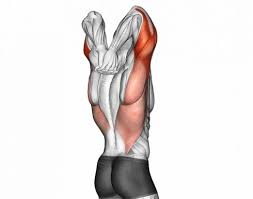
Triceps Brachii Muscle
Table of Contents
What is Triceps Brachii?
The triceps brachii is the muscle that runs down the back of the humerus, which is the long bone of the upper arm and ends at the top of the ulna, which is the long bone of the forearm.
The triceps brachii muscle gets its name because it contains three muscle ‘heads’ or points of origin. These include the :
- Medial head
- Lateral head
- Long head
Triceps brachii is a three-headed muscle of the arm. It represents the only constituent of the posterior muscle group of the arm, spanning almost the entire length of the humerus. The triceps brachii muscle consists of a long, medial and lateral head, that originate from their respective attachments on the humerus and scapula.
The main function of the triceps brachii is the extension of the forearm at the elbow joint. Its long head contributes to the extension and adduction of the arm at the shoulder joint.
Where is the triceps brachii muscle located?
Triceps brachii muscle is located in posterior side of arm(the dorsal compartment of the arm) starts from shoulder joint to ends at the elbow joint.
The lateral intermuscular septum separates the anterior part of the arm from the posterior part, which is where the flexors group of muscle of the arm are located eg.biceps, brachialis, and brachioradialis.
How many joints does the triceps brachii cross?
The triceps brachii muscle crosses two joints, the shoulder joint and elbow joints. The main action of the triceps muscle is extension of the elbow. It is the powerful extensor of the elbow and also extends shoulder joints mainly long heads. The long heads of Triceps muscle cross the shoulder joint and elbow joint and work as a extension of shoulder joint and elbow joint while the lateral head and medial head crosses only elbow joint.
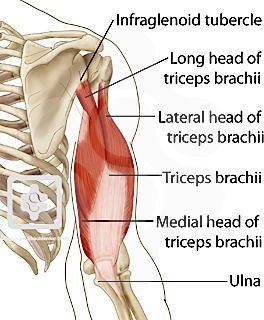
Origin:
The triceps brachii muscle has three heads of origin:
The long head arises from the infraglenoid tubercle of the scapula, which is a rough area at the inferior margin of the glenoid fossa. Its attachment extends slightly above to the adjacent glenoid labrum and blends with the glenohumeral capsule of the shoulder joint, contributing to its stability.
The lateral head originates from a narrow, linear ridge on the posterior surface of the humerus, just superior to radial groove. A portion of the muscle fibers also arises from the lateral intermuscular septum. Its attachment ascends obliquely beginning from the lateral border of the humerus behind the deltoid tubercle. From here, it extends to the surgical neck of the humerus, medial to the insertion of teres minor, and above the attachment for the medial head of triceps.
The medial head is overlapped by the long and lateral head of the triceps. It has a broad origin along the entire posterior surface of the humerus inferior to the radial groove, its attachment extends over an elongated triangular area on the humerus. The apex of the triangle is located on the medial border of the humerus above the insertion of teres major, while the base is the line that connects the medial and lateral epicondyles of the humerus.
Insertion:
Triceps Brachii Muscle is inserted on the Posterior surface of the olecranon process of the ulna, capsule of the elbow joint, and antebrachial fascia.
Nerve Supply:
All three heads of triceps brachii are nerve supply the four branches of the radial nerve (C7, C8). The C-6 root value of the radial nerve innervates the lateral head, while root value C-7 innervates the long head, and root value C-8 supplies the medial head.
Although, according to the latest cadaveric study shows that the medial head of triceps brachii is innervated by the ulnar nerve.
Some researcher claims that the long head of triceps is also innervated by the axillary nerve.
Blood Supply:
The muscle is gets oxygen and nutrients from the branches of the deep brachial artery and the superior ulnar collateral artery, which arises from the brachial artery. Extra supply to the lateral head of the triceps brachii is provided by the posterior circumflex humeral artery.
Triceps brachii function:
The triceps and biceps brachii are the main muscles controlling the movements of the elbow. The main function of the triceps brachii is extension of the forearm at the elbow joint.
Triceps muscle main action is active extension, which occurs both as a result of the contraction of the triceps brachii muscle and the relaxation of biceps brachii.
During passive extension of the forearm, the extensor action of the triceps is replaced by gravity, and the movement is controlled by active lengthening or eccentric contraction of the biceps brachii and other flexors of the forearm.
It helps in the extension of the elbow joint and also acts as an antagonist of the biceps and brachialis.
The triceps brachii also helps to stabilize the shoulder by keeping the head of the humerus in its correct position in the shoulder joint.
The lateral head is used for movements requiring occasional high-intensity force, while the medial head enables more precise, low-force movements.
When the shoulder joint is internally rotated, the ability of the long head of the triceps brachii to extend and adduct the shoulder is diminished. The shoulder must be externally rotated in order for the long head of the triceps brachii to assist shoulder adduction.
The long head of the triceps has several additional actions reflected upon its attachment points:
Due to its attachment to the scapula, the long head can also act on the shoulder joint, producing an extension of the arm.
As the attachment of the long head also blends with the glenohumeral capsule, it contributes to the shoulder joint stability. To hold the head of the humerus in the glenoid cavity and prevents its inferior displacement.
When the arm is extended, the long head can act on the glenohumeral capsule to pull superiorly on the humerus and produce the adduction of the arm.
The medial head of the triceps is active in all forms of forearm extension, while the long and lateral heads are only significantly active during extension at the elbow that occurs against resistance.
Relation:
The triceps brachii muscle is the only muscle in the posterior compartment of the arm. The superior portion of the long head of the triceps is covered by the posterior border of the deltoid muscle. The long head of the triceps can be palpated as an elevation parallel and medial to the posterior border of the deltoid muscle when the elbow is extended.
The upper triangular space is bounded by teres minor and subscapularis superiorly, teres major inferiorly, and the long head of triceps laterally. This space allows the passage of the circumflex scapular artery and vein from the axillary region to the scapular region.
The lower triangular space, also called the triangular interval, is bounded by teres major superiorly, the long head of triceps medially, and the humerus laterally. This space between the posterior and anterior compartments of the arm allows passage of the radial nerve and the deep brachial vessels.
Which muscles are antagonists to the triceps brachii?
The Triceps brachii muscle is the main extensor muscle of the forearm, and is the antagonist of the Biceps brachii muscle and brachialis muscle which are main flexor of the elbow joint.
Exercise for Triceps Brachii :
Exercise for triceps brachii muscle mainly of 2 types.
- Stretching exercise of Triceps Brachii
- Triceps brachii strengthening exercise

Triceps stretch exercise
Horizontal Tricep Stretching exercise
In Standing position, straighten your arms and bring your right one across your body.
Use your left arm to press the right one firmly against your chest.
Once you feel a nice tricep stretch, hold the position for 10 to 15 seconds.
Repeat for your left arm.
Overhead Tricep Stretching exercise
Stand tall with your shoulders back and chest out.
Straighten your left arm and bring it over your head.
Bend the left arm at the elbow so your left hand is at the base of your neck.
Put your right hand on the right elbow as shown above, and pull it in a slow and controlled motion until you feel the stretch in your left tricep.
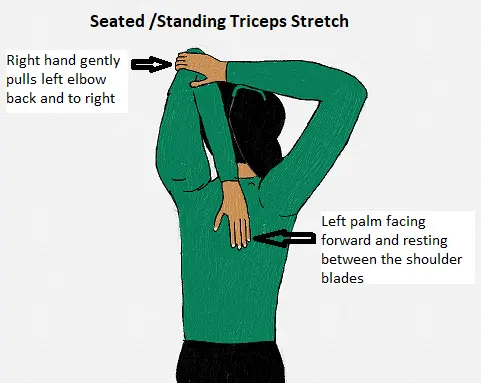
Hold the stretch position for 10 to 15 seconds and repeat for your right arm.
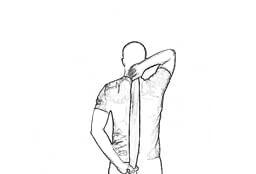
Overhead Tricep Stretch With a Towel:-
Begin the stretch in the same way as the overhead tricep stretch with a rolled-up towel hanging from your right hand.
Bring your left hand down and behind your body. Grab the lower end of the towel with your left hand.
While keeping your right elbow stable, gently pull on the towel with your left arm until you feel a nice stretch. Hold the stretch for 10 to 15 seconds. Repeat for your left arm.
Tricep Stretch Using Wall
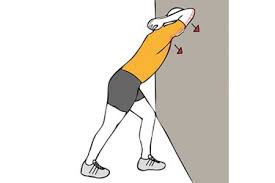
Begin the stretch in the same way as the overhead tricep stretch.
Straighten your right arm and raise it over your head.
Bend your right elbow as shown above, so your right touches your right shoulder.
Hold the stretch for 10 to 15 seconds.
Repeat for your left arm.
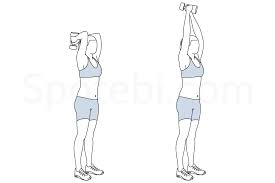
Double Arm Tricep Stretch:
Begin the stretch with both arms extended straight above your head.
Bend both arms at your elbows as shown above, until you feel the stretch in your triceps. You can also lock your fingers for more leverage in the stretch.
Hold the stretch for 10 to 15 seconds.
Strengthening exercise
Triceps strengthening exercise are perform with the helps of Dumbbells, theraband and also uses of Bodyweight
Triceps exercise with dumbbells :
Following exercise are used to strengthen triceps with the helps dumbbells:
Tricep Extensions with dumbbells in standing:
Stands with your feet shoulder-width apart
Grasp the weight with both hands and place it behind your head, aiming for between your shoulder blades
Lift your arms so they’re straight above your head, make sure elbows don’t flare outward too much
Aim for 4 sets of 8 -12 reps.
Tricep Kickback

Stand with your feet together, knees slightly bent, and bent forward at the waist
Hold onto weights with arms hanging straight down and then lift upward, keeping arms close to your side. observe back of your
arm straight and slightly higher than your back, but you will also be able to feel your upper back /shoulder muscles ‘squish’ together.
Bring your forearms back – again, staying close to your body – until your arm is straight, then repeat for 3 sets of 10 -12 reps.

Tricep Dips :
use a small and very secure chair, table, or bench and place your hands on it, shoulder-width apart, behind you.
Put your feet in front of you with a slight bend.
Straighten your arms – without locking them – and then slowly bend your elbows and lower your body toward the floor, until your elbow is at about a 90-degree angle.
Once you reach the ‘bottom’ of the move, straighten your arms to push down on the bench til you’re back ‘at the top.
Do about 10 reps and 2-3 sets.
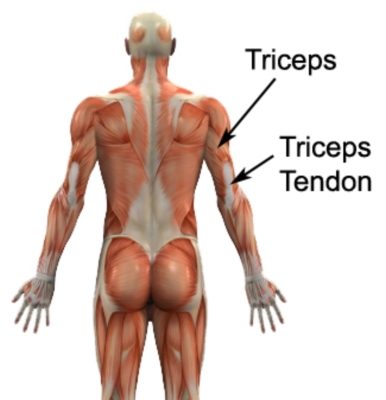
Clinical Importance
Triceps brachii tendon pain
Clinical features include pain and swelling of the posterior part of the elbow. Patients with a rupture of the triceps tendon may present with cubital tunnel syndrome, a snapping elbow, collar stud–shaped olecranon bursitis, or even posterior compartment syndrome.
An injury to the midshaft of the humerus can damage the radial nerve. This injury placement may spare much of the functioning of the triceps muscle and forearm extension may only be weakened, but the patient may present with “wrist drop” due to the paralysis of muscles that extend the wrist.
Any tendon is susceptible to injury; the triceps tendon attachment to the olecranon is no exception. Any activity that overuses the triceps muscle can cause the tendon to become inflamed and damaged, resulting in pain and swelling near the muscle’s attachment to the olecranon.
Examination
A patient with a triceps rupture can have posterior elbow pain, triceps weakness, swelling, and a palpable defect in the tendon.
When the patient is unable to extend his arm against gravity, you can expect a complete triceps rupture. A palpable defect is not always present but sometimes can be found in the posterior arm.



22 Comments