Brachioradialis Muscle Pain: Cause, symptoms, Treatment, Exercise
When you feel pain in the forearm & elbow, it is indicated to be Brachioradialis Pain. this pain feels like shooting pain. This pain occurs due to muscle strain & tendonitis of muscle.
Table of Contents
What is Brachioradialis Muscle Pain?
- Brachioradialis muscle pain usually feels like a shooting pain in the forearm /elbow joint.
- This pain is always confused with the tennis elbow.
- Because both conditions are typically caused by overuse & overexertion.
- This pain is produced due to the Brachioradialis strain & Brachioradialis tendinitis.
- Patient feel the tightness & pain & spasm in the muscle.
- This pain is relieved by RICE therapy & exercise.

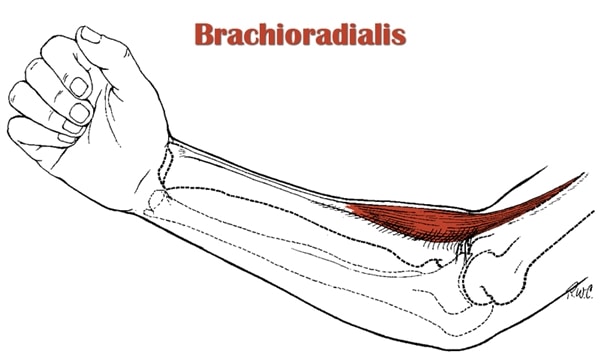
What is the anatomy of the brachioradialis muscle?
- The origin of the brachioradialis muscle is the lateral supracondylar ridge of the humerus bone & upper arm bone.
- Then It travels down to the forearm & inserts on the styloid process of the radius bone.
- The brachioradialis muscle is a superficial muscle so that it is easily seen & palpate.
- Brachioradialis muscle is supplied by the radial nerve.
- The cubital fossa of the elbow joint, also known as the elbow pit is bordered to laterally by the brachioradialis muscle. The fossa contains structures like as the biceps brachii tendon, the median nerve, & the brachial artery.
- The function of This brachioradialis muscle is to flex the elbow joint.
- This brachioradialis muscle is most powerful & active when the forearm is in a neutral position between the pronation & supination movement.
What are the causes of the brachioradialis pain?
- If the patient does overuse the brachioradialis muscle which produces muscle pain.
- Brachioradialis muscle strain:
- If the patient applies sudden force to the forearm/wrist joint which is an overload on the brachioradialis, which is leading to mild/severe tearing of the muscle.
- When this occurs pain & swelling is felt in the forearm, & it is hurt to move the arm normally.
- Brachioradialis tendinitis:
- If the apply repetitively stress on the brachioradialis muscle, like as it occurs in activities of tennis & hammering, which is suffer from the tendinitis.
- It is produced to pain & swelling around the forearm.
- Forearm weakness from the cervical radiculopathy:
- A pinched nerve in the neck is produce forearm pain & weakness.
- This affects the brachioradialis muscle & make moving the arm & difficult in the wrist joint.
- Avulsion fracture of the brachioradialis tendon :
- A high-velocity force onto the forearm muscle is cause the brachioradialis tendon which is breaking away from the radius bone so that it is leading to a tear in the tendon.
- When the torn tendon has also removed the piece of bone, it is known as the avulsion fracture.
- This fracture cause is pain, swelling,& bruising of the forearm.
- When the occur Nerve damage is also given to result, which is leading to numbness & tingling in the arm & hand.
- Overexertion of the muscle:
- When the applied overload on the brachioradialis muscle for extended periods, it is become too tender &, eventually & painful.
- Manual labour & weightlifting are also the two most common causes of Brachioradialis muscle pain.
- If the occur repetitive movements which are produced when the patient play the tennis game & typing on the keyboard.
- Brachioradialis muscle pain is also be caused by physical contact injury such as a fall / a blow from a hard object.
- When the patient suspect you have any condition with the brachioradialis muscle, that patient is must be in contact with the healthcare provider.
- They are give the patient an accurate diagnosis of the condition & give to guide in rehabbing the brachioradialis muscle.
What are the symptoms of Brachioradialis muscle pain?
- The most common symptom of brachioradialis muscle pain is patients feel the extreme tightness of the muscles of the forearm.
- The patient is feeling pain in the forearm & elbow joint. the patient also feels the pain in:
- Back of the hand
- Thumb
- Index finger
- Some Actions which is triggering the pain include:
- Turning a screwdriver
- Turning a doorknob
- Shaking hands with someone
- Drinking with a cup or mug
What is the treatment of Brachioradialis muscle pain?
- An injury into the brachioradialis muscle pain benefits from the proper rehab which helps the move again.
- The starting phase of rehab includes using the R.I.C.E. principle: rest, ice, compression & elevation.
- It helps to control the initial inflammatory response & limit pain with swelling.
Use the RICE principle for pain relief in the starting phase :
- R – Rest = Limit the use of this muscle as much as possible during the 72 hours after the onset of pain.
- I – Ice = For To limit the inflammation & swelling, the patient is applied to the ice for 20 minutes every two hours, the patient is also used to ice pack & frozen peas.
- C- Compression = To decrease the swelling so that loosely wrap the forearm with a medical bandage.
- E – Elevation = To minimize the swelling, keep the forearm & elbow joint elevated.
- Once the brachioradialis muscle pain is recovered & then used to specific exercises which is improve the muscle’s strength.
- exercise also helps in preventing future incidents.
Heat & Ice:
- Ice is used on the forearm & brachioradialis muscle which is help to control the localized swelling, pain,& inflammation.
- Ice must be applied for 10 to 15 minutes.
- Ice therapy is also applied to ice packs.
- After a few days, when the injury of muscle is healed, heat is applied to promote the blood flow & improve tissue mobility.
- Heat is applied for 10 to 15 minutes in the area of pain & several times a day.
- Heat therapy is also applied to the hot pack.
- Must be Care to avoid the burns from heat & frost burns from ice.
Massage:
- When the pain occurs in the muscle it is present with several trigger points in the brachioradialis muscle.
- So that massage is given to benefit from reducing the pain.
- Massage helps to decrease pain, improve tissue mobility & improve blood flow.
- This massage is applied with to help of oli & massager machine.
- This massage is applied in a circular motion.
Kinesiology Tape:
- A physiotherapist is recommended to kinesiology taping for the brachioradialis muscle pain.
- The tape is used to decrease pain, improve muscle function & decrease spasms of the muscle after the injury of the muscle.
What is Physiotherapy treatment for Brachioradialis muscle pain?
- In the physiotherapy treatment include electrotherapy, stretching, exercise & strengthening exercise which is helping to reduce the pain & swelling of muscle
Electrotherapy treatment for the Brachioradialis pain:
- In the electrotherapy treatment SWD, the US, TENS, IFT machines are used for pain relief & reduce swelling & spasms.
- If in the patient tenderness & trigger points are present in the muscle so that used to US = ultrasound therapy for reducing the tenderness & trigger point as well as swellings.
Stretching Exercise for the Brachioradialis muscle pain:
- Standing brachioradialis stretch
- Arms down brachioradialis stretch
- Arms back brachioradialis stretch
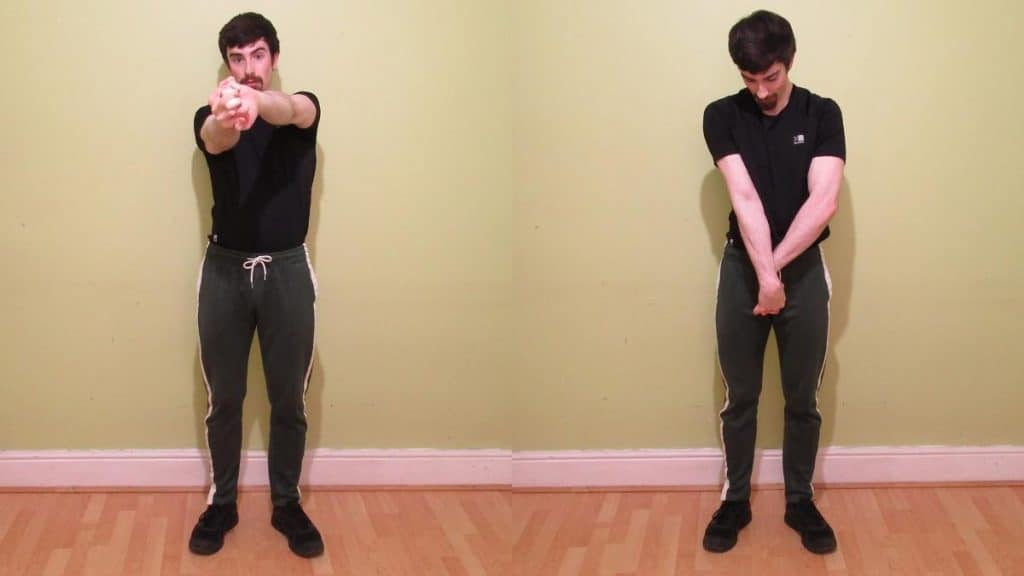

Standing brachioradialis stretch:
- The patient is in a standing position for the stretching.
- Then Place the arms out in front of the with the elbow joint is fully locked out.
- Put one hand on top of the other & interlock the fingers.
- Bend the wrist joint of the bottom hand.
- Rotate the wrist joint onto the left side till the patient feel a strong brachioradialis stretch.
- Hold this stretching position for 30 seconds.
- Repeat this stretching for the other arm by rotating the hands to the right.
Arms down brachioradialis stretch:
- It is a simple stretching exercise for the muscle.
- The patient is in a standing position for the stretching.
- Cross the wrist joints over to one another & interlock the fingers.
- Then, rotate the top wrist joint away from the body while keeping the elbow joint is locked out.
- Repeat the same motion in the other arm.
- Hold this stretching position for 30 seconds.
- This stretching is repeated 2 -3 times per day.
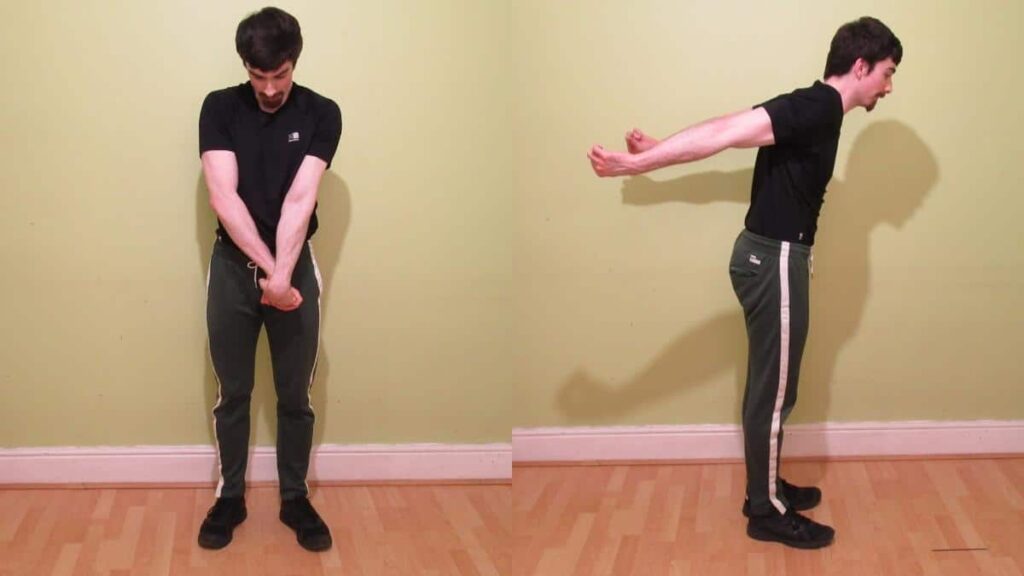
Arms back brachioradialis stretch:
- It is the best stretching exercise for the muscle.
- The patient is Standing up straight with a good/tall posture.
- Place the hands by the sides in a pronated position means palms facing backwards.
- Must be the elbow joints are fully locked out.
- Without moving the hip joint & bending the waist, extend the arms behind the body till they feel the deep brachioradialis stretch which is mentioned a moment ago.
- Hold this stretching position for 30 seconds.
- Repeat this stretching into 1-2 sets.
Exercise for the Brachioradialis muscle pain:
- Hammer curls
- Forearm pronation
- Forearm supination
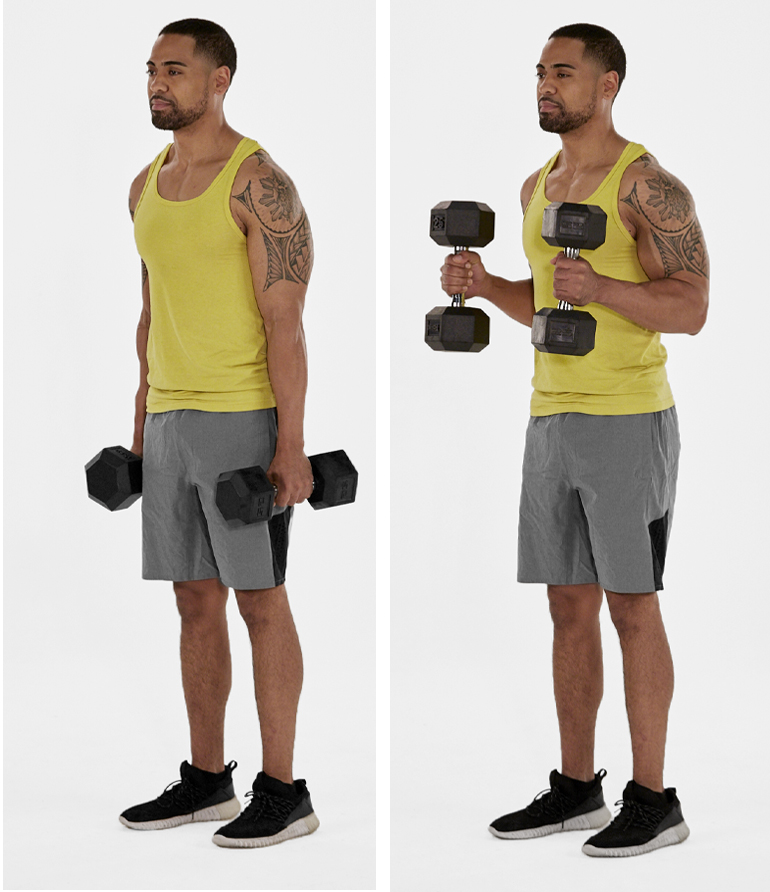

Hammer curls:
- The patient is in a standing & sitting position for the exercise in starting position.
- The patient is Holding a dumbbell in the hand with the arm at the side.
- Keep the hand & wrist in a neutral position.
- Bend the elbow joint up as far as possible.
- Patient hand position is look like holding a cup of water.
- Once the elbow joint is fully bent then slowly lower the weight down.
- Repeat this exercise 10 to 15 times.
Forearm pronation:

- The patient is in a standing & sitting position for the exercise in starting position.
- The patient is Holding a small dumbbell in the hand & rest the forearm on a table with the palm up.
- Slowly turn the palm over till the facing down.
- Hold this exercise position for a few seconds.
- Then return to the starting position.
- Repeat this exercise 10 to 15 times.
Forearm supination:
- The patient is in a standing & sitting position for the exercise in starting position.
- The patient is Holding a small dumbbell in their hand.
- Rest the forearm on a table with the palm facing down.
- Turn the palm over till the facing up.
- Hold this exercise position for a few seconds,& return to the starting position.
- Repeat this exercise 10 to 15 times.
Strengthening exercise for the Brachioradialis muscle pain:
- Reverse Barbell Curl
- Dumbbell Hammer Curl
- Rear Front Rotations
- Arm Kettlebell Reverse Curl
- Resistance Band Hammer Curl
- Arm Kettlebell Hammer Curl
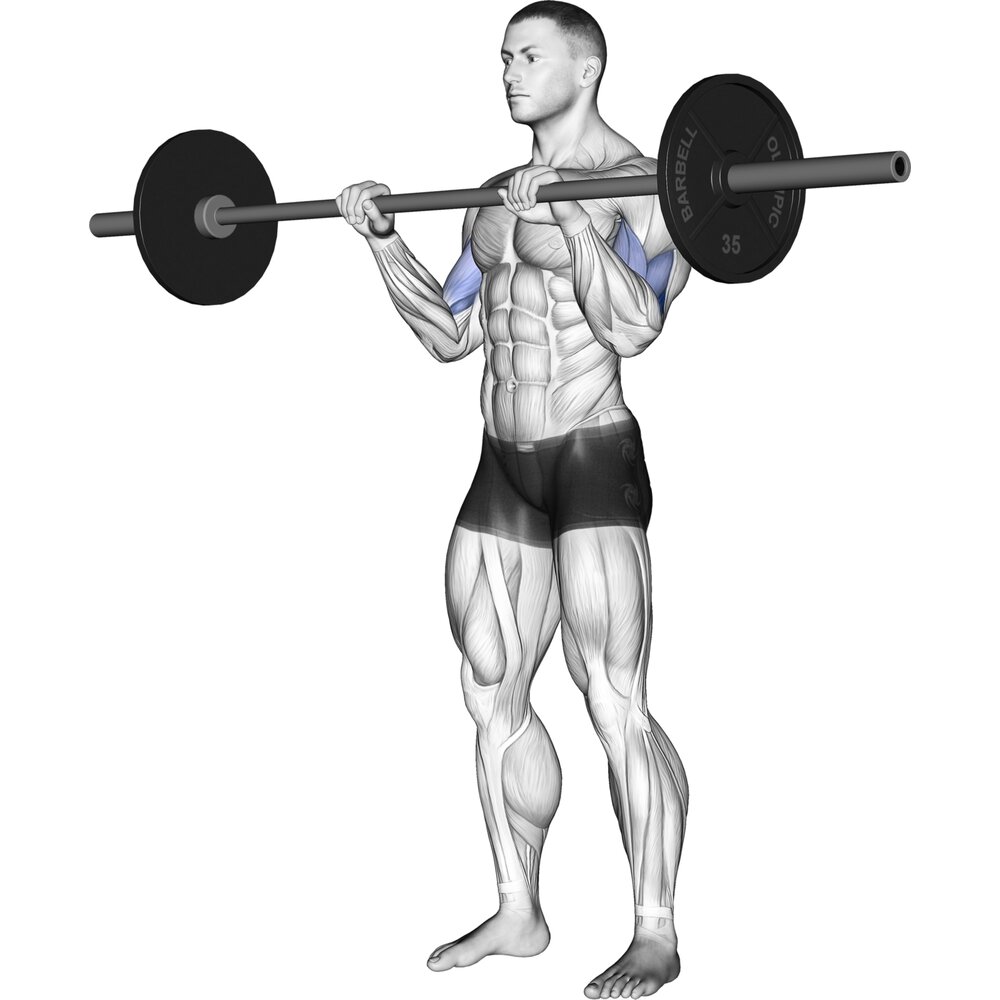
Reverse Barbell Curl:
- This exercise is also known as the overhand curl.
- The patient is holding a barbell with the hands roughly the shoulder joint width apart & palms are facing towards the patient.
- The patient has Assumed a sturdy standing position with the back straight.
- Contract the biceps muscle to curl the barbell upwards.
- Then Squeeze the biceps muscle hard at the top of the repetition & slowly return to the starting position.
- Repeat this exercise 3 times in 1 session & 2 -to 3 sessions per day.
Dumbbell Hammer Curl:
- The patient is holding a pair of dumbbells with the palms facing each other.
- The patient has Assumed a sturdy standing position with the back straight.
- Engage the core muscle & contract the biceps muscle to curl the dumbbells upwards.
- Then Squeeze the biceps muscle hard at the top of the rep & slowly lower the dumbbells into the starting position.
- Repeat this exercise 3 times in 1 session & 2 -to 3 sessions per day.
Rear Front Rotations:
- The patient is holding a pair of dumbbells with the palms facing towards each other.
- Hold the very bottom end of the shafts.
- The patient is in a sturdy standing position & keep the arms by the sides.
- Contract the brachioradialis muscle to flex the wrist joint up & bring the front end of the dumbbells upwards.
- Squeeze the brachioradialis muscle hard & return the dumbbells to the starting position.
- Repeat this exercise 3 times in 1 session & 2 -to 3 sessions per day.
Arm Kettlebell Reverse Curl:
- The patient is holding a kettlebell with one hand & the palm facing towards the patient.
- The patient is in a standing position with the back straight.
- Contract the brachioradialis muscle to curl the kettlebell upwards.
- Squeeze the brachioradialis muscle hard at the top of the rep & slowly return to the starting position.
- Repeat this exercise the 3 times in 1 session & 2 to 3 sessions per day.

Resistance Band Hammer Curl:
- The patient is holding the ends of a resistance band with the palms facing each other.
- The patient is in a sturdy standing position on the resistance band with the back straight.
- Then Engage the core muscle & contract the biceps muscle to curl the hands upwards.
- Squeeze the biceps muscle hard at the top of the rep & slowly lower the hands into the starting position.
- Repeat this exercise the 3 times in 1 session & 2 to 3 sessions per day.
Reverse Dumbbell Zottman Curl:
- The patient is holding a pair of dumbbells with the palms facing towards you.
- The patient is in a standing position with the feet roughly hip joint width apart.
- Must be Keep the back straight, contract the biceps muscle to curl the dumbbells upwards.
- Squeeze the biceps muscle hard at the top & twist the hands so that the palms face forward.
- Then Slowly lower the dumbbells into the starting position & twist the hands so that the palms are facing towards the body again.
- Repeat this exercise the 3 times in 1 session & 2 to 3 sessions per day.
Arm Kettlebell Hammer Curl:
- The patient is holding a kettlebell with one hand & palm facing inward.
- The patient is in a sturdy standing position with the back straight.
- Contract the bicep muscle to curl the kettle-bell upwards.
- Squeeze the bicep muscle hard at the top of the rep & slowly return to the starting position.
- Repeat this exercise the 3 times in 1 session & 2 to 3 sessions per day.