Pain in quadriceps tendon: Cause, Symptoms, Treatment, Exercise
When you feel pain in the walking, step up; it is indicated as quadriceps tendon pain.
This pain is produced by repetitive movements like jumping & kneeling; this overuse leads to tiny tears which produce pain & swelling in the tendon.
This quadriceps tendon injury mostly occurs in athletes, such as volleyball & basketball players.
This pain is relieved by the RICE principle, pain medication & physiotherapy treatment.
Table of Contents
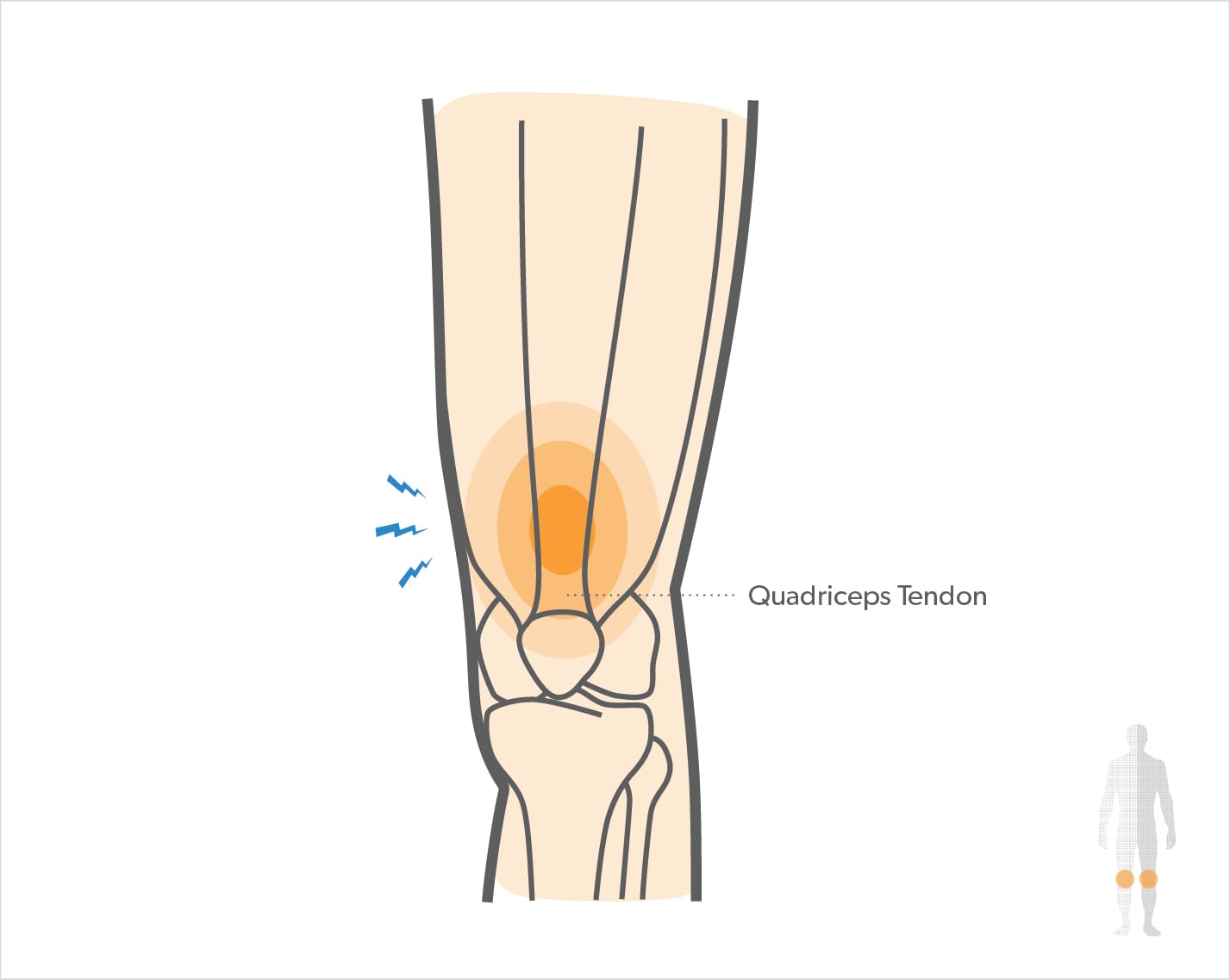
What is the quadriceps tendon?
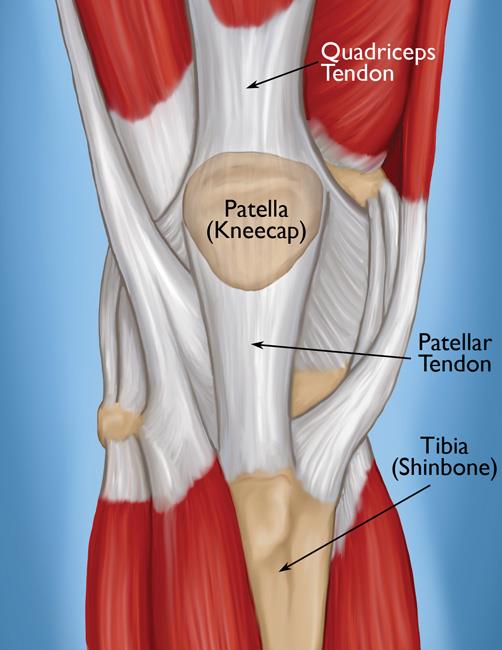
- This quadriceps tendon is a thick tendon which is extending to the patella & made up of contributions from all four quadriceps muscles.
- This tendon is classically in a trilaminar structure:
- Superficial layer: rectus femoris muscle
- Middle layer: vastus medialis muscle, vastus lateralis muscle
- Deep layer: vastus intermedius muscle
- This tendon continues to distal to the patella as the patellar tendon.
- In the human anatomy, this quadriceps tendon works with the quadriceps muscle to extend the leg.
- Four parts of the quadriceps muscle are attached to the shin via the patella means the knee cap where this quadriceps tendon has become the patellar ligament.
What are the causes of the pain in the quadriceps tendon?
Quadriceps tendinitis:
- The most common cause of the quadriceps tendon pain is Quadriceps tendinitis
- Quadriceps tendinitis means inflammation of the Quadriceps tendon.
- The most common cause of quadriceps tendonitis is overuse.
- Some Repeated actions which are produced to quadriceps tendon pain:
- The sudden increase in physical activity
- Poor walking habits
- Poor posture
- Sports
- Trauma, like jumping on a hard surface
- Other Injuries which are also produced by quadriceps tendon pain include :
- Strain from overuse
- Contusion from a direct blow
- Tendon rupture
- Partial tear of the muscle
- Compartment syndrome
- Quadriceps tendon strain:
- This quadriceps tendon is also strained due to overuse & overstretching.
- These Muscle strains are categorized depending on the severity of the injury.
- So that 3 different grades of muscle strains :
- Grade 1 strain = involves the muscle fibers that are stretched but not too torn.
- Grade 2 strain = involves a muscle that is partially torn with the more extensive damage.
- Grade 3 strain = occurs when a muscle is completely torn.
- Some Osgood-Schlatter disease, which is known as apophysitis of the tibial tubercle occurs when the occur to inflammation of the bone where the patellar tendon is attached to the quadriceps muscles to the tibia.
- It is most commonly seen in adolescents, it also occurs in adults.
- Contusions:
- It is usually caused by a direct blow to the quadriceps muscle, which occurs to another person & an object.
- It can damage the muscle fibers & associated with bleeding.
- Peri-patellar tendinosis/jumper’s knee:
- It is an overuse injury where the microtears occur in the area when the quadriceps tendon is inserted into the top & bottom of the patella.
- Instead of the cause the acute inflammation, this area starts to degenerate & scarring.
- This injury most commonly occurs in the people who repeatedly engage in the sports involved to an intense jumping sport like as volleyball.
- Tendon rupture:
- This occurs when the violent contraction of the quadriceps muscle when the tendon is completely torn & rupture.
- This rupture occurs more commonly in patients who are older than 40 years of age.
- This rupture occurs less frequently & typically seen in younger patients.
- This rupture occurs due to many medical conditions including:
- Rheumatoid arthritis
- Gout
- Systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE)
- Metabolic bone diseases like as hyperparathyroidism
- Diabetes mellitus
- Obesity
- Kidney disease
What are the symptoms of the injury in the quadriceps tendon?
- You feel pain in the front of the knee joint, just above the kneecap.
- This pain is dull & gradually which is increases over time.
- This pain is become worse after sitting down for too long & do repetitive movements like jumping, squatting& running.
- You also feel stiffness, mostly in the morning
- You feel swelling & tenderness in the area of pain
- Filling of weakness during walking
- You are feeling to cramping sensation in the area of pain
- Bruising & discoloration of the skin of area pain
- You are heard to popping & tearing sensation in the thigh muscles.
- You also feel decreased ROM = range of motion.
What are the Risk factors for quadriceps tendon pain?
- If you run on the hard surfaces
- When you play jumping sports, such as volleyball & basketball
- If you do daily exercise without warming up & do the exercise without talking to enough recovery time
- When you do repeatedly squat & kneel
Some Other factors which are increase risk include:
- Age:
- when you are older, the quadriceps tendons become less flexible & more prone to inflammation.
- Weight:
- Excess body weight which is put extra stress on the quadriceps tendons.
- Tight muscles:
- tight hamstrings & quad muscles increase pressure on the tendons.
- Chronic disease:
- Some Chronic diseases, like lupus & diabetes, reduce blood supply to the knee.
- This weakens the tendons & increases the risk of the tendon.
- Alignment problems:
- If the joints & bones are not properly aligned means one leg will be placed under more stress.
- Muscular imbalances also produce a similar effect.
What is Diagnosing of the quadriceps tendon pain?
- Physical exam:
- When you meet the doctor first do the visually inspect the knee joint & the surrounding areas.
- Then check the tenderness, swelling & pain.
- Medical history:
- it helps the doctor understand the cause of the injury.
- Imaging tests:
- sometimes doctors advise MRI & ultrasound.
- These all tests take detailed images of the knee tendons.
- and do the proper diagnosis of the causes of the injury
- Plain X-rays:
- it is helpful for the diagnosis of the fracture of the femur & patella.
- Myositis ossificans is also seen in plain films.
- Ultrasound:
- It is useful to determine a partial verse to complete tendon rupture.
- After the diagnosis doctor is advised to you proper treatment.
What is the Treatment for the quadriceps tendon pain?
RICE principle:

The first-line treatment for quadriceps tendon pain is called the RICE principle.
- R- Rest = To protect the injured area, you need to limit the movements which are doing the overworking the knees.
- You are also used to a brace to stabilize the knee means doing the rest for some days & do not do any activity which produces pain.
- I- Ice = You are Applying ice & a cold compress to the area of pain for 20 minutes, which is help to reduce swelling & pain; you are also applying to ice pack & frozen peas but always apply to a towel between the skin & ice which is helpful to you for protection from the ice burn.
- C – Compression = You can also be applied to A compression bandage to the area of pain which helps you decrease the swelling.
- E – Elevation = To further minimize the swelling, must place the injured knee on a raised surface or help of a pillow.
Pain medications:
- You can also take to Non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs – NSAID which are used as an over-the-counter pain reliever.
- You can use the following NSAIDs drugs to treat the tendon pain including:
- Aspirin
- Naproxen
- Ibuprofen
- Sometimes the doctor is suggesting to take the acetaminophen drug instead of an NSAID drug.
- You can also apply volini gel to the area of muscle pain.
Corticosteroid injections:
- When the pain is not relieved after some days then the doctor has advised you to local corticosteroid injections release to the pain.
- This injection is given to the knee joint by a doctor.
- This injection is advised after many treatments.
Surgery :
- Most people with the quadriceps tendon do not need surgery.
- When the non-surgical treatments do not work if the injury is severe, that needs surgical repair.
- During surgery, a surgeon removes the damaged portion of the tendon.
- The Open surgery involves a single large incision.
- Arthroscopic surgery:
- In this surgery, doctor uses small incisions & a tiny video camera & mini surgical instruments.
- It is less invasive than open surgery.
Orthotics:
- These Orthotic devices are shoes that are inserts that support the foot.
- It helps you treat tendon pain by reducing the pressure on the knee.
What is Physiotherapy treatment for the quadriceps tendon pain?
The physiotherapy includes massage, taping & bracing, electrotherapy, exercise, stretching to release pain, swelling spam, and tightness.
Massage :
- This massage helps to you relieve the tender points & trigger points, swellings, or pain.
- Massage is advised by to therapist when you do complain of the trigger & tender points of the tendon pain.
- This massage is applied for 5 to 10 minutes to the area of pain.
- It is applied with the help of oil & powder.
Taping & bracing:
- To off-load the stress on the tendon, a physiotherapist is applied athletic tape on the knee joint.
- Taping reduces knee pain by stabilizing the kneecap.
- Another way is a knee brace, which is help to off-load the stress on the tendon.
Electrotherapy treatment:
- The pain relief in the electrotherapy treatment includes US = ultrasound, SWD = short wave diathermy, IFT = Inferential Therapy, TENS = Transcutaneous Electrical Nerve Stimulation.
- When the tender & trigger points are present in the area of pain therapist is advised to US = ultrasound on the area of pain.
- This machine is applied for 5 minutes to the area of pain.
- This US is applied with the help of gel & not applied to a direct probe on the skin.
- This machine helps you release pain & swelling.
- For release to pain & swelling you can also apply SWD = short wave diathermy, IFT = Inferential Therapy, TENS = Transcutaneous Electrical Nerve Stimulation.
- This machine is applied for 10 minutes to the area of pain.
Stretching :
- Stretching helps to you release tightness & pain in the muscle pain area.
- Lunging Hip Flexor Stretch :
- Standing Quadriceps Stretch :
- Hamstring Stretch in supine
- Wall Hamstring Stretch :
- Seated hamstring stretch :
- Heel and calf stretch:

Lunging Hip Flexor Stretch :
- You are in a kneeling position for stretching.
- Then do the Kneel on the left knee & must keep the right shin onto the ground.
- When they find the ground tough onto the back leg then try to do the stretch on a yoga mat.
- Then Move to the right leg back into behind the body.
- Must be Keep the right foot facing the ceiling.
- The patient is put both hands on the right knee or pushes the body forward.
- Must be Kept the torso & head in the alignment.
- You feel the stretch into the hips and left leg.
- Hold this position for 20 seconds.
- Repeat this stretch the 3 times in 1 session & 3 sessions per day.
Standing Quadriceps Stretch :

- Your Starting position for this stretching is the standing position.
- Then Raise the left arm straight out in front of the body.
- It helps to keep the balance.
- Then Bend to the left knee joint & grab the left ankle.
- Bring the left foot back behind the body.
- Try pulling the leg up & back with the hand onto the ankle joint.
- Must be Kept to the torso & head into the alignment.
- Hold this exercise for 30 seconds.
- Then Repeat this stretch the 3 times in 1 session & 3 sessions per day.

Hamstring Stretch in supine:
- Your Starting position for this stretching is the supine position.
- Then Extend to the right leg in front of the body & Bend to the left leg.
- Wrap the hands around the back of the left thigh
- And pull the leg slowly toward it as soon as you can.
- Hold this stretching position for 30 seconds.
- Repeat this stretch the 3 times in 1 session & 3 sessions per day.
Wall Hamstring Stretch :
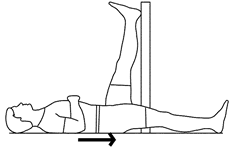
- Your Starting position of the stretching is the supine position.
- You are lying on the floor with your back facing the wall.
- Scoot to the body so that the glutes muscle touch the wall.
- Place one leg onto the wall & try to extend the leg as soon as possible.
- Hold this stretching position for 30 seconds.
- Repeat this stretch the 3 times in 1 session & 3 sessions per day.
Seated hamstring stretch :
- Your Starting position for the stretching is a long sitting position.
- Try to touch the knee with the help of the body lean.
- You feel the stretch position.
- Hold this position for 30 seconds.
- Repeat this stretch the 3 times in 1 session & 3 sessions per day.

Heel and calf stretch:
- Your Starting position for the stretching is a standing position.
- Place the hands onto the wall & move to the one foot back as far as you can comfortably.
- Both Toes & feet to facing forward & heels are flat & with a slight bend into the knee joint.
- You feel the stretch into the back leg.
- Hold this stretching position for 30 seconds.
- Repeat this stretch the 3 times & 3 sessions per day.
Exercise :
This all exercise is helpful to you release the muscle pain & decrease the weakness of the leg.
- Static Quadriceps exercise [ SQE] :
- Knee Extension over to Roll [ VMO ] :
- Straight Leg Raises :
- Side Leg Raises [ hip abduction ] :
- Prone Straight Leg Raises :
- Clamshell exercise :
- Half squats
- Wall Squats :
- Step-Ups :
![Static Quadriceps exercise [ SQE] :](https://samarpanphysioclinic.com/wp-content/uploads/2022/05/Static-Quadriceps-exercise-SQE.jpg)
Static Quadriceps exercise [ SQE] :
- The starting position for the exercise is a long sitting & supine position.
- For exercise Put any pillow, sand beg & fold the towel under the knee.
- Push the knee joint into the bed.
- Hold this exercise position for 10 seconds & then relax.
- Repeat this exercise 10 times for 1 session & 3 sessions per day
Knee Extension over to Roll [ VMO ] :
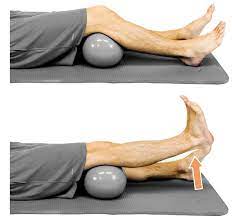
- Your Starting position for the exercise is a long sitting & supine position.
- Must be Put the rolled towel under the knee.
- Pull the toes up towards the shin.
- Then fully straighten the knee joint.
- Hold the position for 10 seconds & then relax.
- Repeat this exercise 10 times for 1 session & 3 sessions per day

Straight Leg Raises :
- Your Starting position is supine.
- You are lying on the back of the floor.
- Bend the one knee joint & place the foot flat on the floor.
- Must be Keep straight the other leg & raise the leg to the height of this opposite knee joint.
- Always keep the pelvis still not use the abdominal muscles.
- Repeat this exercise 10 times for 1 session & 3 sessions per day.
Side Leg Raises [ hip abduction ] :
![Side Leg Raises [ hip abduction ]](https://samarpanphysioclinic.com/wp-content/uploads/2022/03/e-Leg-Raises-hip-abduction-exercise-1.jpg)
- The starting position of this exercise is side-lying.
- You are lying on one side with the legs stacked.
- Bend to the bottom leg for the support.
- Then Straighten to the top of the leg & raise to 45 degrees.
- Hold this exercise position for 10 seconds & then brief to relax.
- Repeat this exercise 10 times for 1 session & 3 sessions per day.

Prone Straight Leg Raises :
- Your Starting position is the prone position.
- You are lying flat on your stomach.
- Must be Keep the legs straight.
- Then Tighten the muscles of the bottom & the hamstring of the one leg.
- Lift to one leg toward the ceiling.
- Hold this exercise position for 10 seconds.
- Repeat this exercise 10 times for 1 session & 3 sessions per day
Clam-shell exercise :
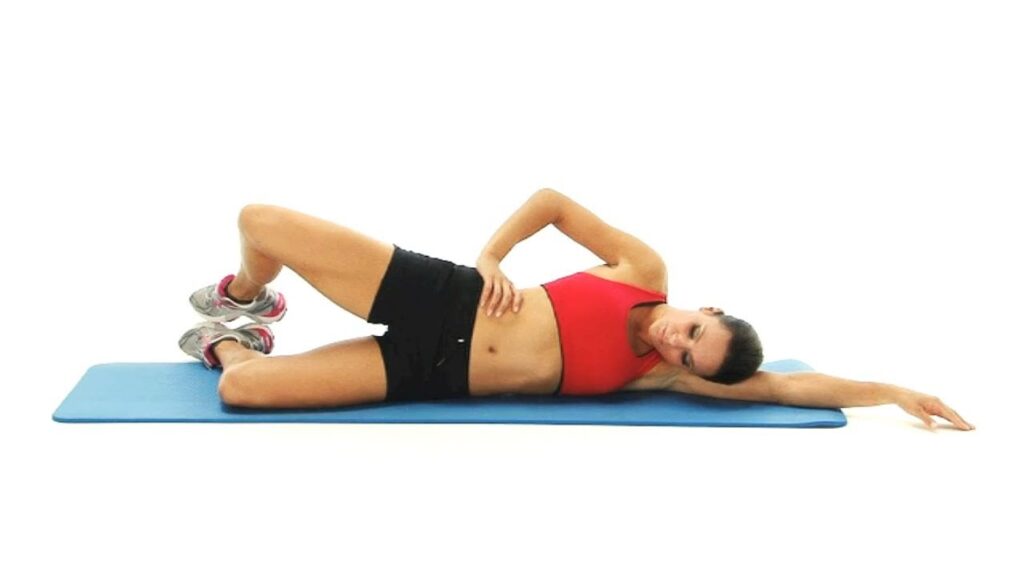

- Your Starting position for exercise is the supine position.
- You are lying on to the side with the bent knee joint & keep the affected leg on to the top.
- Extend to the lower arm under the head/bend to the arm like a pillow for the head.
- Place the hand on the hip joint for support.
- Engage the abdominal muscle & keep the hip joint facing downward during the exercise.
- Slowly lift the leg as high up as possible & must be kept to the feet together.
- Then return to the starting position.
- Repeat this exercise 10 times for 1 session & 3 sessions per day.

Half squats:
- Your Starting position for exercise is a standing squat position & With to the feet are shoulder-width to apart.
- Then Place the hands on the hip joint & out for the balance.
- See the straight-ahead then slowly squat down position about 10 inches.
- It is the halfway point to a full squat.
- Stop for a few seconds, and after that stand up by pushing through to the heels.
- Repeat this exercise 10 times for 1 session & 3 sessions per day
Wall Squats :

- The starting position of the exercise is the standing position near the wall.
- Must keep the feet on to the floor.
- You are standing with your back against a wall.
- Must be Keep the feet about to shoulder-width apart.
- Then Slowly bend the knee joint & must keep the back & pelvis against the wall.
- Do not bend to them deeply.
- Hold this exercise position for 10 seconds.
- Repeat this exercise 10 times for 1 session & 3 sessions per day

Step-Ups :
- Your Starting position for exercise is a standing position.
- Then Place one foot onto a platform & step bench to the lowest step onto a staircase.
- Must be Kept straight to the pelvis level.
- Bend to the knee joint & slowly lower to the opposite foot onto the floor.
- Then Lightly touch the toe onto the floor or rise to back up the position.
- Repeat this exercise 10 times for 1 session & 3 sessions per day
Recovery from the pain :
- Recovery of this tendon pain depends on the many factors including:
- severity of injury
- age
- overall health
- This range returns in a few days for a contusion & takes too many months for a ruptured tendon.
What are the complications of quadriceps tendon pain?
- Myositis ossificans:
- When the large muscle the quadriceps muscle is injured, the body is laying down excess calcium as part of the healing process. This condition is called myositis ossificans which is produced by pain & decreased range of motion = ROM in the affected leg.
- Compartment syndrome:
- May occur as a complication of trauma to the anterior compartment of the thigh, where the quadriceps muscle group is located. Crush injuries or a fractured femur are often the cause. Compartment syndrome is a surgical emergency, and the compartment needs to be opened to relieve the pressure and prevent permanent muscle and nerve damage.
- Other Complications are weakness & loss of knee motion.
- when do surgery include complication like as a blood clot, infection & wound breakdown
Is it possible to prevent quadriceps tendon pain?
- Sometimes these injuries occur & cannot be entirely prevented because An accidental direct blow is given as to the result of contusion, exit can occur during a sporting activity.
- Overuse injuries must be preventable, mostly when the patient ignores the warning signs of mild discomfort & continues with repetitive activities which is lead to further damage.
- It’s often possible to prevent the muscle strains by making the quadriceps muscle adequately stretched before the vigorous activity.
- So must do the Individuals always stretch & warm up before exercising like People who do physical labor at work & around the house which is doing a few minutes to warm up before engaging in the activities.
- Similarly, after exertion, a muscle is need to be cooled down, stretched, & rested which is prevent muscle strains, tendinitis & even tendon rupture.