Superior gemellus muscle Origin, Insertion, Function, Exercise
Table of Contents
Introduction
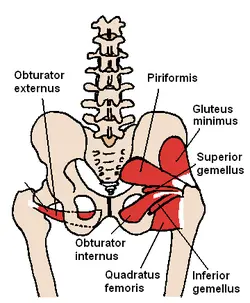
- The superior gemellus muscle is a small triangular muscle in the gluteal part that together with the inferior gemellus & obturator internus muscles form the tricipital (three-headed) triceps coxae which occupies the space between the piriformis muscle (superiorly) & quadratus femoris muscle (inferiorly). Together these muscles work primarily to laterally rotate the extended thigh & are also hip stabilizers steadying the femoral head in the acetabulum.
What does Gemellus mean?
- Gemellus is a Latin word that means “the twin” in English where the Superior gemellus muscle & Inferior gemellus muscles work & look similar to twins.
Origin & insertion of Superior gemellus muscle
- The superior gemellus muscle arises from the posterior (gluteal) surface of the ischial spine of the bony pelvis. it sources laterally towards the femur, passing through the lesser sciatic foramen. the tendons of both Gemelli muscles & obturator internus fuse anterosuperiorly to the trochanteric fossa of the femur, finally inserting into the medial surface of the greater trochanter as a unique triceps coxae muscle.
Relation
- The triceps coxae muscle, or the 3-headed muscle of the pelvis, is situated deep to the gluteus maximus muscle, filling the space bounded by the piriformis muscle superiorly & quadratus femoris inferiorly. From superior to inferior, the triceps coxae is composed of the superior gemellus, obturator internus & inferior gemellus. These 3 muscles have their own origins, yet share a common insertion. In some instances, the 3 muscles insert into the femur independently in the same superoinferior order they extend through the gluteal region of the pelvis
- In some cases, the fibers of the piriformis muscle can partially blend with the superior gemellus & thus insert into the femur with the triceps coxae common tendon.
- The neurovascular bundle of the hip & thigh, containing the sciatic nerve, pudendal nerve, inferior gluteal artery, posterior femoral cutaneous & inferior gluteal nerves, passes through a slit between the piriformis muscle & superior gemellus muscle on its way from the pelvis to the lower limb.
Function of Superior gemellus muscle
- Superior gemellus muscle work as a part of the triceps coxae muscle group to produce external (lateral) rotation & abduction of the thigh. The movement constructed by contraction of this muscle group is pivoted upon the position of the leg
- External (lateral) rotation – when the lower limb is in an anatomical position, the triceps coxae work to rotate the proximal femur externally. This function is important as along with the gluteus maximus muscle part of the gluteus medius, piriformis muscle, obturator externus & quadratus femoris, the triceps coxae muscles externally rotate the lower extremity in the carry-between phase of the gait cycle.
- Abduction – when the hip is flexed at 90 degrees, the triceps coxae function pulls the proximal femur medially. The distal femur moves correlated laterally, & the end result is the abduction of the thigh. This abduction from a seated position is the movement you perform when positioning the lower limb out of the car, for example.
- In addition, attaching between the proximal end of the femur & the hip bone, the superior gemellus muscle plays a role in stabilizing the head of the femur in the acetabulum of the pelvis.
Nerve supply
- The superior gemellus muscle is supplied by the sacral plexus, via the nerve to the obturator internus (L5-S1/2).
Blood supply
- The muscle is supplied by branches of the internal iliac artery; internal pudendal, inferior gluteal & occasionally by the superior gluteal artery as well.
Clinical Important
- Together with its twin: the gemellus inferior muscle as well as the obturator internus & piriformis, the gemellus superior is a deep stabilizer of the hip joint. These four muscles work with the gluteus maximus muscle to resist the anterior forces of the hip.
- It is difficult to assess the gemellus superior in isolation due to its proximity to the other external rotators muscle of the hip. Testing of the external rotator muscle would be done in a normal hip assessment.
Streching exercise of Superior gemellus muscle.
Superior gemellus muscle stretch
- Bent over lunging hip flexor stretch
- To do this stretch, kneel & step back with the left leg while bending the right knee. Bend forward & place the hands on the ground with the elbows to the outside of the right knee. Push the left leg straight out & drop the hips while working to balance on the ball of the left foot. Do the same exercise on the other side. Do 10 repetitions on both sides.
Strengthening superior Gemellus superior muscle exercise:
- To strengthen the gemellus superior, you might strengthen your Hip rotator muscles.
Three-point hip rotation:
- Keep your position on the hands & knees on a soft mat. Bring the left knee towards your chest while keeping your knee flexed. Then gradually rotate the leg externally to the left & then to the back, then bring the knee back to the chest. Complete a total of 8 to 10 repetitions on the opposite leg. Keep the stretch movement gradual, gentle & pain-free.
FAQ
The gemellus superior muscle is a small muscle in the posterior-lateral part of the hip. It works with the gemellus inferior & obturator internus, to form the triceps coxae, to externally rotate the hip. These 3 muscles also work as the deep stabilizers of the hip.
To do this stretch, kneel & step back with the left leg while bending the right knee. Bend forward & place the hands on the ground with the elbows to the outside of the right knee. Push the left leg straight out & drop the hips while working to balance on the ball of the left foot.
The superior gemellus muscle is supplied by the nerve to the obturator internus (L5, S1, S2), a branch of the sacral plexus. The nerve exits the pelvis via the greater sciatic foramen inferior to the piriformis muscle & typically between the posterior cutaneous nerve of the thigh & the pudendal nerve.
The superior gemellus acts as a part of the triceps coxae muscle group to produce external (lateral) rotation & abduction of the thigh. The motion made by contraction of this muscle group depends on the leg’s position.
A way to distinguish between the two muscles is to trace them back to their origins & understand their proximities to each other. The piriformis is larger & is superior to the gemellus superior. The piriformis originates in the sacrum, while the gemellus superior originates on the ischial spine.
trochanteric fossa
The superior gemellus muscle travels almost horizontally to insert into the middle part of the medial aspect of the greater trochanter, called the trochanteric fossa, a smooth faceted area of bone bounded posteriorly by the intertrochanteric crest.