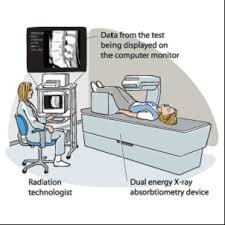
DEXA (DXA) Scan: Bone Mineral Density Test
A DEXA scan is an imaging test that counts bone density (strength). DEXA scan results may provide helpful details about the risk for osteoporosis (bone loss) and fractures (bone breaks). This test may also measure body composition, namely body fat and muscle mass.
Table of Contents
What is a DEXA scan?
- A DEXA scan is a kind of medical imaging test.
- It uses very small levels of x-rays to count how dense the bones are.
- DEXA stands for “dual-energy X-ray absorptiometry.”
- Doctors use DEXA scans to be the most useful, easy, and inexpensive test to diagnose osteoporosis.
- The test is fast and painless.
What is osteoporosis?
- Osteoporosis is a word used to demonstrate brittle bones and also the risk of having a broken bone.
- As a person ages, the bones may lose thickness and strength.
- Osteoporosis accurately means “porous bone.”
- DEXA tests help the doctor track the bone density and risk of having a broken bone over time.
- Doctors often use DEXA tests to help diagnose osteoporosis. Osteoporosis results when a person loses bone faster than the body may generate new bone tissue.
- This is most usual in postmenopausal females.
- Over time, bones get weaker.
- Brittle bones break more easily.
- Doctors sometimes call osteoporosis a “silent” disease because it does not hurt.
- Many individuals initially realize they have osteoporosis after they break a bone from a minor fall.
What is Osteopenia?
- Osteopenia is a word used to demonstrate “low bone mass.”
- Many people, incorporating those who are slender and very active, have had lower bone mass all of their lives.
- But this does not certainly mean that they will progress to osteoporosis.
- Many world-class sports people have low bone mass but their bones are healthy and very strong.
- Osteopenia is not “pre-osteoporosis,” but sometimes, if an individual has other risk factors for fracture, an osteoporosis medication will be suggested to help prevent future fractures.
How does a DEXA scan work?
- DEXA scans count the mineral content in certain bones, namely the hip, spine, and/or wrist. It works this way:
- A person will be suggested to lie on a special DEXA x-ray table.
- The technologist will help position the patient correctly and use positioning devices like foam blocks to help hold the desired position.
- As the arm of the DEXA machine passes over the entire body, IT uses 2 different x-ray beams.
- The beams use very small radiation to keep up the test safer and help to characterize bone from other tissues.
- The scanner translates the bone density measurement data into images and graphs.
- Bone is most easily seen in white, while the fat and muscle tissue looks like shadows in the background on the technologist’s computer monitor.
- These outcomes are then reviewed and interpreted by a radiologist or other physician trained in DEXA interpretation.
- A doctor is sent a copy of the written report to discuss with the patient and consider what treatment is most appropriate.
Who gets a DEXA scan?
- A doctor considers too many factors when deciding who can benefit from a DEXA scan and how frequently.
- Doctors frequently suggested a DEXA scan to assess bone health for osteoporosis and fracture risk if a patient is older than 50, has had a broken bone, or has other illnesses that put bone health at risk.
- Research shows females begin losing bone mass earlier and faster than men.
- So doctors generally suggested females get a DEXA scan to screen for osteoporosis at younger ages compared to males.
- A doctor can suggest a DEXA scan if a person has one or more risk factors for osteoporosis or fractures:
Increased age:
- Many people lose bone mass as they get aged.
- The National Osteoporosis Foundation suggests people at average risk get a DEXA scan starting at 65 (female) and 70 (male).
Family history:
- If one or more family members have had osteoporosis or more than one fracture, a person may be at a higher risk for bone loss.
Previous fracture injuries:
- Breaking a bone, especially after age fifty, can be a sign that a person is at greater risk.
- Porous (less dense) bones are fractured more easily.
Medications:
- Some medications, like the steroid prednisone, cancer drugs, and drugs used after an organ transplant may weaken the bones.
Overall health:
- Many chronic medical disorders may make the bones more likely to break.
- Risky conditions involve rheumatoid arthritis, lupus, diabetes, liver disease, and kidney disease.
What else do doctors use DEXA scans for?
A doctor can also order a DEXA scan to:
- Track bone health changes over time.
- Monitor the response to treatment, like an osteoporosis medication.
- Evaluate body composition, like how much fat and muscle mass the body has (and where).
How frequently should a DEXA scan be done?
- Medicare permits a DEXA scan to be done once every 2 years, and this is the currently suggested timeframe.
- There are exceptions to this rule if a person has certain diseases.
- The doctors will think about several factors, like age, level of fracture risk, previous DEXA scan, and current medications.
- Doctors will then make a personalized plan for how to assess and protect bone health.
TEST DETAILS
How should a prepare for a DEXA scan?
- Most individuals do not require to change their daily routine before a DEXA scan.
- Eat, drink, and take any medications as a person normally would, unless doctors tell the person otherwise.
- A person will be asked to fill out a questionnaire that asks about the current health, the family history of broken bones, smoking history, and current medications.
- Before the test, please do the following:
- Stop taking calcium supplements 24 hours before the test:
- This includes multivitamins as well as antacids like TUMS® (generally used to treat heartburn).
- Wear comfy-fitting clothing with no metal: Wear comfortable clothes.
- Try to choose items that do not have metal (zippers, buttons, or buckles).
- Sweatpants and a casual top can be perfect choices.
- Tell the doctor if a person might be pregnant: DEXA scans use low radiation levels.
- Medical experts suggested avoiding all radiation exposure at the time of pregnancy to protect the developing fetus.
How is a bone density test done?
- DEXA bone density tests are outpatient procedures. A patient can be able to wear regular clothes at the time of the test. Or a person can be asked to change into a hospital gown.
- There are no needles or injections in the DEXA scan test.
- A DEXA test is similar to having a standard X-ray.
How long does a DEXA scan take?
- A DEXA scan generally takes at most 20 to 25 minutes.
- Many people are in and out of the room in less than thirty minutes.
How accurate are DEXA scans?
- DEXA scans give a high degree of precision and accuracy.
- Medical experts consider DEXA scans to be a perfect test for diagnosing osteoporosis.
- Unlike x-ray machines, DEXA machines are checked daily for their ability to count bone minerals accurately, and no two DXA machines are exactly alike.
- That is why the doctor will insist that a person have all of the DEXA tests done on the same machine.
FAQ
Normal bone density — Individuals with normal bone density have a T-score between +1 and -1. Individuals who have a score in this range do not typically require treatment, but it is useful for them to take steps to prevent bone loss, like having an adequate quantity of calcium and vitamin D and doing weight-bearing exercises.
There is no particular cure for osteopenia, but it is important to preserve bone density as much as possible. Treatment involves simple strategies to keep the bones as healthy and strong as possible and prevent progression to osteoporosis.
Bone density tests are suggested for all women age 65 and older, and for younger females at higher-than-normal risk for a fracture. Males can want to discuss osteoporosis screening with their doctor if they are over age 70 or at high risk for thinning
bones.
Osteoporosis is not reversible, but medication, a nutrient-dense diet, and weight-bearing exercise may help prevent further bone loss and rebuild bones. Osteoporosis weakens bones so they are more likely to fracture.
As a person ages, the body may reabsorb calcium and phosphate from their bones instead of keeping these minerals in their bones. This makes the bones weaker. When this process reaches a central stage, it is called osteoporosis. Many times, a person will
fracture a bone primary they even know they have bone loss.




One Comment