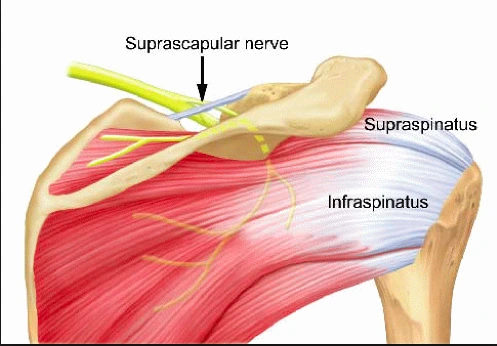
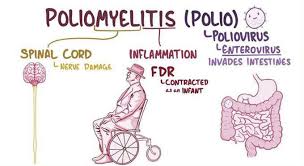
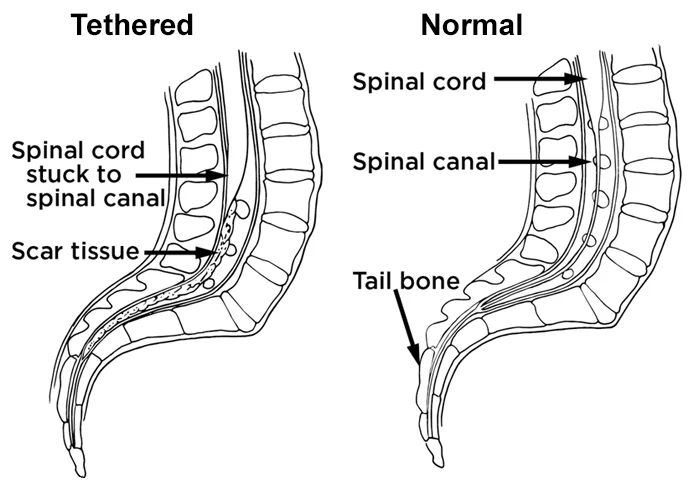
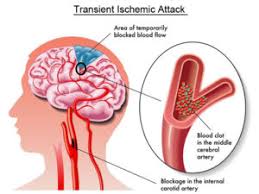
Dystonia
Defination Dystonia is a neurological condition that affects the movement of muscles in the body. It is characterized by involuntary muscle contractions that cause abnormal and often painful movements, postures, and spasms. Dystonia can affect various parts of the body, including the face, neck, arms, legs, and torso, and can occur in both children and…