Wrist Ligament
Table of Contents
Introduction
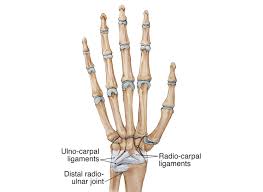
The wrist joint is a complex joint that connects the bones of the forearm (radius and ulna) to the bones of the hand (carpals). The wrist joint is made up of several ligaments, which are strong, fibrous tissues that connect the bones and provide stability to the joint. the wrist joint ligament also called as carpal ligament.
The ligaments of the wrist joint include the radial collateral ligament, ulnar collateral ligament, palmar radiocarpal ligament, dorsal radiocarpal ligament, and triangular fibrocartilage complex. These ligaments work together to provide stability to the wrist joint and allow for smooth movement.
Injuries to the wrist joint ligaments are common and can result in pain, swelling, and instability. Common causes of wrist joint ligament injuries include falls, sports injuries, and repetitive strain injuries. Treatment may involve rest, physical therapy, immobilization with a brace or cast, or surgery depending on the severity of the injury.
Ligaments of the Wrist Joint
The wrist joint is a complex joint that connects the bones of the forearm (radius and ulna) to the bones of the hand (carpals). The wrist joint is supported by several ligaments that provide stability and allow for smooth movement. the ligaments of the wrist joints are as mentioned below
- The radial collateral ligament
- The ulnar collateral ligament
- The palmar radiocarpal ligament
- The dorsal radiocarpal ligament
- The triangular fibrocartilage complex
The radial collateral ligament is located on the outer side of the wrist and connects the radius bone to the scaphoid and trapezium bones of the hand. This ligament provides stability to the wrist joint when the hand is moved away from the body.
The ulnar collateral ligament is located on the inner side of the wrist and connects the ulna bone to the triquetrum and pisiform bones of the hand. This ligament provides stability to the wrist joint when the hand is moved toward the body.
The palmar radiocarpal ligament is located on the palm side of the wrist and connects the radius bone to the carpal bones of the hand. This ligament provides stability to the wrist joint when the hand is bent backward.
The dorsal radiocarpal ligament is located on the back side of the wrist and connects the radius bone to the carpal bones of the hand. This ligament provides stability to the wrist joint when the hand is bent forwards.
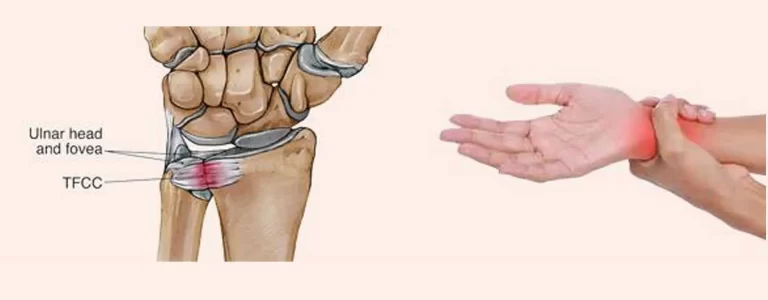
The triangular fibrocartilage complex is a group of ligaments and cartilage that are located on the ulnar side of the wrist. This complex provides stability to the wrist joint and helps to absorb shock.
Functions of the Wrist Joint Ligament
The wrist ligaments are responsible for providing stability and support to the wrist joint. There are several ligaments in the wrist joint, each with a specific function.
- Radial Collateral Ligament: This ligament runs along the outer side of the wrist joint and provides stability to the joint when the hand is moved towards the thumb side.
- Ulnar Collateral Ligament: This ligament runs along the inner side of the wrist joint and provides stability to the joint when the hand is moved towards the little finger side.
- Palmar Radiocarpal Ligament: This ligament is located on the palm side of the wrist joint and provides stability to the joint when the hand is bent forward.
- Dorsal Radiocarpal Ligament: This ligament is located on the back side of the wrist joint and provides stability to the joint when the hand is bent backward.
- Triangular Fibrocartilage Complex (TFCC): This is a group of ligaments and cartilage that provide stability to the joint between the ulna bone and the wrist bones.
The wrist ligaments work together to prevent excessive movement of the wrist joint, which can lead to injury. They also help to distribute forces evenly across the joint during activities that involve gripping or weight-bearing. In addition, the ligaments provide proprioceptive feedback to the brain, which helps us to perceive the position and movement of our wrist joints.
Overall, the wrist ligaments play a crucial role in maintaining the stability and function of the wrist joint. Any injury or damage to these ligaments can result in pain, weakness, and instability of the wrist joint.
Injuries of the wrist joint ligament
Injuries to the wrist ligaments can occur due to trauma, overuse, or degeneration. Some common injuries of the wrist ligaments include:
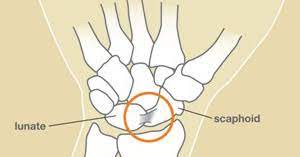
- Sprains: A wrist sprain occurs when one or more of the ligaments in the wrist are stretched or torn. This can happen due to a fall on an outstretched hand, a sudden twist or turn of the wrist, or repetitive stress on the wrist joint. Symptoms of a wrist sprain include pain, swelling, stiffness, and difficulty moving the wrist.
- Ligament tears: A ligament tear occurs when one or more of the ligaments in the wrist are completely torn. This can happen due to a severe injury or trauma to the wrist joint. Symptoms of a ligament tear include severe pain, swelling, bruising, and instability of the wrist joint.
- TFCC tears: Tears in the triangular fibrocartilage complex (TFCC) can occur due to repetitive stress, trauma, or degeneration. Symptoms of a TFCC tear include pain on the ulnar side of the wrist, clicking or popping sounds during movement, and weakness in grip strength.
- Wrist instability: Wrist instability occurs when the ligaments in the wrist are stretched or torn, leading to abnormal movement of the bones in the wrist joint. This can happen due to a traumatic injury or repetitive stress on the wrist joint. Symptoms of wrist instability include pain, weakness, and a feeling of looseness in the wrist joint.
Assessment of the wrist joint ligament injuries
Assessment of carpal ligament injuries typically involves a thorough physical examination and medical history review. The healthcare professional may ask questions about the patient’s symptoms, such as pain, swelling, and difficulty moving the wrist joint.
During the physical examination, the medical professional will assess the range of motion of the wrist joint, looking for any limitations or pain with movement. They may also perform specific tests to evaluate the stability of the ligaments, such as the Watson test or the scaphoid shift test.
Imaging studies, such as X-rays, MRI, or ultrasound, may also be ordered to confirm the diagnosis and assess the severity of the injury. X-rays can help identify fractures or dislocations, while MRI or ultrasound can provide more detailed information about soft tissue injuries, such as ligament tears.
so in conclusion, a comprehensive assessment of carpal ligament injuries is important to accurately diagnose the injury and develop an appropriate treatment plan.
Treatment of the wrist joint ligament injuries
The treatment of carpal ligament injuries depends on the severity of the injury and the specific ligament affected. RICE (rest, ice, compression, and elevation) may be enough to relieve pain and swelling in minor cases. In order to control pain and inflammation, nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory medications (NSAIDs) may also be administered.
In moderate to severe cases, immobilization of the wrist with a splint or cast may be necessary to allow the ligaments to heal. Physical therapy may also be recommended to improve the range of motion, strength, and stability of the wrist joint.
In some conditions, surgery may be required to repair or reconstruct damaged ligaments. This may involve using sutures or grafts to repair the ligament or using a tendon from another part of the body to reconstruct the ligament.
After treatment, it is important to follow a rehabilitation program to restore the full function of the wrist joint and prevent future injuries. This may involve exercises to improve strength and flexibility, as well as modifications to activities that may put stress on the wrist joint.
so in the end, the treatment of carpal ligament injuries is individualized based on the specific injury and the patient’s needs and goals. It is important to work closely with a medical professional to develop a treatment plan that is appropriate for your situation.
Physiotherapy treatment for wrist joint ligament injuries
Physiotherapy treatment for carpal ligament injuries typically involves a combination of manual therapy, exercises, and modalities to reduce pain, and inflammation, and restore function.
Manual therapy techniques, such as soft tissue mobilization, joint mobilization, and stretching, can help to improve the range of motion, reduce muscle tension, and promote healing. The physiotherapist may also use modalities such as ice or heat therapy, ultrasound, or electrical stimulation to reduce pain and swelling.
Exercises are also a very important component of physiotherapy treatment for carpal ligament injuries. Strengthening exercises can help improve the stability of the wrist joint and prevent future injuries. Exercises that involve a range of motion can keep joints flexible and prevent stiffness. The physiotherapist may also prescribe specific exercises to target the injured ligament and promote healing.
In addition to manual therapy and exercises, the physiotherapist may provide education on proper ergonomics and body mechanics to prevent further injury. They may also recommend the use of braces or splints to support the wrist joint during daily activities.
so in the end, physiotherapy treatment for carpal ligament injuries is focused on reducing pain, improving function, and promoting healing to allow the patient to return to their normal activities as soon as possible.
Risk factors for the wrist joint ligament injuries
Carpal ligament injuries are caused by repetitive stress on the wrist and hand, leading to damage to the ligaments that support the wrist joint. Some of the risk factors that increase the likelihood of developing carpal ligament injuries include:
- Repetitive motions: Performing repetitive motions with the hands and wrists, such as typing or using a mouse, can cause strain on the ligaments and tendons in the wrist.
- Poor posture: Poor posture while working can cause stress on the wrists and hands, leading to ligament injuries.
- Awkward positions: Holding the wrist and hand in awkward positions for extended periods of time can cause damage to the ligaments.
- Forceful exertion: Using excessive force with the hands and wrists, such as when lifting heavy objects, can cause ligament injuries.
- Age: As people age, their ligaments become less flexible and more prone to injury.
- Gender: Women are more likely to develop carpal ligament injuries than men, possibly due to differences in anatomy and hormonal factors.
- Medical conditions: Certain medical conditions such as arthritis, diabetes, and thyroid disorders can increase the risk of developing carpal ligament injuries.
- Genetics: Some people may be genetically predisposed to developing carpal ligament injuries due to differences in their ligament structure or other factors.
By understanding these risk factors, individuals can take steps to prevent carpal ligament injuries by modifying their work habits and environment.
How to prevent the wrist joint ligament injuries
Preventing carpal ligament injuries involves adopting healthy habits and making adjustments to your work environment. Here are some tips to prevent carpal ligament injuries:
- Maintain proper posture: Maintaining proper posture can help reduce the strain on your wrists and hands. Keep your shoulders relaxed, your elbows close to your sides, and your wrists straight.
- Take breaks: Take frequent breaks from repetitive tasks that involve your hands and wrists. Stretch your hands and fingers during these breaks.
- Use ergonomic equipment: Use ergonomic equipment such as an ergonomic keyboard, mouse, or wrist pad. These tools can help reduce the strain on your wrists and hands.
- Adjust your workstation: Adjust your workstation to ensure that your wrists are in a neutral position while you work. Your keyboard should be at elbow height, and your monitor should be at eye level.
- Strengthen your muscles: Strengthening the muscles in your hands and wrists can help prevent injuries. Consider doing exercises such as wrist curls, grip strengthening exercises, and finger stretches.
- Maintain a healthy lifestyle: Maintaining a healthy lifestyle can help prevent carpal ligament injuries. Eat a properly balanced diet, exercise regularly, and get enough sleep.
By following these tips, you can reduce your risk of developing carpal ligament injuries. If you do experience pain or discomfort in your hands or wrists, seek medical attention promptly to prevent further damage.
FAQ
A band of strong, fibrous tissue called a wrist ligament links the bones in the wrist joint.
There are many different types of wrist ligaments, including the scapholunate ligament, lunotriquetral ligament, radiocarpal ligament, and ulnocarpal ligament.
Wrist ligament injuries can be caused by trauma or repetitive stress to the wrist joint, such as from sports injuries, falls, or overuse.
Symptoms of a wrist ligament injury can include pain, swelling, stiffness, and limited range of motion in the wrist joint.
A wrist ligament injury is typically diagnosed through a physical examination, X-rays, and/or MRI or CT scans.
Treatment options for a wrist ligament injury may include rest, ice, compression, elevation, physical therapy, and surgery in severe cases.
Wrist ligament injuries can be prevented by avoiding repetitive stress on the wrist joint, maintaining good posture and ergonomics, and wearing protective gear during sports or other activities that involve the wrist.