be flexible: Balance what you eat and your physical activity over several days.
Be sensible: Enjoy all foods; just don’t overdo it.
Be active: Walk the dog; don’t just watch the dog walk!
Seek assistance from a registered dietitian (RD) to help guide you in making these significant lifestyle changes toward healthier eating.




36 Comments