Median Nerve Injury Cause, Symptoms, Treatment, Exercise:
Table of Contents
What is a Median nerve injury?
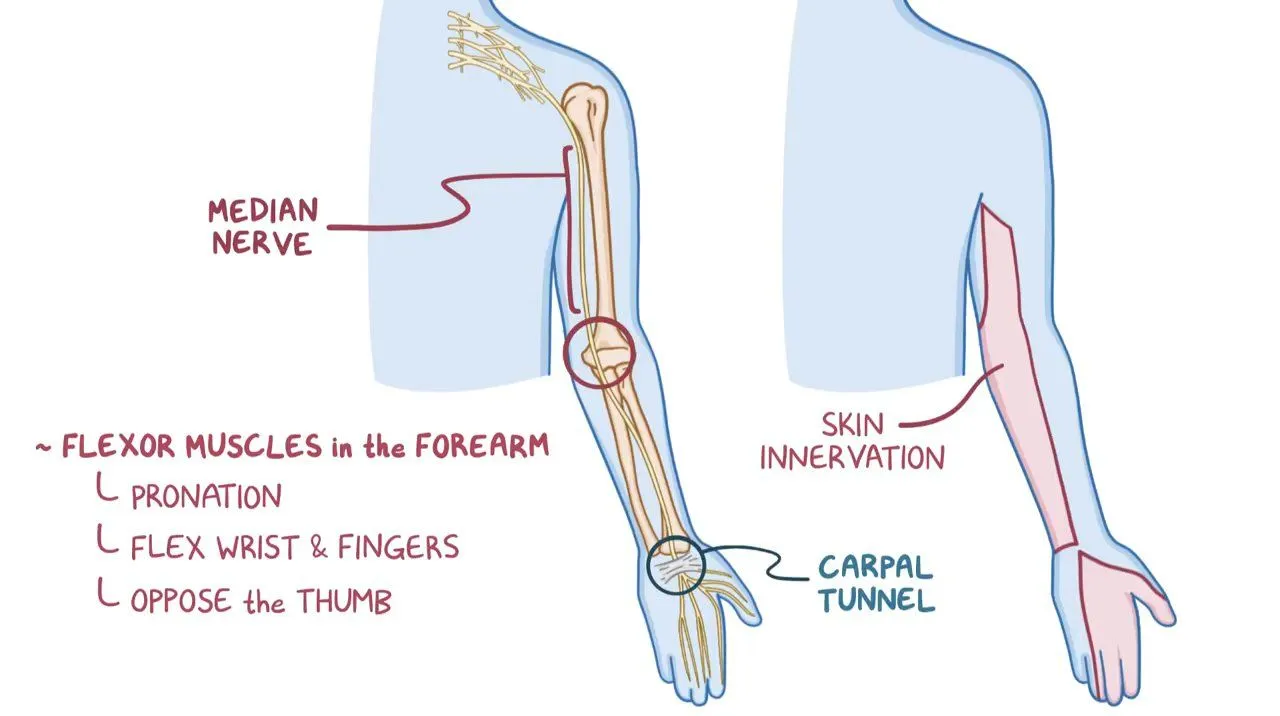
It is the essential peripheral nerve in the upper limb. It passes on the medial side of the arm between the brachialis and the biceps brachii muscles. Most of the muscles in the forearm are supplied by the median nerve. For example, it controls movements like the abduction of the thumb, flexion of the wrist, and flexion of the digital phalanx of the fingers. because of its importance, it is also called the eye of the hand.
Median nerve injury is divided into two groups: high and low median nerve injuries. If the injury is in the elbow and forearm areas, this will be called high median nerve injury. If the injury is in the wrist, this will be called low median nerve injury.
Anatomy of Median nerve:
The median nerve is one part of five nerve branches of the brachial plexus. The brachial plexus starts as nerve roots from the cervical spine in the neck. The median nerve roots are C6, C7, C8, T1, and sometimes C5. The median nerve is formed in the axilla by a branch from the medial and lateral cords of the brachial plexus, on either side the axillary artery fuse together to create the nerve anterior to the artery. The median nerve is related to the brachial artery within the arm, from the axilla it goes down and enters the cubital fossa. The nerve runs into the cubital fossa medial to the brachialis tendon and passes between the two heads of the pronator teres muscle. The nerve runs down the forearm between the flexor digitorum profundus muscle and the flexor digitorum superficialis muscle.
The median nerve emerges in between the flexor digitorum superficialis and the flexor carpi ulnaris muscles which are just above the wrist. At the wrist, the nerve gives the palmar cutaneous branch that supplied the skin of the center portion of the palm. The nerve continues through the carpal tunnel into the hand, lying in the carpal tunnel anterior and lateral to the tendons of the flexor digitorum superficialis muscle.
In the hand, the nerve divides into a muscular branch and palmar digital branches. The muscular branch supplies sensation to the thenar eminence and the palmar digital branch supplies sensation to the palmar aspect of the lateral 3 ½ digits and the lateral two lumbricals.
Branches of the median nerve:-

The median nerve has many different branches in the different parts of the whole upper limb.
The forearm gives 2 branches.
1)Muscular branches
2)Anterior interosseus nerve
On the hand, it gives 3 branches.
1)cutenues branch
2)palmar digitorum nerve
3)Recurrent branch
What is the function of the median nerve?
The median nerve gives both sensory and motor (movement) functions to your forearm, wrist, and hands. The nerve starts at your axilla, its main functions are in your forearm or hand.
The median nerve stimulates muscles in your forearm, and gives the motor functions are following:
flex and straighten your wrists, thumbs, and first three fingers.
Rotate your forearm and hand to turn your palm facing downward(Pronation movement.)
The median nerve also gives sensory functions like touch, pain, and temperature to the,
Bottom side of the thumb, first and middle fingers, and part of the ring finger.
Forearm.
Top (nail bed) side of the first and middle fingers.
What are the causes of median nerve injury?
The two most common places for the median nerve to become injured or compressed are at the elbow and at the wrist joint.
Many elbow injuries can affect the median nerve, including a fracture, or dislocation.
When the median nerve is compressed at the elbow joint, it’s known as Pronator teres syndrome. This is caused by repetitive turning, grasping, and twisting of the hand and wrist, it also affects those who in jobs work heavy manual labor, weightlifting, or racket sports. Pronator teres syndrome can also be caused by any type of body abnormalities, a tumor, or scar tissue.
When the median nerve is compressed at the wrist, it’s known as carpal tunnel syndrome. This is a common condition that affects women more than men. It happens to many different causes.
What are the symptoms of median nerve injury?
Symptoms are depending on the type of injury. pain produces particular at night due to compression of the median nerve, a tingling sensation, numbness, and weakness in the hand.
wrist pain, numbness, weakness, or tingling.
Sensation loss in the thumb, index fingers, long fingers, and the radial aspect of the ring fingers.
Pain, burning, or tingling sensation in the forearm.
Grip strength was reduced.
Tenderness or pain in the elbow.
Decreased or restricted movement like abduct and oppose of the thumb due to paralysis of the thenar muscles. This is called “ape-hand deformity”
Weakness in forearm rotation movement and wrist and finger flexion movement.
Difficulty in Activities of daily living like brushing teeth, tying shoes, making phone calls, turning door knobs, and writing due to median nerve injury.
Fracture, trauma, or dislocation that has caused damage to the nerve due to that numbness or weakness are present in the forearm or hand.
If the nerve has been severely damaged so the muscle becomes wasting.
When should you go to the doctor?
You should meet your doctor if you experience the following problems:
Difficulty picking up or holding the items or things.
Pain, loss of sensation, or weakness in the forearm, wrist, thumb, or fingers.
Difficulty in performing everyday activities like buttoning a shirt.
Severe elbow or wrist pain.
these many symptoms are felt in your body so that time, you should meet your doctor and they check the signs and diagnose the symptoms properly.
Clinical Examination:-
The first doctor takes the whole history and then checked some special tests, wrist and hand movement and the sensations are also checked with light things.
Motor(movement) function examination:
Decrease pronation movement of the forearm
Decrease flexion and radial deviation movement of the wrist
Thenar muscle atrophy
Inability to flexion movement of thumb;
Sensory examination:-
Sensation loss in the thumb, radial 2 1/2 fingers, and the corresponding portion of the palm.
with median nerve injury, the thumb cannot be pronated & nail is < 100 deg.
Special tests are 1)Phalen’s test and 2) tinnel’s sign.
Tinel’s sign: In this test, the physician taps over the median nerve at the wrist to see if a produces a tingling sensation or not in the fingers. if the tingling is present so that the test is positive and if not so that the test is negative.
Phalen’s test(Wrist flexion test): In this test, the patient put his or her elbow on a table and does the wrist to fall forward freely. patient with carpal tunnel syndrome will experience numbness and tingling in the fingers within 60 seconds. If The more quickly
symptoms appear, and carpal tunnel syndrome is more severe.
What is the Treatment for median nerve injury?
When the median nerve was injured at the elbow or wrist by acute injury ( fracture or dislocation), If the soft tissues are injured the treatment is the compression, applying ice, and keeping the arm elevated. when the bone fracture is present, it is unlikely to heal in the correct way, or it is putting pressure on the nerve, which may require surgery.
Patients take physiotherapy treatment for early and fast recovery or back to their own normal activity which are unable to do due to median nerve injury.
Medical treatment:-
Avoiding the activities which produce pain or stress in the involved arm, forearm, or wrist area.
RICE Principle: Rest, Ice, Compression, and Elevation can use to reduce the tension on the median nerve.
Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) to decrease pain and inflammation.
Immobilization, and strapping can be beneficial to rest, and enhance recovery.
Steroids injection may be given for reducing inflammation.
In severe conditions, surgery may be necessary. Surgery involves removing the tissue or parts of the bone which compress the nerve.
Physiotherapy Treatment:-
Manual Therapy:-
Soft Tissue Mobilization: it is given the improve the functional movement of affected parts like the forearm, hand, or wrist.
Neurodynamic Techniques: increase sensation, nerve mobilization, and others are used to decrease neuropathic pain.
Functional Massage: it is given to improve the patient quality of life, decreasing pain or spasm also reduced.
Carpal Bone Mobilization Technique: it is beneficial to improve wrist movement and pain reduction.
Therapeutic Exercises:- In this exercise includes stretching and strengthening exercises to improve range of motion and strengthen muscles of the arm, forearm, or wrist area to support, stabilize and reduce the stress on the median nerve.
Neuromuscular Reeducation:- it improves the stability, improves functional movement. It also decreases friction on the joint surfaces in daily activities.
Active movement exercise: If the patient does the functional movement without pain, then asked the patient to do all active movement exercises repeatedly during frequent working time or activity.
Neural gliding exercise:- Therapist first check the proper muscle and median nerve tension test by ULTT(UPPER LIMB TENSION TEST FOR MEDIAN NERVE )when it’s entrapped and then the therapist gives the nerve gliding and nerve flossing exercise to the patient.
Electrophysical Therapy:-
Ultrasound Therapy: it is given to the decreasing the neuropathic pain and faster healing process.
Laser Therapy: it is beneficial to pian relief and acceleration of healing for the injured area.
Other modalities are electrical stimulation and ice massage to decrease pain and inflammation involving the joint area.
Both treatments had a positive effect on nerve conduction, pain decreasing, functional activity, and subjective symptoms in particular with carpal tunnel syndrome. However, manual therapy gives a better result in all symptoms compared to the other therapy treatment.
Median nerves mainly supplied superficial muscles are pronator teres, flexor carpi radials, and palmaris longus. when any reason the median nerve is injured that the affect these muscle’s functional and sensory function and the physiotherapy treatment improve the muscular function and gradually improves that muscle strength so that patient back to their normal functional activity gradually.
For example:-
If the median nerve is injured at the elbow and the patient has difficulty rotating the forearm downward (pronation movement). Physiotherapy treatment for improving the movement and strength of the pronator teres muscle. first, assess the patient condition and check the pronation movement. if the patient cant do this movement so treatment are following gradually :
1) Electrical stimulation:
First palpate the muscle, the pronator muscle origin from the common flexor tendon at the medial epicondyle of the humerus. It passes crossly from medial to lateral and forms the medial border of the cubital fossa. so that it feels the antecubital fossa, slightly medially, and pronate/supinate the forearm and electrical stimulation in IG mode is given that point to encourage the muscle electrical activity after that gradually go for the surge faradic (SF)mode to improve the particular that movement.
2)pain management :
patient advise the ice massage, rest on that part, and the therapist gave the other electrical modality like TENS, US, LASER THERAPY for the reduction of pain, also given the functional massage.
3)therapeutic exercise:-
If the patient can’t do the movement actively so the therapist gives the movement by the passive movement exercise, and gradually go for the active, active assisted movement (pronation movement of the forearm). once the pain subsides and active movement achieves in full range then go for the strengthening exercise.
strengthening exercise:-
Grasp a dumbbell with your palm, Sit on a bench or chair with back support, and put your arms hand rest and your thumb facing upward. Rotate the dumbbell so your thumb is facing down, then return on the thumb upward position. Repeat this 10 to 15 count.
Pronator stretch:–
Bend one elbow to your body and put the other hand on the back of your hand. With help from the back hand, rotate your forearm to bring the palm of your hand facing upward until you feel a stretch in the forearm. Hold the stretch for 20-30 seconds. repeat 3 times and relax.
4)Sensory function:-
To improve the sensory stimulation given the pinching and tapping, brushing and icing are used to affected muscle or part.
5)Neural gliding exercise :
The therapist gave the median nerve gliding exercise to improve the movement and pain reduction for the pronator muscle of the forearm. patient Stand with your affected arm out to the side hand support on the wall, likely 30 degrees away from your body. With your elbow straight, hold your hand on the wall, ensuring the patient hand height is lower than your shoulder height. Gently rotate the body away from your arm until you feel a gentle stretch down the arm. slightly flex your neck to the opposite shoulder and leave the tension off your hand simultaneously to glide the nerve. Back to your starting position and continue to alternate between these two positions.
How to prevent of median nerve injury?
Occupation therapy and wearing splints should help a lot in the prevention of repetitive median nerve injury. However it is not possible to totally avoid trauma to the arm and wrist, patients may decrease the compression by doing proper actions during repetitive activities. Also, strengthening and increasing flexibility will reduce the risk of nerve compression.



2 Comments