Triceps coxae muscles: Anatomy, Function
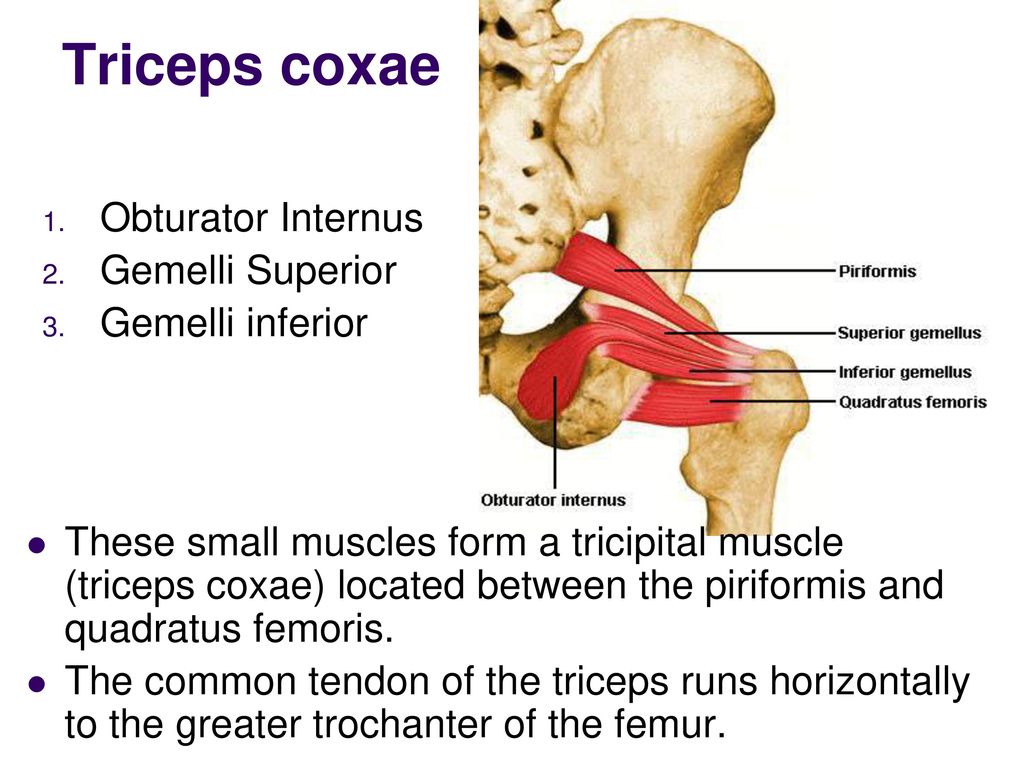
The triceps coxae is the tricipital (three headed) group of 3 muscles located in the posterior hip which act together on the hip, mainly to external rotation the extended thigh. This muscles are the superior gemellus, obturator internus and inferior gemellus muscles(in order from superior to inferior), located in between the piriformis muscle (superiorly) and quadratus femoris muscle (inferiorly).
When the obturator internus and superior and inferior gemellus muscles counted as group muscle, inserting onto common tendon into the greater trochanter of the femur.
Table of Contents
Triceps coxae – three headed muscles are:
- Obturator internus muscles
- superior gemellus muscles
- inferior gemellus muscle
Obturator internus muscles
Obturator internus is a deep hip rotator muscle that arises from the medial surface of the ischium and inserts into the femur. It is used to abduct the hip and rotated the thigh laterally. It is innervated by the anterior division of the obturator nerve (L2, L3)a branch of sacral plexus.
The obturator nerve also have a nerve supply to muscles of the medial compartment of the thigh (obturator externus and adductors longus and brevis), and the knee (sartorius). The obturator internus has a weak attachment to the medial side of the ischium. It runs from superior to inferior.
This muscle is mainly a part of a muscle of the lower limb and the piriformis, quadratus femoris, superior gemellus and inferior gemellus muscles, all together located in the deep layer of muscles of the gluteal region, covered by the inferior half of the gluteus maximus muscle.
The obturator internus muscle, the superior and inferior gemelli muscles are together named as the triceps coxae. They have a common tendon, inserting at the greater trochanter of the femur.
Here in this article we give information about the origin, insertion and exercise of the obturator internus muscle.
Origin :
Pelvic surface of the obturator membrane; bony boundaries of the obturator foramen.
Pelvic surface of the body of the ischium , ischial tuberosity , ischiopubic rami , and ilium below the pelvic brim .
Obturator fascia.
Insertion :
The tendon of the obturator internus leaves the pelvis through the lesser sciatic foramen .
Here it bends at a right angle around the lesser sciatic notch and runs laterally to be inserted into the medial trochanter of the femur.
Nerve Supply :
Nerve to obturator internus (L5-S1).
Blood Supply :
Obturator artery; internal pudendal artery
Function of the Obturator internus:
Main action of the muscles are Abducts & laterally rotates the extended hip and abducts the flexed thigh at the hip, and stabilizes the hip during walking, stair climbing, jumping .
Due to their attachment on the greater trochanter of the femur, obturator internus and the gemelli muscles act together as lateral rotation of the extended thigh. They also helps in abduct the flexed thigh.
The obturator internus muscle, with piriformis, superior and inferior gemelli, pectineus, quadratus femoris and obturator externus works as an important postural muscle, providing stability to the hip joint, particularly when the hip is flexed.
Gemellus muscles
There are 2 gemelli muscles- this are gemellus inferior muscle and the gemellus superior muscle, This two small muscles with the tendon of the internal obturator muscle. The gemelli muscles are the part of the external rotator group of six muscles of the hip that rotate the femur in the hip joint.
Gemellus superior muscle
The superior gemellus muscle is the higher placed gemellus muscle that originates from the outer (gluteal) surface of the ischial spine, and joins with the upper part of the tendon of the internal obturator. It is small muscle than the gemellus inferior. In some variations, where the fibres of the gemellus superior extend further than average, and are inserted onto the medial surface of the greater trochanter of the femur.
Nerve supply:
Internal obturator nerve(L5, S1, S2) of the sacral plexus.
Blood supply:
The inferior gluteal artery.
The gemellus inferior muscle
The gemellus inferior muscle originates from the upper part of the ischial tuberosity, just below the groove for the internal obturator tendon. It joins with the lower part of the tendon, and is inserted at the medial surface of the greater trochanter. It is sometimes absent also.
Blood supply :
The inferior gluteal artery.
Nerve supply:
the quadratus femoris nerve– L4 to S1.
Functions of the Triceps coxae muscle:
Triceps coxae (internal obturator muscle, the gemellus superior and gemellus inferior) help to stabilize the femoral head in the acetabulum(Hip joint). It is also help to external rotation of the extended hip and abduct the flexed hip by assisting the internal obturator. The 2 gemelli muscles act to compensate the reduced power of the internal obturator as it turns around the lesser sciatic notch.


2 Comments