Abnormal posturing: Cause,Types,Prognosis,Treatment
Abnormal posturing is an involuntary muscle contraction which leads abnormal types of Body position mainly flexion and extension position mostly associated with severe brain and spinal cord related conditions. In this condition one group of muscles tone increased while opposite group muscles loose their tone. This posturing may also seen without a stimulus.
Abnormal posturing is an important indicator of the severity of damage that has occurred to the upper motor neurone related condition, it helps Doctors to measure the severity of a condition with the Glasgow Coma Scale (for adults) and the Pediatric Glasgow Coma Scale (for infants)
Poor posture is defined as when your spine is positioned in abnormal positions, in which the spinal curves are highlight and this results in the joints,
muscles and vertebrae being in pressured positions. This prolonged bad positioning results in a build up of pressure on other body parts. Abnormal posture may be a associated with certain conditions of the brain or spinal cord.
Abnormal spinal curvature is an important factor for adult poor posture in which abnormality in alignment, formation, or curvature of one or more part of the spine. Adult spinal deformity (ASD) mostly seen in more than 60% of the older people and develops with multiple other conditions such as disk degeneration, vertebral fracture, and spondylotic changes.
Table of Contents
Causes of Abnormal posturing:
Following are the few most common Causes of Abnormal posturing are:
- Haemorrhage in the brain from any cause
- Brain tumour
- Brain Abscess
- Hemorrhagic Stroke
- Brain affected mainly due to side effect of drugs, poisoning or fungal , Bacterial infection
- Head- brain injury
- Brain injury due to liver failure
- Increased pressure in the brain from any cause such as Hydrocephalus
- Low blood sugar (hypoglycaemia)
- Brain tumour
- Infections, such as meningitis
- Intracerebral hemorrhage.
- Reye syndrome ( liver function and brain damage related problems that mostly affects children)
- Brain injury from lack of oxygen
- Cerebral malaria
- Lead poisoning
This abnormal Posturing can be caused by conditions that increases in intracranial pressure such as traumatic brain injury, stroke, intracranial hemorrhage, brain tumors, brain abscesses and encephalopathy.
Stroke usually mostly occurs on one side of the body and may also called spastic hemiplegia.
Brain herniation is mostly associated with Decerebrate and decorticate posturing. Brain herniation is a highly life-threatening condition in which parts of the brain are pushed hard structures within the skull. In brain herniation, mostly decorticate posturing seen, and, if the condition is not treated immediately, gradually develops into decerebrate posturing. Decerebrate posturing is seen on one side of the body while decorticate posturing seen on the opposite side of the body when severe brain damage occurs.
It has also been seen in patients such as Creutzfeldt–Jakob disease, diffuse cerebral hypoxia, and brain abscesses.
Posturing has also been seen in cases of judicial hanging, where strapping of the arms and legs may hide the effect.
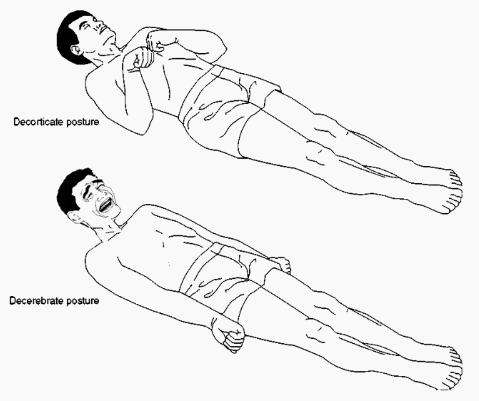
Types of abnormal Posturing:
There are mainly 3 types of abnormal posturing :
- Decorticate posturing, in which the arms flexed over the chest
- Decerebrate posturing- the arms extended at the sides
- Opisthotonus- the head and back are arched backward.
Decorticate posturing:
Decorticate posture is an abnormal posture in which a patient’s Body is in rigid-stiff with both arms flexed over the chest, while fingers clenched , wrist flexed, and both legs are in extended full-straight. The arms are bent in toward the body and the wrists and fingers are bent and held on the chest. This type of posturing is a sign of severe damage in the brain.
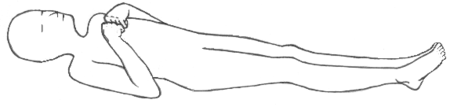
People who have this condition should require emergency medical treatment. It may occur on one or both sides of the body.
Other name of Decorticate posture are decorticate response, decorticate rigidity, flexor posturing, or, colloquially, mummy baby.
It is a sign of severe damage to the area of the midbrain, which is located between the brain and spinal cord. The midbrain controls motor movement. However Decerebrate symptoms is serious condition but as compared to decerebrate posture, it is less severe.
A neuro-muscular response to the trauma showing decorticate posturing in response to pain gets a score of three in the motor section of the Glasgow Coma Scale, mainly due to the flexion of muscles of upper body parts.
There are two parts to this posture:
It is the facilitation of the rubrospinal tract while at the same time disinhibition of the red nucleus. The rubrospinal tract stimulates motor neurons in the cervical spinal cord that are supplying the flexor muscles of the upper limb. The rubrospinal tract and medullary reticulospinal tract producing flexion type of posturing while the medial and lateral vestibulospinal and pontine reticulospinal tract responsible forthe extension posturing in the upper limb.
The second part of this posture is the disruption of the lateral corticospinal tract which stimulates motor neurons in the lower spinal cord supplying flexor muscles of the lower limb, while at the same time, the pontine reticulospinal and the medial and lateral vestibulospinal stimulates the extension movement of the lower limb greatly overcome the medullary reticulospinal tract.
Mainly these two tracts effects by lesions above the red nucleus leads to the specific flexion posture in the upper limb and extensor posture in the lower limb.
This abnormal posture shows that there may be severe damage to brain areas are the cerebral hemispheres, the internal capsule, and the thalamus. It may also sign of midbrain damage. This posture is usually indicative of more severe damage at the rubrospinal tract, and the red nucleus is also involved, indicating a lesion lower in the brainstem.
Decerebrate posturing
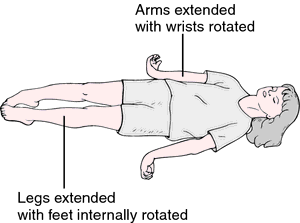
Decerebrate posturing is a type of abnormal posture in which Body is in extendser rigid body position – the arms and legs are in extended rigid straight out, the toes being pointed downward, and the head and neck being arched backward. The muscles are in rigid that body is in extended. This type of abnormal posture usually means there has been severe damage to the brain.
Decerebrate posturing is also called decerebrate response, Decerebrate posture or extensor posturing.
In this position the involuntary extension of the upper limb in response to external stimuli. In decerebrate rigidity, the head is hyperextended back, the arms are also extended by the sides, and the legs are extended.
Decerebrate posturing is caused by damage to the cerebral cortex but the clinical symptoms varies depend on the site of the lesion. Causes of decerebrate rigidity are seizures,tumors, vascular lesions, and trauma. Spontaneous nystagmus or eye deviation is also seen in decerebrate rigidity. This type of rigid posture usually shows that there has been severe damage to the brain.
In Decerebrate rigidity is a rare type of posture seen in people who have injuries to their brainstem and is a rarely seen medical condition, in which the body position- upper extremities are held outstretched and internally rotated. In this position, the arms are pronated with the forearms held vertically, the toes being pointed downward, and the head and neck being arched backward. The legs are also extended and pronated.The patient is rigid, with the teeth clenched. This kind of rigid posture seen mostly in severe midbrain lesions.
Decerebrate rigid posture can occur on one side or both sides, or in just the arms or limbs. It is also associated with another type of abnormal posture called decorticate posture. A person who have decorticate posture on one side of the body while at the opposite side decerebrate rigid posture in few severe cases.
Opisthotonos may occur in severe cases of decerebrate rigid posture where a severe muscle rigidity of the neck and back are seen. The Nobel Laurette Charles Sherrington first time described decerebrate rigidity posture in 1898 after transecting the brainstems of live monkeys and cats.
Decerebrate rigid posture are considered pathological rigid responses to usually unpleasant stimuli from an external or internal, in which stereotypical extended body movements of the trunk and limb are seen.
Opisthotonos posturing:
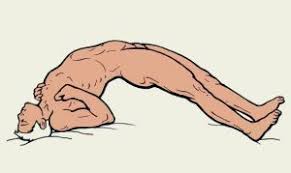
Opisthotonos is the term that used for an abnormal posture that can be seen when the muscles in your neck, back, and legs are become in severe spasm / spastic and contract. These severe form of contractions cause your body to bend backward into a rigid arch, with your head pointing toward your feet.
Opisthotonos is not a disease or condition, but a symptom of many different serious health disease or conditions. However relatively rare condition and It is usually a symptom of severe neurological conditions that are life threatening and require emergency medical treatment.
Opisthotonos derived from Greek work where opistho means Behind whereas tonos meaning tension, is condition of a severe muscle spasm or spasticity in which an individual’s head, neck and body enter into arching position.
This hyperextended posture is an extrapyramidal effect and is caused by spasticity of the axial muscles with the spinal column. It is seen mostly in severe form of cerebral palsy and traumatic head injury or tetanus where severe muscular spasm are associated.
Prognosis:
The prognosis depends on the cause, Diagnosis and severity of symptoms and also age and other related factors.
This abnormal posture could indicate severe brain damage of nervous system injury and sometimes permanent brain damage, which could result in:
- seizures
- paralysis
- inability to communicate
- coma
Normally people showing decerebrate or decorticate rigidity are in a coma and have poor prognoses, with risks for cardiac arrhythmia or arrest and respiratory failure.
Factors that involved positively in survival in TBI with decerebrate rigid posture are younger patient age, admission within as early as possible hours of injury, and extradural hematoma. Negative factors are mostly acute subdural hematoma and older age.
Treatment of Abnormal posturing:
- Emergency ICU Treatment (Mostly Neauro. NICU).
- Emergency Craniotomy for evacuation of extra-axial hematoma can improve survival.
- Remove the cause (Treatment depends upon Diagnosis and symptomatic) eg. correcting if possible metabolic derangements or / and treating infections.
- Symptomatic supportive treatment are started.
Physiotherapy treatment in Abnormal posturing:
Physiotherapy treatment and exercises are used to treat and improve the symptoms of abnormal posturing. The most common treatment is postural rehabilitation, which uses exercises and physiotherapy treatments to improve the muscles that support the spine, limb and to improve the posture of the spine.
Correcting Postural exercises are used to improve the posture of the spine, limb and to strengthen the muscles that help support the spine. It is often treated with a series of exercises that are designed to improve the posture of the spine and limb, strengthen the muscles that support the spine, and stretch the muscles that are tight due to the position of the head and shoulders.
Following are the most commonly follow treatment are used , However it vary depends upon symptoms, causes and Diagnosis of the condition.
- Relax Passive Movement
- Chest Physiotherapy
- Reduce rigidity / spasticity
- Regular Stretching exercise
- Rehabilitation Program
- Postural correction
- Regular Ankle Movement
- Stretching exercise
- Regular change the position if patient is in coma stage (Mostly supine to side lying position to avoid Bed sore)
- Range of Motion exercise :
- Passive relax passive range of motion (ROM) exercise helps to avoid joint stiffness and deformities. One a daily passive movement of all four limb and trunk are required.
Stretching exercise:
To reduce spasticity / rigidity regular Stretching exercise are the best treatment option.
Stretching exercise of tight muscles mainly Hamstring, calf and adductors muscles stretching exercise are important in lower limb and relax passive movement to maintain range of motion are also equally important.
In Upper limb according to assessment of spasticity/rigidity stretching exercise are started. Maintain Range of Motion with the help of relaxed passive movement of all joint is beneficial.
To improve Balance of Sitting Balance and standing Balance, according to assessment Balance exercise are started for overall rehabilitation to improve condition.
Strengthening exercise:
Strengthening exercise of weak muscles according MMT (Manual muscle testing) are started , that will help overall posture correction and Rehabilitation. All four limb and trunk muscle strengthening exercise are also depends upon assessment.