Snapping ulnar nerve
Table of Contents
Description
The ulnar nerve is one of the predominant nerves withinside the arm that runs from the neck right down to the hand. It travels alongside the internal aspect of the top arm, at the back of the elbow, and alongside the internal of the forearm.
Snapping ulnar nerve, additionally referred to as ulnar nerve subluxation or snapping triceps syndrome, refers to a circumstance in which the ulnar nerve acts out of its ordinary role and snaps again into location whilst the arm is moved. When the ulnar nerve snaps, it can produce a clicking or snapping sensation, frequently observed via way of means of ache or discomfort.
The snapping sensation may be felt or maybe visible because of the nerve actions inside and out of its groove at the back of the elbow joint. This motion can be brought about via positive arm movements, which include flexing or extending the elbow.
Snapping withinside the elbow is an unusual purpose of aches. A snapping triceps tendon may cause severe elbow pain in younger children, particularly in younger weightlifters. Because snapping triceps syndrome is an extraordinary circumstance it’s far more frequently misdiagnosed.
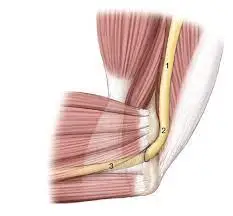
Our elbow is a complex hinge joint. The electricity to flex or bend the elbow comes from the Biceps and Brachialis muscle tissue. The electricity to increase the elbow comes from the Triceps muscle. The Triceps attaches to a bone at the again of the elbow we name the olecranon.
In a positive, small organization of humans, the internal or medial triceps has an unusual or greater tendon. That tendon attaches alongside the internal aspect of the elbow rather than the again of the elbow.
In weight lifters, while the triceps will become large and more potent the greater medial band can also additionally begin snapping over a bone at the internal aspect of the elbow. We name that bone the medial epicondyle.
Initially, humans are involved via way of means of snapping themselves, however, it doesn’t harm so they maintain running out. Eventually, the internal aspect of the elbow will begin to harm whenever the tendon snaps over the bone. This ache is because of inflammation of the snapping tendon.
Anatomy of snapping ulna nerve
The snapping ulnar nerve, additionally referred to as ulnar nerve subluxation or snapping triceps syndrome, is a circumstance characterized via way of means of the unusual motion or displacement of the ulnar nerve in the elbow joint.
The ulnar nerve is one of the predominant nerves withinside the arm that offers sensation to the little finger and 1/2 of the hoop finger, in addition to controlling positive muscle tissue withinside the hand. The anatomy of a snapping ulnar nerve includes the subsequent structures:
Ulnar nerve:
- The ulnar nerve originates from the brachial plexus withinside the neck and travels down the arm, passing thru a slender tunnel referred to as the cubital tunnel on the elbow.
- It then maintains alongside the internal of the forearm, offering the muscle tissue and pores and skin of the hand.
Cubital tunnel:
- The cubital tunnel is a groove fashioned via way of means of the bony bump at the internal element of the elbow (medial epicondyle) and a ligament (cubital tunnel retinaculum) that stretches throughout the groove.
- The ulnar nerve runs thru this tunnel and is surrounded via way of means of gentle tissues and shielding structures.
Osborne’s ligament:
- Also referred to as the ligament of Struthers, Osborne’s ligament is a fibrous band that extends from the medial epicondyle to a bony prominence referred to as the medial supracondylar ridge.
- This ligament can from time to time purpose compression or entrapment of the ulnar nerve.
Triceps tendon:
- The triceps muscle is positioned at the again of the top arm and is liable for straightening the elbow joint.
- Its tendon attaches to the olecranon process, the bony prominence behind the elbow.
- In instances of snapping the ulnar nerve, the ulnar nerve can also additionally revel in unusual motion or displacement because it slides backward and forward over the medial epicondyle at some stage in elbow flexion and extension.
- This motion can arise because of diverse factors, which include an enlarged Osborne’s ligament, muscle imbalances, or repetitive trauma.
The snapping sensation or sound may be felt or heard because the nerve shifts inside and out of its ordinary role.
Snapping the ulnar nerve can purpose signs and symptoms which include aches, tingling, numbness, weakness, or a “clicking” sensation withinside the elbow or hand. If left untreated, it can cause additional nerve inflammation, inflammation, or maybe nerve damage.
Causes of snapping ulnar nerve
Snapping ulnar nerve, or ulnar nerve subluxation, may be because of diverse elements. The actual motive might also additionally range from character to character, however right here are a few not unusual place reasons related to this situation:
Anatomical abnormalities:
- Certain anatomical versions or abnormalities withinside the systems across the ulnar nerve can contribute to its snapping.
- For example, an enlarged or hypertrophic Osborne’s ligament, which is a fibrous band close to the medial epicondyle of the elbow, can impinge at the ulnar nerve, inflicting it to snap inside and out of its everyday position.
Repetitive movement or trauma:
- Repetitive motions or sports that contain bending and straightening the elbow joint can place strain on the ulnar nerve and its surrounding systems.
- This repetitive strain can cause infection, inflammation, and eventual subluxation of the nerve.
- Athletes, musicians, and people worried about sports that require repetitive elbow actions can be a better chance.
Muscle imbalances or weakness:
- Imbalances or weaknesses withinside the muscle mass that surround and assist the elbow joint can affect the steadiness and motion of the ulnar nerve.
- If the muscle mass does now no longer characteristic properly, it could bring about extraordinary pulling or transferring of the nerve throughout elbow movement, main to snapping.
Traumatic injury:
- A direct blow or trauma to the elbow place can motivate harm to the systems helping the ulnar nerve,
- main to its instability and snapping.
- Fractures, dislocations, or different disturbing accidents withinside the elbow region might also additionally make a contribution to the improvement of a snapping ulnar nerve.
Overuse or immoderate stress:
- Activities that contain repetitive or extended stress at the elbow joint, together with leaning at the elbows for lengthy intervals or resting the elbows on tough surfaces can boom the chance of ulnar nerve subluxation.
- The sustained stress can boost infection and displacement of the nerve.
Congenital elements:
- In a few instances, people can be born with sure anatomical versions or predispositions that make them extra at risk of snapping the ulnar nerve.
- These congenital elements can encompass variations withinside the form or length of the bones, ligaments, or different systems withinside the elbow place.
It’s essential to word that snapping the ulnar nerve will have more than one contributing element, and in lots of instances, it is able to now no longer be attributed to an available reason. Diagnosis and remedy have to be accomplished with the aid of using a scientific expert who can examine the particular instances and broaden the perfect control plan primarily based totally on character needs.
Epidemiology of snapping ulnar nerve
- The epidemiology of snapping ulnar nerve, or ulnar nerve subluxation, isn’t well-documented, and particular records on its occurrence and prevalence are limited.
- However, the situation is normally taken into consideration to be especially uncommon in comparison to different peripheral nerve issues.
- Snapping the ulnar nerve can have an effect on people of diverse age agencies and occupations, however sure elements might also additionally boom the chance.
- For example, individuals who interact in sports that contain repetitive or forceful elbow actions, together with athletes, musicians (mainly the one’s gambling string instruments), and guide people can be extra at risk of growing the situation.
- While there are no unique records on the superiority of snapping ulnar nerve, it’s far anticipated that the situation money owed for a small share of instances of ulnar neuropathy is a broader time period encompassing diverse ulnar nerve issues.
- Ulnar nerve entrapment or compression on the elbow, called cubital tunnel syndrome, is extra usually said than snapping the ulnar nerve.
- It’s really well worth noting that snapping ulnar nerve can be underdiagnosed or misdiagnosed because of its relative rarity and the lack of knowledge among healthcare professionals.
- Some people with slight signs and symptoms won’t are seeking scientific attention, whilst others can be misdiagnosed with opportunity situations affecting the ulnar nerve or different systems withinside the elbow place.
- Further studies and epidemiological research are had to benefit a higher knowledge of the superiority, chance elements, and demographics related to snapping ulnar nerve.
- Consulting with a healthcare expert or expert with knowledge in peripheral nerve issues can offer extra correct data and steering concerning this situation.
Symptoms of snapping ulnar nerve
The signs and symptoms of snapping ulnar nerve, or ulnar nerve subluxation, can range from individual to individual. The circumstance is characterized via way of means of the bizarre motion or displacement of the ulnar nerve withinside the elbow joint, and the signs and symptoms might also additionally encompass:
Snapping sensation or sound:
- The maximum distinguished symptom of a snapping ulnar nerve is the snapping or clicking sensation that takes place withinside the elbow joint throughout the motion.
- This sensation can be felt or maybe heard because the ulnar nerve shifts inside and outside of its everyday function.
Pain or soreness:
- Snapping the ulnar nerve can motivate aches or soreness withinside the internal aspect of the elbow.
- The ache might also additionally vary from a mild, stupid pain to a sharp, capturing ache.
- It is frequently irritated via way of means of sports that contain bending and straightening the elbow or repetitive motions.
Numbness or tingling:
- Compression or infection of the ulnar nerve can result in sensations of numbness or tingling, generally felt withinside the ring finger and little finger.
- This numbness and tingling sensation might also additionally make bigger to the palm and again of the hand, affecting particular regions furnished via way of means of the ulnar nerve.
Weakness or clumsiness:
- In a few cases, snapping the ulnar nerve can bring about a weak point or clumsiness withinside the hand.
- Grip energy can be reduced, and exceptional motor skills, consisting of buttoning garments or conserving small objects, can be affected.
Worsening signs and symptoms with activity:
- Snapping ulnar nerve signs and symptoms are frequently exacerbated via way of means of sports that contain repetitive elbow motions, consisting of lifting, throwing, or gambling a musical instrument.
- The snapping sensation and ache might also additionally boom throughout those sports and subside with rest.
- It’s critical to word that the severity and frequency of signs and symptoms can range.
- Some people might also additionally revel in intermittent signs and symptoms that come and go, even as others might also additionally have chronic soreness.
- If left untreated, snapping the ulnar nerve can result in additional nerve infection, inflammation, or maybe nerve harm.
- If you think you will be experiencing signs and symptoms of a snapping ulnar nerve, it is endorsed to seek advice from a healthcare expert or an expert, consisting of an orthopedic doctor, or a neurologist, for the right assessment and prognosis.
- They can carry out a radical exam and suggest suitable remedy alternatives primarily based totally on your particular circumstance.
Diagnosis of snapping ulnar nerve
Typically, there is no scientific diagnosis or prognosis for “snapping ulnar nerve.” However, in case you suspect trouble together with your ulnar nerve, consisting of cubital tunnel syndrome, there are numerous steps a healthcare expert might also additionally take to diagnose the circumstance. These steps might also additionally encompass:
Medical history:
- The health practitioner will ask you approximately your signs and symptoms after they started, and any elements that get worse or alleviate them.
- They may inquire approximately your career or sports that would make contributions to nerve compression.
Physical exam:
- The health practitioner will observe your arm, elbow, and hand to test for symptoms and symptoms of nerve compression.
- They might also additionally check your muscle energy, determine your variety of movement, and observe regions of tenderness or swelling.
Tinel’s signal:
- This check entails tapping over the ulnar nerve on the elbow to elicit tingling or electric sensations down the arm or into the fingers.
- A high-quality Tinel’s signal can suggest nerve infection or compression.
Nerve conduction studies (NCS):
- NCS measures the velocity and energy of electrical impulses withinside the nerves.
- This check can assist examine the feature of the ulnar nerve and decide if there may be any nerve harm or compression.
Electromyography (EMG):
- EMG entails putting exceptional needles into particular muscle tissues to evaluate their electric activity.
- This check can assist pick out muscle weak points or abnormalities that can be associated with nerve dysfunction.
Based on the consequences of those diagnostic steps, a healthcare expert could make a greater correct prognosis and suggest suitable remedy alternatives. It’s critical to seek advice from a certified healthcare company for the right assessment and prognosis of your signs and symptoms.
Differential diagnosis
When comparing a snapping sensation regarding the ulnar nerve, it is critical to bear in mind different ability reasons except for cubital tunnel syndrome. Here are some viable differential diagnoses:
Ulnar nerve subluxation/dislocation:
- The ulnar nerve can from time to time circulate out of its everyday function on the elbow, inflicting it to snap or pop because it slides again into place.
- This circumstance is called ulnar nerve subluxation or dislocation.
Ulnar nerve entrapment at different sites:
- While cubital tunnel syndrome entails compression of the ulnar nerve on the elbow, the nerve also can be entrapped or compressed at different places alongside its pathway.
- These encompass the wrist (Guyon’s canal) or withinside the muscle tissues of the forearm.
- These situations may motivate snapping or popping sensations.
Tendon snapping:
- The snapping sensation will be associated with tendons transferring over bony systems withinside the elbow or forearm vicinity as opposed to the ulnar nerve itself.
- Conditions consisting of snapping triceps syndrome or snapping medial triceps tendon can motive comparable signs and symptoms.
Ligamentous instability:
- Instability or laxity withinside the ligaments across the elbow joint can result in bizarre motion or snapping sensations.
- This will be because of situations consisting of ligamentous sprain or instability.
Radial nerve involvement:
- Snapping sensations originating from the radial nerve, which travels alongside the outdoors of the arm, can on occasion be unsuitable for ulnar nerve issues.
- Radial nerve entrapment or snapping can arise at diverse sites, such as the radial tunnel.
These are only some ability differential diagnoses for snapping ulnar nerve-like signs and symptoms. A healthcare expert, consisting of a neurologist or orthopedic expert can be capable of determining your particular signs and symptoms, behavior a radical exam, and doubtlessly order extra checks to reach a correct prognosis.
Medical treatment
Medical treatment for a torn ulnar nerve or related conditions depends on the underlying cause and severity of the symptoms. Here are some possible treatments that your healthcare practitioner may consider:
Conservative treatment:
- In mild cases, conservative treatments may be recommended first.
- These may include modifying activities, avoiding repetitive movements or positions that aggravate symptoms, and using ergonomic aids or pillows to reduce pressure on the nerve.
Physical therapy:
- A physical therapist can provide exercises and stretches to improve flexibility and strength in the affected area.
- They may also recommend methods such as ultrasound or electrical stimulation to help relieve symptoms and promote healing.
Medications:
- Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs), such as ibuprofen, may be prescribed to reduce pain and inflammation associated with nerve irritation.
- In some cases, oral corticosteroids or corticosteroid injections around the affected nerve may be recommended to reduce inflammation and relieve symptoms.
Wearing a brace:
- Wearing it at night can help keep the elbow in a neutral position, reducing pressure on the ulnar nerve during sleep and reducing symptoms.
Nerve gliding exercises:
- These exercises involve gentle movements of the affected nerve to promote mobility and reduce adhesions or entrapment.
- A physical therapist can guide you in performing these exercises correctly.
Injections:
- If conservative measures are ineffective, a doctor may consider administering a therapeutic injection of local anesthetic and corticosteroid around the ulnar nerve to reduce inflammation and relieve pain.
Surgical intervention:
- In severe or severe cases where conservative measures have failed, surgery may be recommended.
- The specific surgical procedure depends on the underlying cause but may involve releasing restrictive structures or moving the ulnar nerve to a less compressed position.
It is important to note that the appropriate course of treatment depends on the individual case and it is best to consult a doctor for an accurate diagnosis and personalized treatment. They will consider your symptoms, medical history and perform a thorough examination to determine the most appropriate course of action.
Physiotherapy treatment
Physical therapy can play a crucial role in the treatment of an ulnar nerve tear or related conditions. A physical therapist will assess your condition and prepare a customized treatment plan. Below given are some usual physical therapy exercises that may be used:
Range of motion exercises:
Gentle exercises that improve mobility and flexibility of the affected joint, including the elbow, wrist, and fingers. This can help reduce nerve compression and relieve symptoms. Here are some mobility exercises that can help your elbow, wrist, and fingers. Be sure to do these exercises without pain and consult a doctor or physical therapist for personal guidance and to make sure they are appropriate for your condition:\
Elbow movement:
Elbow flexion and extension:

- Sit or stand with arms outstretched. Slowly bend your elbow, bringing your hand to your shoulder.
- Hold for a few seconds, then slowly extend your elbows back to the starting position.
- Repeat it 10 times.
Pronation and supination:
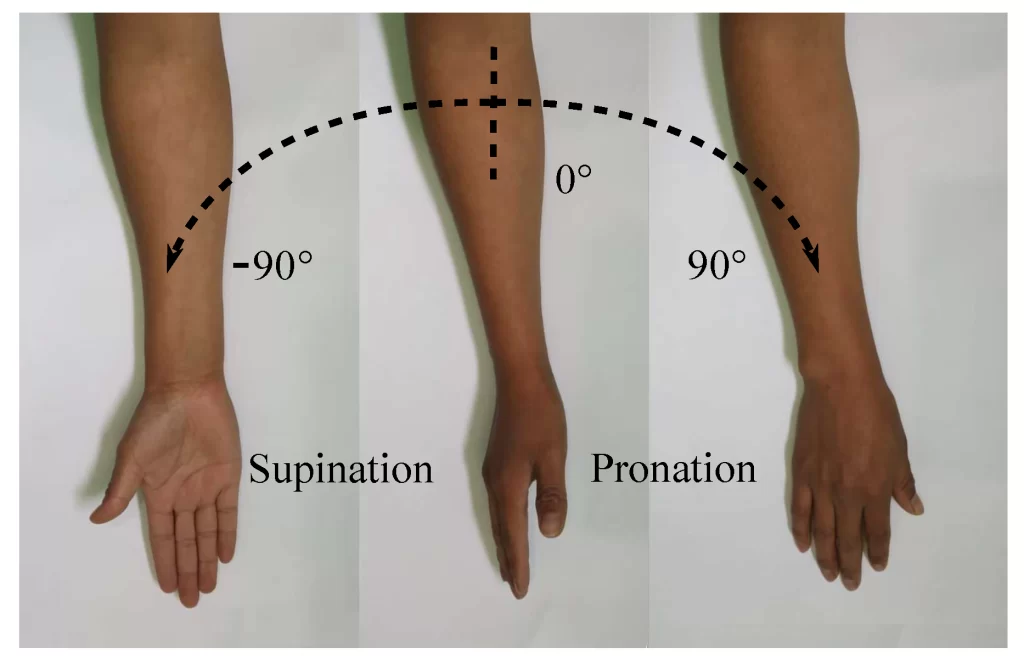
- Sit with your elbows bent at a 90-degree angle, palms down (prone).
- Slowly rotate the forearm so that the palm is facing up (supinated).
- Hold for a few seconds and then rotate your forearm back to the starting position.
- Repeat it 10 times.
Wrist movement exercises:
Wrist flexion and extension:
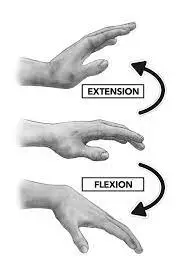
- Sit or stand with your arm on the table, palms down.
- Slowly bend your wrist as you raise your arm up. After holding this position for a few while, carefully return your arms to their original position.
- Repeat as many times as you want.
- To extend the target wrist, repeat the same exercise with the palm facing up.
Radial and ulnar deviation:
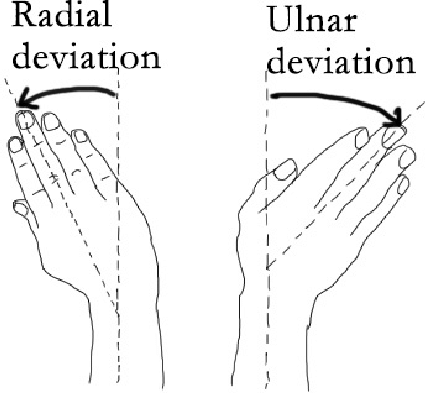
- Keep your forearm on the table, palm up. Push the wrist towards the thumb (radial deviation).
- Hold for a few seconds, and move the wrist to the little finger (elbow deviation).
- Repeat it 10 times.
Finger range of motion exercises:
Bending and extending the fingers:
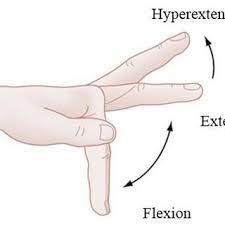
- Start with the arm extended and the fingers straight. Slowly bend the fingers into a fist, bringing the fingertips to the palm.
- Hold for a few seconds and then gradually extend your fingers back to the starting position.
- Repeat it 10 times.
Abduction and adduction of fingers:
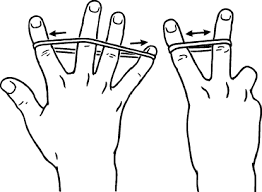
- Start with your fingers extended and slightly apart. Slowly extend your fingers as far as you want (catch). Hold for a few seconds and then bring the fingers together again (adduction).
- Repeat it 10 times.
- Remember to perform these exercises and if you feel pain or discomfort, reduce the movement or contact a health professional.
Strengthening exercises:
Targeted exercises to strengthen the muscles around the elbow, forearm, and hand. Strengthening these muscles can provide better support for the ulnar nerve and improve overall function. No doubt! Here are some strengthening exercises that can target the elbows, forearms, and hand muscles.
Note that performing these exercises with proper form and in a pain-free range is important. If you have any health conditions or problems, it is best to consult a doctor or qualified physical therapist before starting a strengthening program. Exercises for strengthening elbows and forearms:
Wrist flexion:
- Sit or stand with your forearm on the table or on your thigh, palm up.
- Maintain a light stop or a weighted object.
- Slowly bend your wrist upwards as you lift the weight.
- Maintain for a second and then gradually lower the weight back to the initial position.
- Repeat it 10 times.
Reverse Wrist Curls:

- Similar to wrist curls, but palm down.
- Maintain the weight in the hand, palm down.
- Bend the wrists up as you lift the weight.
- Maintain for a second and then gradually lower the weight back to the initial position.
- Repeat it 10 times
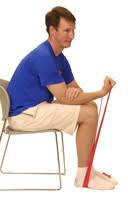
Pronation and supination with a resistance band:
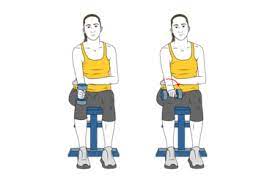
- Sit on the table with your forearms, palm up.
- Hold the resistance band or tube with both hands.
- Keep your elbow at your side and rotate your forearm outward (supination) against the resistance of the band.
- Maintain for a second, then gradually rotate the forearm inward (prone).
- Repeat it 10 times
Exercises to strengthen arms:
Grip Strengthening with Hand Gripper:

- Hold the grip in your hand with your fingers around it.
- Squeeze the gripper as much as possible without causing pain.
- Maintain for a few seconds and then gradually release the handle.
- Repeat it 10 times
Finger extension with rubber band:

- Place the rubber band around your fingers, just below your fingertips.
- Start with your fingers hooked, then spread your fingers against the resistance of the rubber band.
- Maintain for a few seconds and then gradually back to the starting position.
- Repeat it 10 times.
Remember to start with lighter resistance or weights and gradually increase as your strength improves. If you experience pain or discomfort during these exercises, stop and consult a doctor or qualified physical therapist for further guidance.
Nerve mobilization techniques:
These techniques involve specific movements and stretch to mobilize and release the ulnar nerve, reducing potential attack or entrapment. It can help relieve symptoms and improve the functioning of the nervous system. The goal of nerve mobilization techniques in the ulnar nerve is to improve its mobility and reduce restrictions or infections that can cause symptoms. Here is an example of a nerve mobilization technique that specifically targets the ulnar nerve:
Ulnar gliding exercise:
- Begin by sitting or standing in a comfortable position with a straight back.
- Extend the affected arm straight out in front of you, palm up.
- Lower the elbow slightly and turn the palm down.
- Gently bend the wrist to bring the fingers to the forearm (wrist flexion).
- With the other hand, gently grasp the fingers of the affected hand and pull them deeper into the wrist crease until you feel a slight tension or stretch on the inside of the forearm.
- Keeping your wrist bent, slowly extend your elbow to bring your arm closer to your body.
- You should feel a gentle pulling sensation on the inside of your hand and under your arm.
- Hold this position for a few seconds, making sure the tension or stretch is felt but not painful.
- Relax your hand and return it to the starting position, palm up.
- Repeat this set for the recommended number of repetitions as directed by your doctor or physical therapist.
- It is important to note that nerve mobilization techniques must be performed gently and in a painless range. Avoid straining or overstretching the nerve.
Posture and ergonomics training:
The physiotherapist guides you in maintaining the correct posture and ergonomics in daily activities and work. This helps minimize stress and pressure on the ulnar nerve.
Modalities
- Various methods can be used to reduce pain and inflammation.
- These may include ultrasound, electrical stimulation, cold therapy, or heat therapy.
- The choice of method depends on the specific case and the specific goals of the treatment.
Manual therapy techniques.
Manual techniques such as soft tissue mobilization, joint mobilization, or myofascial release can be applied to release tight muscles and tissues that may contribute to nerve compression. Soft tissue mobilization is a technique commonly used in physical therapy and rehabilitation for a variety of musculoskeletal disorders, including nervous system problems such as ulnar nerve entrapment. Ulnar nerve entrapment occurs when the ulnar nerve, which runs from the neck to the arm, is pinched or irritated.
Soft tissue mobilization
Soft tissue mobilization for ulnar nerve entrapment usually involves the following steps:
Evaluation:
- A physical therapist or healthcare professional will perform a thorough evaluation to determine the extent of ulnar nerve entrapment and identify potential contributing factors.
- They will assess your range of motion, strength, and any tenderness or tightness.
Manuals:
- Soft tissue mobilization techniques are aimed at removing muscle tension, scar tissue, and adhesions around the ulnar nerve.
- This can involve a variety of exercise techniques, including:
Massage:
Gentle massage techniques can help relax muscles and improve blood flow to the affected area.
Myofascial release:
This technique involves applying constant pressure to release tension and tension in the connective tissue surrounding muscles and nerves.
Trigger Point Therapy:
Certain tension points or “trigger points” can be identified and treated with pressure or deep tissue massage.
Stretching:
Gentle stretching exercises can help improve flexibility and relieve tension around the ulnar nerve. Relieves tension and promotes flexibility of the structures surrounding the ulnar nerve. Here are some stretching exercises to help relieve symptoms associated with ulnar nerve entrapment:
Wrist flexor stretch:
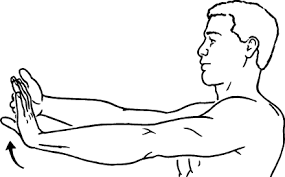
- Extend the affected arm in front of you, palm up.
- With the other hand, slowly bend the wrist back until a person feels a stretch in the forearm and wrist.
- Hold the stretch for 10-15 seconds and then release.
- Repeat the stretch 3-5 times and do the exercise several times throughout the day.
Wrist Stretch:
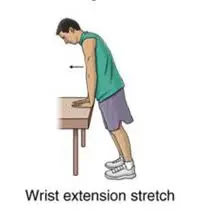
- Extend the affected arm in front of you, palm down.
- With your other hand, gently bend your wrist forward until you feel a stretch in the back of your forearm and wrist.
- Hold the stretch for 10-15 seconds and then release.
- Repeat the stretch 3-5 times and do the exercise several times throughout the day.
Ulnar nerve stretching:
- Sit or stand in a good position and relax your shoulders.
- Extend the affected arm out to the side at shoulder height, elbow straight, and palm up.
- Slowly tilt your head away from your outstretched hand while bending your wrists and fingers down.
- Maintain this position for some time and then back to the starting position.
- Repeat the movement 10-15 times and do the exercise several times a day.
Upper trapezius stretch:
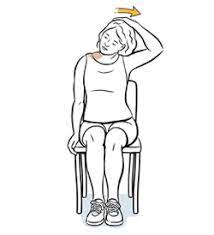
- Sit or stand in a good position and relax your shoulders.
- Tilt your head to the opposite side while gently pulling your head down with the hand on the same side.
- You should feel the tension in the sides of your neck and shoulders.
- Hold the stretch for 15-30 seconds and then switch sides.
- Repeat the stretch 3-5 times on each side and do the exercise regularly.
- Remember to do these stretches lightly and within your pain tolerance.
If you experience increased pain or discomfort during or after exercise, it is important to consult a doctor or physical therapist for further guidance. They can offer e.g. create a personal training plan and make sure the stretches are done correctly to maximize their effectiveness.
Nerve gliding exercises:
- Nerve gliding exercises involve moving the ulnar nerve through its normal range of motion to improve its mobility and reduce pressure.
- These exercises are usually prescribed as part of a comprehensive treatment plan and should be performed under the guidance of a healthcare professional.
Home exercises and self-care:
- Your physical therapist can provide specific exercises and self-care techniques for you to do at home.
- These may include stretching, strengthening, and postural correction exercises to help relieve the ulnar nerve.
- It is important to note that soft tissue mobilization is only one part of a comprehensive treatment plan for ulnar nerve entrapment.
- Depending on the cause and severity of your condition, other measures may be recommended, such as activity modification, ergonomic adjustments, and bracing.
- It is best to consult a doctor or physiotherapist who can provide guidance and treatment tailored to your specific needs.
Patient education:
- A physical therapist can teach self-management strategies, including activity modification, ergonomic principles, and home exercises.
- This allows you to actively participate in recovery and prevent future episodes.
- It is important to consult a qualified physical therapist who specializes in nerve disorders for proper treatment.
- They will create a comprehensive treatment plan based on your specific needs and closely monitor your progress throughout the rehabilitation process.
FAQs
Sprain: Your ulnar nerve may not stay in place. It may snap over the medial epicondyle as you
move it. Its repetitive clicking is unnerving. Strain: If you bend your elbow for long periods of time, such as while sleeping, you can strain the nerve.
Treatment includes rest; non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs; physical therapy; hands below the elbow; and sometimes steroid injections. Surgery is rarely necessary. Using the right equipment and technique to move the upper arm can help prevent the condition.
When the ulnar nerve is displaced as part of severe triceps syndrome, the first pop occurs at approximately 70-90 degrees of flexion when the nerve is displaced. The middle end of the triceps usually snaps at about 115 degrees of flexion.
Elbow sprains can be caused by scar tissue from previous injuries or surgeries. In fact, a hard
tennis or golf swing can tear the scar tissue in the elbow joint, causing popping and pain, swelling, and bruising.
Almost everyone experiences a joint rupture at some point, and it’s usually harmless. If the pop is
accompanied by mild pain, you can treat it with over-the-counter anti-inflammatory medications, ice, and rest. But if the pain persists or worsens despite home care, you may need additional treatment.