Scalene Muscle Pain: Cause, Symptoms, Treatment, Exercise
When you feel the pain in the one side of the neck & shoulder region, it is indicated to be Scalene Muscle pain. You can also feel neck muscle soreness & stiffness & limited range of motion of the neck.
Table of Contents
What is Scalene Muscle pain?
- Scalene muscles are of differing lengths & which is located laterally on each side of the neck.
- In this muscle pain patient feels the pain due to any reason such as excessive coughing, extended periods of head tilted & sleeping on the stomach with head to one side.
- The patient feels unilateral neck & shoulder pain, also feel to numbness, tingling & weakness in the arm & also a decrease in the ROM of neck movement.
- This muscle pain is created by many associated conditions like Torticollis & Myofascial pain syndrome.
- This muscle pain is reduced by medication and physiotherapy treatment.
What is the anatomy of the Scalene Muscles?
These scalene muscles are located in the space between the collarbone, trapezius & sternocleidomastoid muscles.
These Scalene muscles are a group of three muscles which is referred to as the scalene triangle.
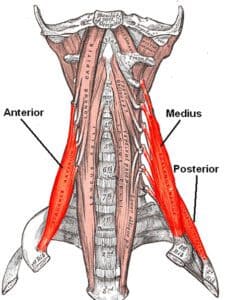
- Anterior scalene muscle:
- Which is also called the scalenus anterior muscle
- This Anterior scalene muscle is the lateral neck muscle which is located too deep behind the sternocleidomastoid muscle.
- This muscle originates at the 3,4,5 & 6 cervical vertebrae & attached to a narrow & flat tendon on the inner border of the first rib & the upper surface of the second rib.
- The function of this muscle is to flex & laterally bend the neck to the same side as the muscle.
- Middle scalene muscle:
- It is also called the scalenus medius muscle.
- This muscle is the longest & largest of the three lateral neck muscles which are located deeply placed behind the sternocleidomastoid muscle.
- This muscle is attached to the sixth cervical vertebra & positioned along with the vertebrae column, & this muscle is attached to the upper surface of the first rib.
- The middle scalene muscle helps the cervical lateral flexion & rotation movements of the neck.
- The posterior scalene muscle:
- It is also called the scalenus posterior.
- This muscle is the smallest & the most deeply seated behind the sternocleidomastoid muscles.
- This muscle originates at the lower second & third cervical vertebra & is attached by a thin tendon to the outer surface of the second rib behind the anterior scalene.
- This muscle lifts the second rib & tilts the neck to the same side of the muscle.
What is the cause of this Scalene Muscle pain?
- This muscle pain occurs due to overburdened, muscle fibers tightening & accrue to waste products
- When the scalene muscles become very tight, it produces too many muscle trigger points in the head, jaw, cheek, & behind or above the eye.
- This tightness leads to tension headaches & also pulls the first rib upwards.
- Some activities of our daily routine lead to Scalene Muscle pain:
- Do the excessive coughing
- Whiplash
- If you suffer from breathing conditions like COPD, asthma, & emphysema.
- Extended periods of head tilted
- When you carry something heavy like a backpack & purse
- Pulling & lifting the things with the arms at waist level
- If you wearing a tight collar or tie
- Bad posture such as hunching, rounding shoulder & forward head posture.
What are the symptoms of this Scalene Muscle injury?
- Patients feel pain as persists or worsens.
- You feel one side neck to shoulder pain.
- Become to muscle knots in the area of pain.
- Also available to trigger points which activate the pain.
- You also feel pain in the head & jaw.
- The presence of numbness & tingling.
- Filling like electric shock = dull or sharp pain..
- Weakness in the neck movement & arm.
- In the area of pain also present spasms, swelling & inflammation.
- In the area of pain, tenderness is also present.
Which Conditions are occurring with this Scalene Muscle pain?
Torticollis:
- This condition is also known as a wry neck.
- In this condition occurs to the neck muscles, including the scalene muscles, are constantly contracted in a shortened position.
- Which is given to result in a tilted head from unilateral scalene spasms & rigidity.
Forward head posture position:
- This condition is also referred to as text neck
- This condition commonly occurs in sitting at a computer, driving, dentistry & any position where the head is forward while the shoulder joint is hunched over for extended periods.
- The consequence becomes noticeable with the strained muscles of the neck & worsened posture.
Breathing:
- These scalene muscles are accessory muscles for breathing.
- During inhalation, the scalene muscles lift the upper ribs which creates a volume in the chest cavity.
- When The scalene muscles are contracted, it is open space for the lungs which is expand the thorax by lifting the top ribs.
- If occur to any respiratory issues the scalene muscles begin to work harder, which produces tension & tightness.
Scalene syndrome:
- In the Scalene syndromes are compressions of structures around the neck area.
- This syndrome involves the anterior & middle scalene muscles, which is become too tight & squeeze the neurovascular components which are located between the two muscles.
- This condition is common with some activities where the head is forward & downward like computer & dental work.
- When your head is forward & rounded shoulder posture is greatly affected by the causing of chronic shortening of the scalene muscles.
- This condition can also contribute to thoracic outlet syndrome.
Scalene myofascial pain syndrome:
- This common type of myofascial pain syndrome is a painful condition that originates in the neck & radiates down the arm.
- This syndrome is primary/secondary.
- The Primary pain syndrome condition gives to results from the chronic overuse of the scalene muscles, poor posture & repetition in the microtrauma.
- In Secondary pain, syndrome conditions result from medical issues such as osteoarthritis, trauma & complex regional pain syndrome.
- This condition produces muscle weakness & stiffness which limits the movement of the neck
Thoracic outlet syndrome:
- There are available to multiple causes of thoracic outlet syndrome, but what is associated with the scalene muscles is when the brachial plexus & subclavian artery are compressed between the anterior & medial scalene muscles.
- This syndrome is produced by weakness, pain, tingling & numbness of the shoulders, upper arm, elbow, forearm, hand & fingertips meaning the whole affected upper limb.
Cervical radiculopathy:
- This condition is also more commonly known as the pinched nerve.
- When the scalene muscles have become too tight, it is produced to narrow the brachial plexus pathway & trap a nerve, which causes a pinched nerve in the neck so that it is felt through the arm to the hand.
- When these Scalene muscles become tight, which is pinch the structures of the nerves, arteries & veins which is pass through the area to cause burning, tingling, aching & numbness in the arm & neck
What is a diagnosis of the Scalene Muscles pain?
- When you feel any severe symptoms of this muscle pain as soon as possible contact the doctor.
- When you meet the doctor, the doctor follows the assessment to try to cause this muscle pain.
- The first doctor asks questions about the history of the patient & tries to know about the reason for the pain.
- In the observation, part observes the swelling & spasms of the muscle.
- In the palpation, part palpates to swelling & temperature.
- The examination, part examines the tenderness, ROM & strength of the neck & shoulder movement.
- In some conditions, doctors also suggest MRI & X-rays for proper diagnosis.
What is the Treatment of the Scalene Muscles pain?
RICE principle:
- In the starting phase of the muscle pain, the health care provider advises to RICE principle to reduce the pain.
- R – rest = When you feel pain doctors advise you to rest not to do any movement of the neck & use a thin pillow for support.
- I – ice = You can apply ice to the area of pain for 20 minutes, you can also use an ice pack or frozen peas on the area of pain for release to muscle pain & swellings.
- C – compression = You can also apply bandages & taping reduce to swelling & spasms.
- E- elevation = For this muscle, elevation is not possible because if you elevate to the area of pain, it may produce pain.
Pain medication:
- Medical treatment for this Scalene muscle pain:
- Which is used in the starting phase of muscle pain to reduce the muscle pain.
- You are used to pain relief drugs such as NSAIDs =
- Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs including ibuprofen or naproxen.
- You are also applying volini gel & diclofenac gel on the area of pain decrease to pain.
- Always drink plenty of Water which helps to move the soft tissues & maintain flexibility.
- You can take to break in every exercise or some work in which the neck is constantly crouched over for extended periods, which leads to fatigue of muscle & weaken the muscles.
- Sleeping in a neutral position means using a proper pillow that is not too high & too low which is lead to causes the scalene muscles to extend or flex movement.
What is Physiotherapy treatment for Scalene Muscle pain?
- The physiotherapy treatment includes massage, stretching & strengthening exercises which is help to reduce the pain & decrease the weakness of muscles.
Massage for the Scalene Muscles pain:
- For pain relief massage is also applied to the area of pain & points which is the muscle tenderness & trigger points of muscle pain.
- This massage helps to relieve the tension & pain.
- This massage is applied with to help of oil & powder.
- In the message type for this muscle pain also applied to MFR on the trigger points of release of the muscle pain.
Stretching for the Scalene Muscles pain:
Stretching helps you release the muscle pain, tightness, or spams of muscle.
Position for stretching :
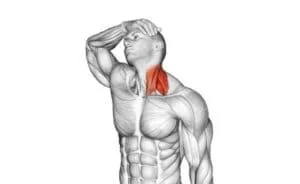
- Lower & anchor the shoulder joint of the side to be stretched position by placing the side’s hand under the buttock.
- Then Bring the opposite hand over the head so that the fingers make contact with the top of the ear.
- Gently pull the head & neck so that it is tilted to the opposite side of the side which the side wants to stretch then relax the neck muscles.
- Then Try to pull the ear down to the shoulder joint
- Now, the patient is rotating the head & the degree of rotation is used to determine the target scalene muscle.
- Stretch for Posterior Scalene muscle
- To target the posterior scalene muscle, turn the face toward the arm which arm is the pull.
- Stretch for Anterior Scalene muscle
- To target the anterior scalene muscle, turn the face away from the pulling arm.
- stretch for Medial scalene muscle
- To target the middle scalene muscle, look straight up at the ceiling & just slightly toward the pulling arm.
- Then Concentrate on the muscle with the help of your efforts on the muscle & stretch the muscle till you feel the stretching filling.
- Then Hold this stretching position for around 30 seconds & do the 3 times in 1 session & perform 3 sessions per day.
Strengthening exercise for the scalene muscle pain:
- Scalene PNF strengthening
- Strengthen the scalene exercise
Scalene muscle PNF strengthening:
- For strength, the scalene muscle sits in a comfortable chair.
- Then Place the palm of the right hand on the right side of the head.
- This hand acts as a stabilizer for this exercise.
- Then start to move the right ear toward the right shoulder joint while maintaining the resistance which is provided by the right hand.
- Repeat this exercise 8 to 12 times on every side.
- By strengthening this scalene muscle, the patient increases the ability to stabilize the cervical spine, which reduces the risk of a future injury.
Strengthen the scalene exercise:
- The patient is sitting & stands up straight with the resistance band looped around the head.
- Then Hold the ends of the band firmly to one side ensuring there is some tension in the band.
- Pull the band away from the head, resisting the movement by keeping the head in a neutral position.
- Hold this exercise position then relax & repeat this exercise.