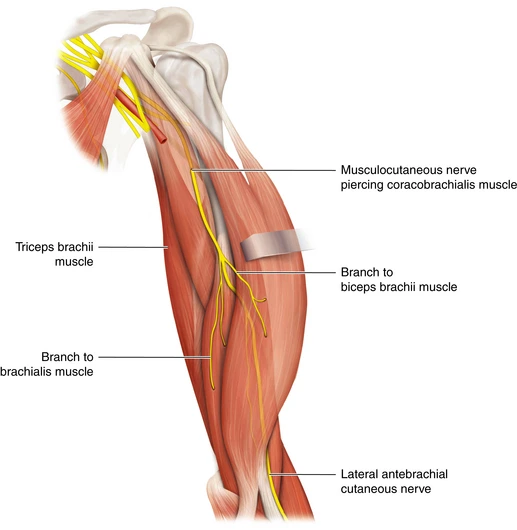
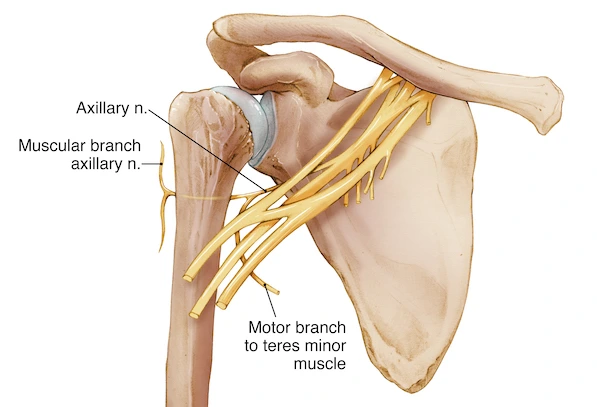
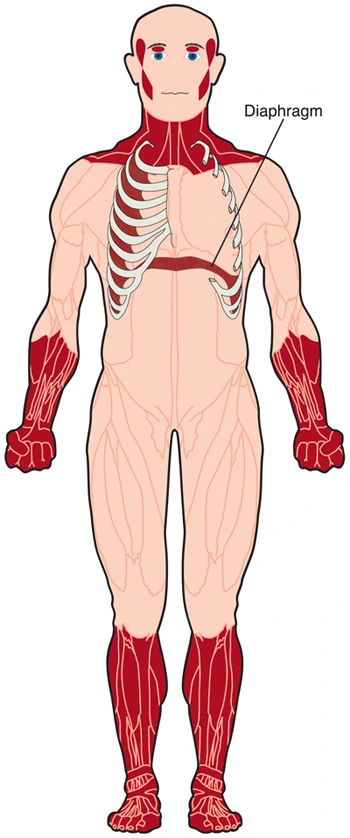
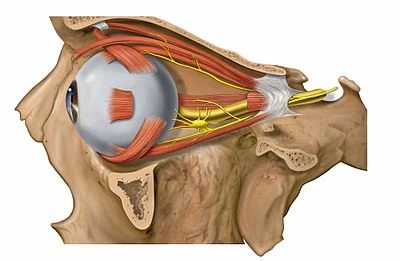
The Sacral Plexus
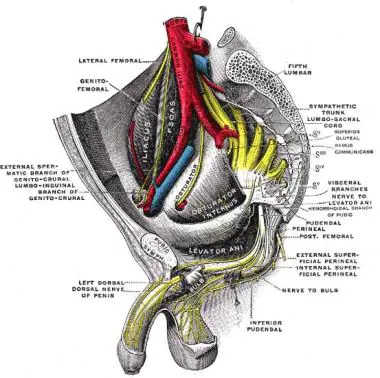
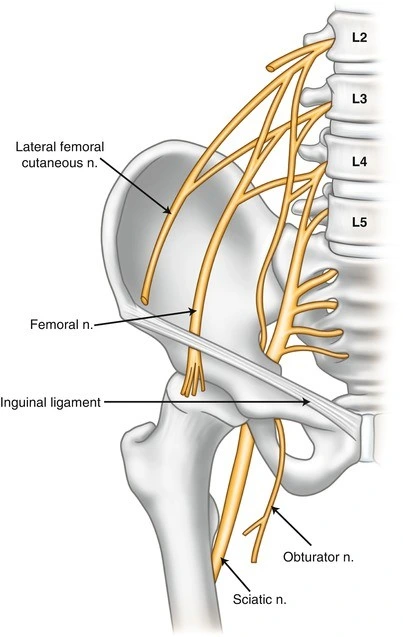
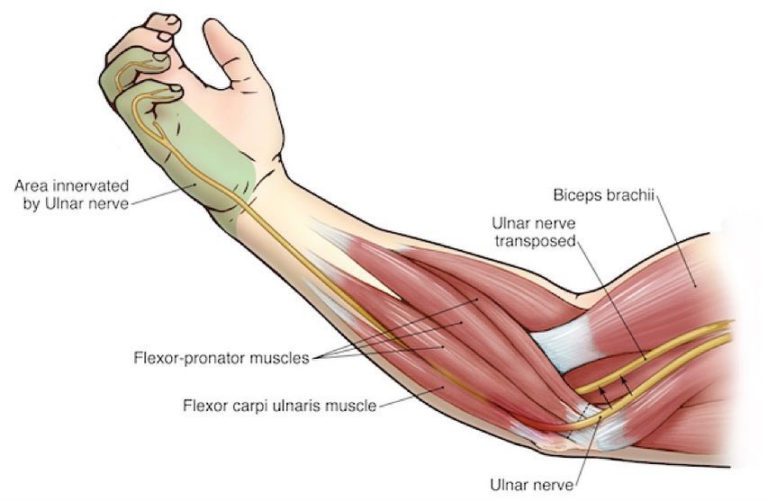
What is the sacral plexus? The sacral plexus is placed on the posterolateral wall of the pelvic cavity, fibbing anterior to the Piriformis. The sacral subsidies part out of the anterior sacral foramina and course laterally & inferiorly on the pelvic wall. A majority of the nerves originating from the sacral plexus pass through the…