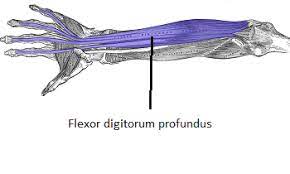
Flexor Digitorum Profundus Muscle
Table of Contents
Description
The flexor digitorum profundus muscle is a deep muscle situated in the forearm. It is one of the muscles responsible for flexing the fingers. The muscle originates from the ulna bone and interosseous membrane in the forearm and passes through the carpal tunnel before dividing into 4 tendons that insert into the distal phalanges of the 4 fingers (index, middle, ring, and little).
The flexor digitorum profundus muscle is innervated by the anterior interosseous nerve, which is a branch of the median nerve. The muscle is also supplied with blood by the anterior interosseous artery, which goes with the anterior interosseous nerve.
The flexor digitorum profundus muscle works together with other muscles in the forearm to allow for flexion of the fingers. It is also involved in wrist flexion, ulnar deviation, and supination of the forearm. The muscle is important for tasks that require gripping and holding objects, such as writing, typing, and playing musical instruments.
Structure of Flexor digitorum profundus
- The flexor digitorum profundus muscle is a deep muscle situated in the forearm.
- It has its origin in the proximal two-thirds of the anterior and medial surfaces of the ulna, the interosseous membrane, and the deep fascia.
- The muscle belly is situated deep to the flexor digitorum superficialis muscle.
- The muscle fibers of the flexor digitorum profundus muscle converge to form four tendons, which pass through the carpal tunnel, and insert into the distal phalanges of the four fingers (index, middle, ring, and little fingers).
- The tendons are surrounded by synovial sheaths which facilitate smooth gliding of the tendons during finger flexion.
- The flexor digitorum profundus muscle is innervated by the anterior interosseous nerve, which is a branch of the median nerve.
- The anterior interosseous nerve provides motor innervation to the deep muscles of the anterior compartment of the forearm, including the flexor pollicis longus, pronator quadratus, and flexor digitorum profundus muscles.
- The blood supply to the flexor digitorum profundus muscle is provided by the anterior interosseous artery, which runs with the anterior interosseous nerve through the interosseous membrane of the forearm.
- The muscle is an important muscle for finger flexion and is involved in many activities that require the use of the hands, such as grasping, holding, and manipulating objects.
Origin and insertion of flexor digitorum profundus
- The flexor digitorum profundus muscle is a muscle in the forearm that helps to flex the fingers.
- It originates from the upper three-quarters of the anterior and medial surfaces of the ulna and the interosseous membrane (a thin sheet of fibrous tissue that runs between the ulna and the radius bones of the hand.
- The muscle then divides into four tendons, one for each of the four fingers (excluding the thumb).
- These tendons pass through a fibrous sheath along the fingers and attach to the distal phalanges (bones at the tips of the fingers) on the palmar side.
- Specifically, the tendon for the index finger (second digit) attaches to the distal phalanx of the index finger, the tendon for the middle finger (third digit) attaches to the distal phalanx of the middle finger, the tendon for the ring finger (fourth digit) attaches to the distal phalanx of the ring finger, and the tendon for the little finger (fifth digit) attaches to the distal phalanx of the little finger.
Overall, the flexor digitorum profundus muscle is responsible for flexing the distal interphalangeal joints (DIP joints) of the fingers, which allows for gripping and holding objects.
Nerve Supply:
The flexor digitorum profundus muscle is innervated by the anterior interosseous branch of the median nerve, which arises from the median nerve in the proximal forearm.
Blood supply
- The arterial supply of the flexor digitorum profundus muscle comes from the anterior interosseous artery, which is a branch of the ulnar artery.
- The anterior interosseous artery runs alongside the anterior interosseous nerve, which supplies the muscle, and provides blood supply to the muscle belly.
- The anterior interosseous artery gives off muscular branches, which penetrate the muscle tissue and supply it with oxygenated blood.
In addition to the anterior interosseous artery, the muscle may also receive some blood supply from small branches of the radial and ulnar arteries that surround the muscle.
Functions of the Flexor Digitorum Profundus Muscle
- The flexor digitorum profundus muscle is responsible for flexing the distal interphalangeal (DIP) joints of the fingers.
- Specifically, it helps in bending the four fingers, i.e., the index, middle, ring, and little fingers, at the DIP joint.
- Additionally, the flexor digitorum profundus muscle also assists in wrist flexion when the wrist is in a position of ulnar deviation (i.e., tilting towards the little finger side).
- The muscle works in coordination with other flexor muscles of the forearm, such as the flexor digitorum superficialis muscle, to provide fine control and strength to the movement of the fingers during gripping, grasping, and manipulation of objects.
Moreover, the flexor digitorum profundus muscle plays a role in stabilizing the hand and wrist, helping to maintain the correct alignment of the hand and fingers during various activities.
Associated conditions
The flexor digitorum profundus muscle can be affected by various conditions, including:
Tendinitis:
Inflammation of the tendon of the flexor digitorum profundus muscle can occur due to overuse or repetitive strain injuries.
Tendinopathy:
This is a degenerative condition of the tendon, which can result from chronic wear and tear, aging, or injury.
Tendon rupture:
A complete or partial tear of the tendon can occur due to trauma or degenerative changes in the tendon.
Nerve injuries:
Injury or compression of the median nerve or its branches that supply the muscle can result in weakness or loss of function of the flexor digitorum profundus muscle.
Fractures:
Fractures of the distal radius or the wrist can cause damage to the muscle, leading to pain and weakness.
Dupuytren’s contracture:
This is a condition characterized by the thickening and contraction of the palmar fascia, which can affect the movement of the flexor tendons, including the flexor digitorum profundus muscle.
Trigger finger:
Inflammation and swelling of the tendon sheath can result in the finger getting stuck in a bent position, affecting the function of the flexor digitorum profundus muscle.
Exercise of flexor digitorum profundus muscle
Finger curls:

- Sit at a table with your affected forearm resting on the table, palm facing up.
- Hold a lightweight or resistance band in your hand and slowly curl your fingers towards your palm, then release them back to a straight position.
- Repeat for 10 to 15 repetitions, and then change to the other hand.
Grip strengthening:

- Hold a small ball or grip strengthener in your affected hand and squeeze it tightly, then release it.
- Repeat for 10 to 15 repetitions, and then change to the other hand.
Wrist flexor stretch:
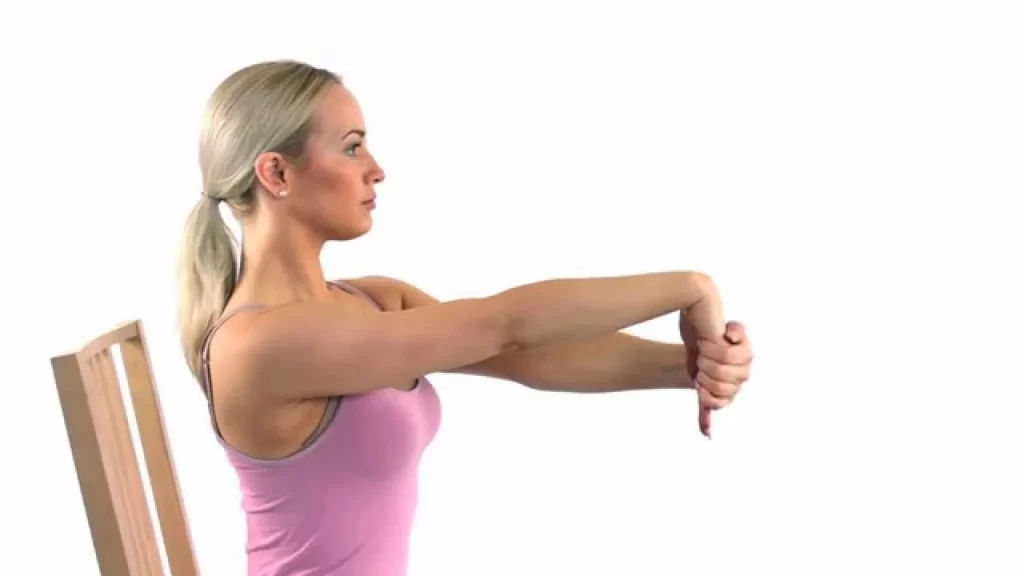

- Hold the arm out in front of you while your palm is facing down.
- Use the other hand to gently pull your fingers back towards your wrist until you feel a stretch in your forearm.
- Hold for 5-15 seconds, & relax.
Pronation/supination:

- Hold a lightweight in your affected hand, with your elbow bent and your forearm resting on a table.
- Slowly rotate your forearm so that your palm faces up, then rotate it back down so that your palm faces down.
- Repeat for 10 to 15 repetitions, and then switch to the other hand.
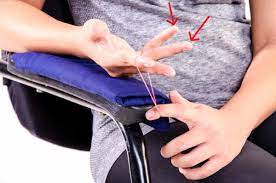
Finger flexion with resistance band
- Sit at a table with your affected forearm resting on the table, palm facing up.
- Hold a resistance band around the tips of your fingers and curl your fingers towards your palm against the resistance of the band.
- Hold for 5 seconds and then release.
- Repeat for 10 to 15 repetitions, and then switch to the other hand.
Reverse wrist curls with weight:
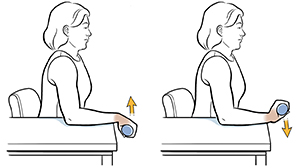
- Hold a weight in your affected hand and sit with your forearm resting on a table, palm facing down.
- Bend your wrist up towards your forearm against the resistance of the weight, hold for 5 seconds, and then release.
- Repeat for 10 to 15 repetitions, and then change to the other hand.
Finger push-ups:

- Start in a plank position with your fingers flat on the ground, shoulder-width apart.
- Slowly lower your body towards the ground by bending your elbows, keeping your fingers flat on the ground.
- Push back up to the starting position using your fingers.
- Repeat for 10 to 15 repetitions.
Wrist flexion with weight:
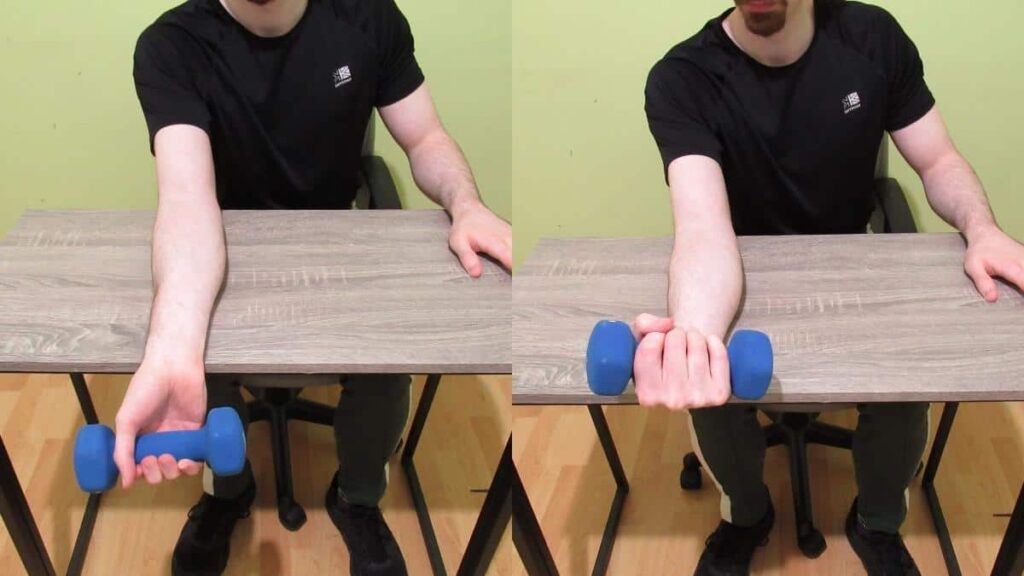

- Hold a weight in your affected hand and sit with your forearm resting on a table, palm facing up.
- Bend your wrist up towards your forearm against the resistance of the weight, hold for 5 seconds, and then release.
- Repeat for 10 to 15 repetitions, and then change to the other hand.
Remember to start with lighter weights or resistance and gradually increase as you build strength and endurance. Always consult with a qualified healthcare professional before starting any exercise program to ensure that the exercises are safe and appropriate for your specific needs and condition.
FAQ
The flexor digitorum profundus muscle is innervated by the anterior interosseous nerve (a
branch of the median nerve)
If the flexor digitorum profundus muscle is injured, it can result in a decreased ability to flex
the fingers at the DIP joint and/or weakened grip strength.
A trigger finger is a condition where a finger becomes locked or catches when it is bent or
straightened. It is caused by inflammation of the flexor tendon sheath, which can be related to
overuse or repetitive strain on the flexor tendons, including the flexor digitorum profundus
muscle.
superficialis muscles?
The flexor digitorum profundus muscle originates from the ulna and interosseous membrane
and inserts on the distal phalanges, while the flexor digitorum superficialis muscle originates
from the humerus and ulna and inserts on the middle phalanges. The flexor digitorum
pro fundus muscle is responsible for the flexion of the DIP joint, while the flexor digitorum
superficialis muscle flexes the PIP joint.
The flexor digitorum profundus muscle is an important muscle for finger flexion and grip
strength. Injuries or conditions that affect this muscle can result in decreased hand function
and mobility.


6 Comments