Forearm muscle pain: Cause, Symptoms, Treatment, Exercises
When you feel the pain during the hand & arm movement, it is indicated as forearm muscle pain. this pain is highly disruptive to the daily life of the patient. this pain results from different causes & each cause is requiring a different treatment approach.
Table of Contents
What is forearm muscle pain?
- The forearm is composed of the radius & ulna bones, which span the length of the forearm and intersect at the wrist joint.
- Many muscles are in the forearm which performs the hand & arm movement.
- If any injury occurs in the arm & hand which is lead to forearm muscle pain.
- As a result of the forearm muscle injury & if the patient feels discomfort in the forearm which is a wide-ranging impact on mobility & interferes with daily functioning.
- When the forearm pain occurs, the patient feels difficulty typing on a keyboard & grip an item with the help of a hand.
- In most cases, a person is manage the forearm pain with rest & structured activity.
- This muscle pain is reduced by exercise & electrotherapy.
Muscles of the forearm:
- The muscles of the forearm are divided into two compartments:
- Anterior Compartment
- Posterior compartment

Muscles of the Anterior Compartment of the Forearm:
- The anterior compartment of the forearm muscle is divided into 3 parts depending on the layer of muscle
- Superficial muscles:
- Flexor carpi ulnaris
- Flexor carpi radialis
- Palmaris longus
- Pronator teres
- All muscles originate from a common tendon, which arises from the medial epicondyle of the humerus bone.
- Intermediate muscle :
- Flexor digitorum superficialis.
- This muscle has two heads – one head originates from the medial epicondyle of the humerus bone & the other head is originate from the radius bone.
- Deep muscles :
- Flexor pollicis longus
- Pronator quadratus
- Flexor digitorum profundus
- This anterior compartment muscle group is perform the pronation of the forearm, flexion of the wrist joint & flexion of the fingers.
- This anterior compartment muscle group are mostly innervated by the median nerve & receives the arterial supply from the ulnar artery & radial artery
Muscles of the Posterior Compartment of the Forearm:
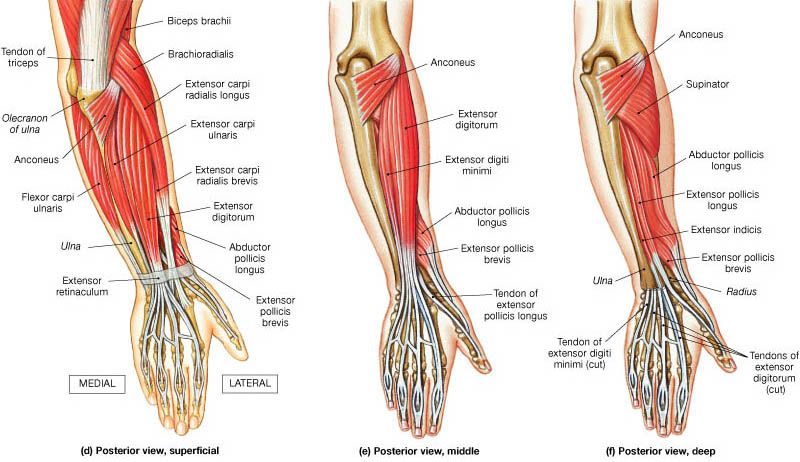
- The muscles of the posterior compartment of the forearm are commonly known as the extensor muscles.
- The general function of the Posterior Compartment of the Forearm muscles is to produce extension at the wrist joint & fingers.
- This all posterior Compartment of the Forearm muscles are all innervated by the radial nerve.
- The posterior compartment of the forearm muscle is divided into 2 parts depending on the layer of muscle
- Superficial Muscles:
- Extensor carpi radialis brevis
- Extensor digitorum
- Extensor carpi ulnaris
- Extensor digiti minimi
- Brachioradialis
- Extensor Carpi Radialis Longus & Brevis
- Deep Muscles:
- The supinator
- Abductor pollicis longus
- Extensor pollicis brevis
- Extensor pollicis longus
- Extensor indicis.
What are the causes of the forearm muscle pain?
Forearm muscle pain is caused by injury, nerve entrapment & arthritis.
- Injury:
- When to occur acute trauma, like a fall which is become to causes a fracture in one of the forearm bones & damage to the ligaments & tendons.
- Overuse:
- Some sports, like tennis & certain types of weightlifting, when put a high degree of pressure on the muscles in the forearm which is cause strain.
- When Excessive use of computers also occurs the muscle strain in the forearm, which is known as repetitive strain injury (RSI).
- This Pain increases in RSI = repetitive strain injury which is become common in the workplace and mostly occurs growth of computer-based labour.
- Forearm muscle tightness due to inactivity of hands mostly after injury
- Nerve entrapment:
- When the nerves are become too compressed, which is produced pain, numbness or a tingling feeling in & around the affected region.
- Nerve entrapment is caused by a range of different syndromes which is affecting the forearm muscle.
- The most common Nerve entrapment syndrome is carpal tunnel syndrome which is become to cause by forearm muscle pain.
- Arthritis:
- Arthritis occurs in the wrist & elbow joint, which is produce a dull ache pain in the forearm muscle.
- An underlying condition:
- Certain medical conditions, like as angina, which is produced by pain in the forearm.
- The forearm muscle pain is due to sports injury & inflammation in the forearm muscle.
- This Forearm muscle pain is also related to an infection, a nerve problem, a growth & even cancer.
- Some other situations which are produced forearm muscle pain include:
- Sports injuries
- Tendinitis
- Dislocation
- Overuse injury
- Bone fracture
What are the symptoms of the forearm muscle injury?
Forearm muscle injury symptoms is depending on the underlying disease, disorder & condition.
- The patient feels Muscle weakness in the forearm muscle
- In the patient also present Redness, warmth & swelling in the area of pain.
- Reduced mobility means a range of motion = ROM of the elbow & wrist joint
- The patient feels the Shoulder, arm, hand & finger means whole upper limb pain
- Tenderness is also present in an area of pain
- Sometimes present to Visible deformity of the elbow & wrist joint
- The patient feels the Numbness & tingling in the arm
- Sometimes occur to Skin discoloration like as bruising
- Symptoms that might indicate a serious condition
In which condition immediate contact to doctor for this muscle pain?
- In some cases, forearm pain occurs with the other symptoms which is indicate a serious condition so evaluated immediately in the emergency setting.
- In the immediate condition need medical care call 911 for treatment.
Some serious conditions which need to doctor immediate basis:
- When the Bone is sticking out of the skin
- If occur to Excessive bleeding in the forearm
- Paralysis of the forearm muscle
- If the patient feels Sudden & intense pain in the forearm
What is Treatment for the forearm muscle pain?
RICE principle:
In the starting phase of muscle pain used to RICE principle.

- R – rest = Reducing the activity involving the forearm which helps the injured tendon, ligament, muscle, bone & nerve to recover. A person is do the rest periodically rather than remaining inactive for sustained periods.
- If the person presents with sports-related forearm pain avoid the sport till the pain is entirely subsided.
- I – ice = Applied to ice on the area of pain for 20 minutes which is help to reduce inflammation & pain .you can is also used an ice pack & frozen peas to release the pain.
- C – compression = In the cases whereby movement is very painful, a person is required to splint & sling to restrict the movement & minimize pain.
- E – elevation = Elevate the arm with the help of a pillow reduce to swellings.
Medication for the pain relief:
- Mostly your Doctor prescribes you pain reliever medicine mostly NSAIDs such as Ibuprofen & other anti-inflammatory drugs which are used to manage pain.
- You are also used pain reliever gel and patches such as diofanace gel & volini gel for pain relief.
Hot therapy:
- You are also trying to heat therapy on the swelling area which is also easy the pain.
- You are applied a hot pack to the area of pain to reduce the spasm & swellings.
What is Physiotherapy Treatment for forearm muscle pain?
In physiotherapy, Treatment includes to exercise, stretches & strengthening exercise which is designed to rehabilitate & strengthen the forearm slowly.
Stretching for forearm muscle pain:
- Wrist extensor stretch
- Forearm flexor stretch
- Supinator stretch
- Two-arm forearm stretch
- Praying forearm stretch
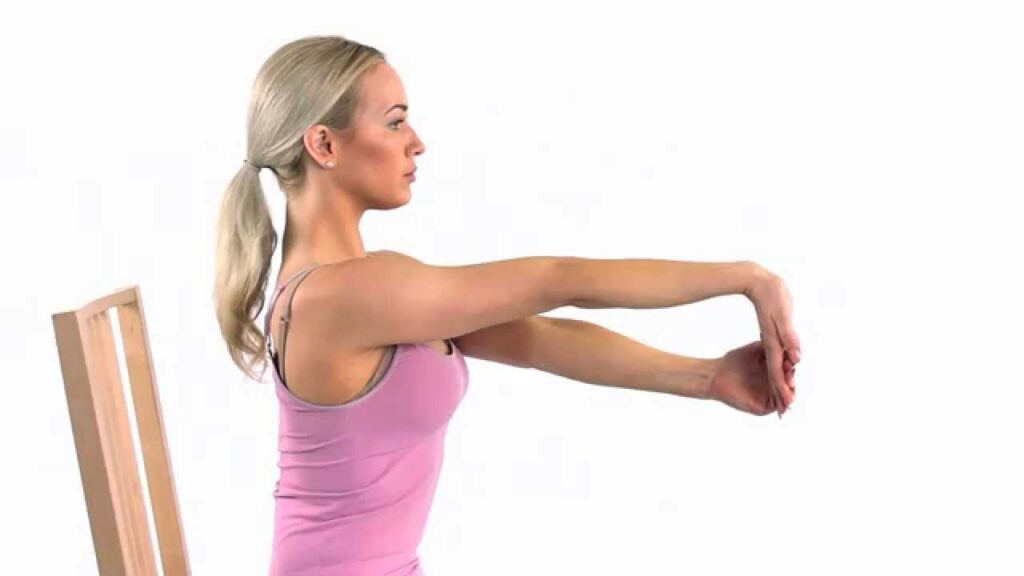

Wrist extensor stretch :
- The patient is in a sitting or standing position for the stretching.
- Hold the arm out parallel to the ground then extend from the shoulder.
- Turn the hand so it is facing downward.
- Use the opposite hand which pulls the outstretched hand down & toward the body.
- Bending the wrist joint & feeling a stretch on top of the hand &forearm.
- Then Slightly rotate the arm inward to feel a further stretch.
- Hold this stretching position for 20 seconds.
- Repeat this exercise five times on each side.

Forearm flexor stretch:
- The patient is in a Standing position for this stretching.
- Place both arms out in front of the body with the elbow joint is locked out.
- Then Raise the palm of one hand like waving to a friend.
- Then, with the other hand, gently pull the fingers towards the body.
- Hold this stretching position for 15-30 seconds.
- Then repeat this stretching on the other arm.
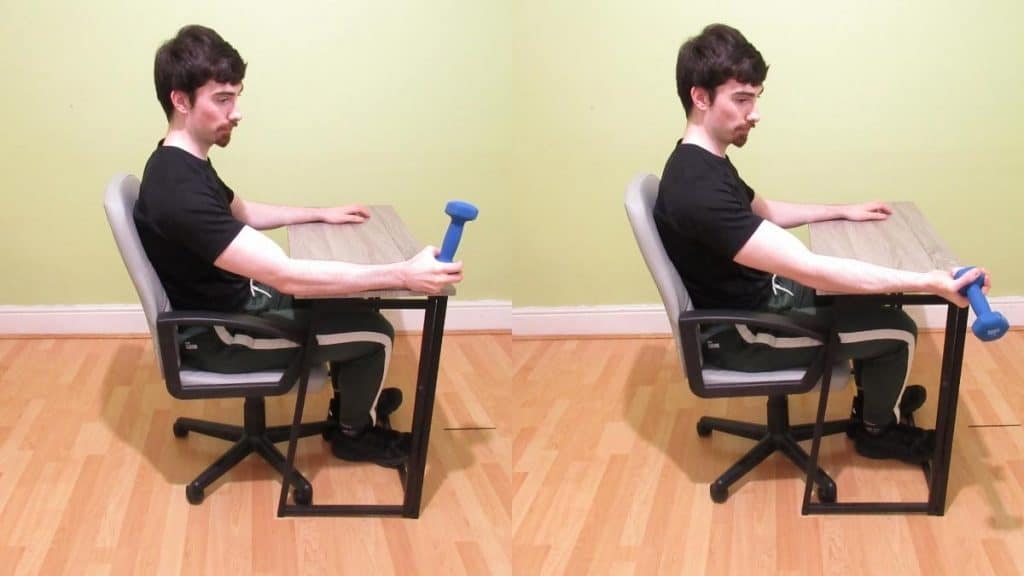

Supinator stretch:
- The patient is in a sitting position for this stretching.
- Hold the one end of a light dumbbell in the hand
- Then rest the arm, palm down, on a flat surface.
- Allow the dumbbell to rotate the hand just beyond neutral.
- Hold this stretching position for 15-30 seconds
- But must keep the weight light.
Two-arm forearm stretch:
- Place the hands out in front of the body, elbow joint locked out & then internally rotate means medial rotation of the shoulder joint so that the backs of the hands are facing each other.
- Then Place one hand over the other hand & interlock all of the fingers.
- Rotate the arms in the opposite direction as the arm is stretched.
- Then, with the non-working arm, push the wrist joint of the stretched arm into flexion.
- Hold this stretching position for 15-30 seconds & then repeat this exercise on the other arm by switching to the top position.

Praying forearm stretch:
- The patient is in a Standing position & sitting upright in a chair.
- Place the palms of the hands together without the interlocking of fingers.
- Raise both elbow joints so that the wrist joint begins to bend.
- Then Keep raising the elbow joint till feel a nice stretch in the undersides of the forearms.
- Hold this stretching for 15-30 seconds.
Exercise for the forearm muscle pain:
Exercise helps you in reducing the pain.
- Elbow bend
- Wrist extension
- Elbow extension
- Wrist rotations
- Forearm squeeze
- Fingertip pushups
- Crab walk
- Plank with shoulder taps
- Isometric wall push
- Sphinx push-ups
- Pull-up bar hang

Elbow bend:
- The patient is Stand up straight with the arms at the sides.
- Bend the right arm upward & allowing the inside of the hand to touch the shoulder joint.
- If the patient can’t reach the shoulder, that stretches only as close to it as the patient can.
- Hold this exercise position for 15 to 30 seconds.
- Then Lower the hand & repeat the exercise 10 times.
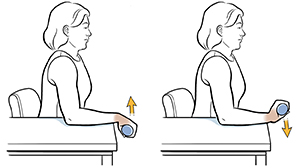
Wrist extension :
- The patient is in a Standing position for to Wrist extension exercise.
- Then extend the affected arm in front of the palm are parallel to the floor.
- With the help of the opposite hand, pull the wrist joint back toward the body.
- Then Pull the wrist joint back till feeling a stretch in the forearm muscle but do not feel any pain
- Hold this exercise position for 30 seconds.

Elbow extension:
- The patient is in a Sitting position for the Elbow extension exercise.
- Place the elbow on a table or chair arm.
- Using the opposing hand, gently push the forearm down towards the table or floor.
- When feeling a stretch but without any pain, hold this position for 15 seconds.

Wrist rotations:
- The patient is in a Sitting position for the Wrist rotations
- Patient is Extended to arms in front of them with hands at shoulder height.
- Make a fist & rotate each wrist clockwise then anticlockwise in a circular motion.
- Perform 10 repetitions in each direction in 1 session.

Forearm squeeze:
- The patient is Use a pair of forearm grips & another object to squeeze like a tennis ball & a sock.
- Extend & flex the fingers to squeeze the item.
- Hold this exercise for 3–5 seconds, then relax the grip for a few seconds.
- Continue this exercise for 10–15 minutes at 1 time.
- Do this exercise 2–3 times per day.

Fingertip push ups:
- The patient is kneeling by a bench & sturdy object & bringing the fingertips down on the surface.
- Slowly & with control, the patient brings the chest to the bench, and then bends the elbow joint at a 90-degree angle.
- Then Return to the starting position.
- Do this exercise in 2–3 sets of 8–12 repetitions.
Crab walk:

- The patient is Coming into reverse tabletop position.
- Place the hands under the shoulders joint, with the fingers are facing toward your feet.
- Align the ankle joint directly under the knee joint.
- Then Walk forward on the hands & feet for up to 1 minute at a time.
- Do the 3 – 4 times per days
Plank with shoulder taps:

- The patient is Kneeling on the floor & a yoga mat.
- Place the hands are directly under the shoulder joint — like a pushup position.
- Curl the toes under & lift the body into plank position.
- Must be Steady the core muscle.
- Lift the right hand from the ground & touch the opposite shoulder.
- Then, return to hand to the floor.
- Do this exercise for 30–60 seconds and as the longer patient can.
- Repeat this exercise 2–3 times.
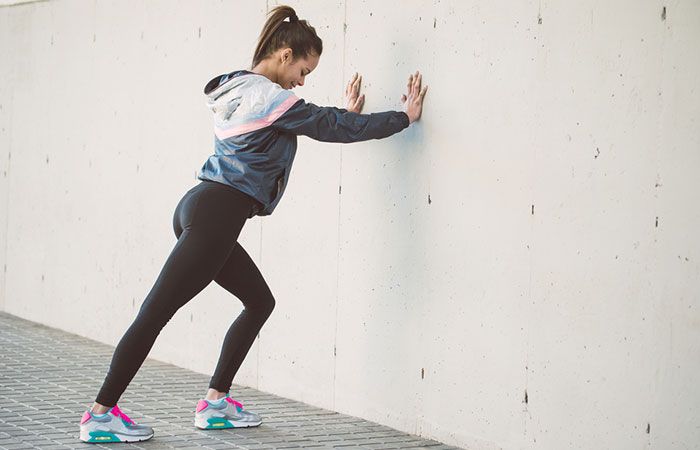

Isometric wall push :
- The patient is in a standing position in front of the wall with their hands are on the wall.
- Keeping the arms straight but not locking the elbow joint.
- Then press them firmly into the wall for 30 seconds.
- After 30 seconds Release the pressure.
- Repeat this exercise 2–3 times per day.
Sphinx push-ups :
- The patient is in Start in a forearm plank position, either on the toes & on the knees.
- Then Press the hands down firmly & try to lift the forearms till the arms are straight.
- Lower back down with the control.
- If can not go all the way at first, just do an inch & two at a time.
- Release the pressure.
- Repeat this exercise 2–3 times per day.

Pull-up bar hang:
- First Grip the pull-up bar with the hands about the shoulder distance apart, palm facing forward.
- Hang for up to 30 seconds, with the arms straight & ankles crossed behind you.
- Release.
- Repeat this exercise 2–3 times per day.
- Then Make it harder for this exercise: Wrap two small towels around the bar & grip the instead.
Strengthening exercise the forearm muscle pain:
This strengthening exercise helps you strengthen the muscle of the forearm & reduce the weakness of the forearm.
- Palms-up wrist curl
- Palms-down wrist curl
- Grip crush
- Wrist dumbbell curls
- Farmer’s walks
- Pinch-grip plate holds
- Reverse barbell curl with the thumb-less grip
Palms-up wrist curl:

- In the sitting position rest the wrist joint on the knee joint & on a flat surface, with the palms are facing up.
- The patient is holding a dumbbell in each hand.
- Then raise the hands as high as possible, keeping the arms still. but the wrist joint should not rise off the surface means the wrist joint is in rest position
- After a slight pause, lower the hands into the starting position.
Palms-down wrist curl:
- In the sitting position rest the wrist joint on the knee joint & on a flat surface, with the palms are facing up.
- The patient is to Hold a dumbbell in each hand, raise the hands as high as the patient can, and must keep the arms still.
- But the wrist joint does not rise off the surface means the wrist joint is resting.
- After a slight pause, return the hands to the starting position.
Grip crush:
- The patient is in a sitting position & rests the left wrist joint on the knee & a flat surface, with a holding dumbbell.
- Then Relax & open the hand so that dumbbell rolls toward to fingertips.
- Tighten the hand & curl the wrist up and squeeze the weight as tightly as possible.
- After performing the 10 repetitions & repeat on the opposite side.
Wrist dumbbell curls:
- The patient is in a sitting position on a bench & chair then holding a moderately heavy dumbbell in each hand.
- Then Place the forearms on the thighs, so that the wrists are on top of the knees.
- Palms are facing up & down.
- Slowly lower the weights as far as the patient can.
- Then Grip the weights tightly & move only the hands.
- Curl the weights up as far as the patient can.
- Then Return to the starting position.
- Repeat this exercise 3 sets of the 12 reps till the muscles are done.
- Alternatively, you can do one side at a time.
Farmer’s walks :
- The patient is in a Standing position tall & holding a pair of heavy dumbbells & kettlebells at the sides.
- Then Slowly walk from one end of the workout space to the other end & back.
- This exercise aims to do this Farmer’s walk exercise for 30–45 seconds per set.
- Then do the Rest.
- Repeat this exercise 2–3 times per day.
Pinch-grip plate holds :
- With the straight fingers, pinch & hold a relatively heavyweight plate between the thumb & four fingers of the hand.
- But this exercise is Do one side at a time.
- Hold this position for 30–45 seconds per set & as long as the patient can.
- Then do the Rest.
- Repeat this exercise 2–3 times per day.
Reverse barbell curl with the thumb-less grip:
- The patient is in a Standing position then holding a barbell with the palms facing down & hands shoulder distance apart. Keep the thumb alongside the rest of the fingers for a “thumbless grip.”
- Keep the elbow joint close to the sides then slowly bring the barbell toward the shoulders.
- Then Work on bending only at the elbow joint to focus on the forearms.
- Return into the starting position then move too slowly the entire time.
- Then Try to do the 3 sets of the 12 rep.
What is a home treatment for forearm pain?
- Resting the forearm which usually helps to reduce the degree of inflammation & swellings.
- Applied to Icing on the affected area with the cloth-covered ice pack for 10 to 15 minutes at a time which also helps to reduce the swelling.
- Taking over-the-counter pain-relieving medication, like ibuprofen (Advil) or acetaminophen (Tylenol), which is help to reduce the pain & discomfort.
- Use to a splint & bandage which limits the mobility & also helps in healing.
What is Prevention of the forearm muscle pain?
- Avoid activities which are put excessive strain on the forearm, like tennis & certain types of weightlifting.
- Taking to regular breaks from extended periods of computer use & using an ergonomic keyboard at work.
- Do the Strengthening exercise of the forearm & increasing the grip strength through resistance training.


One Comment