Navicular Fracture
Table of Contents
Introduction
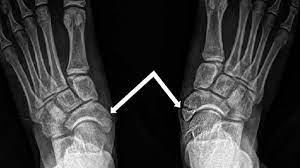
A navicular fracture is a type of bone fracture that occurs in the navicular bone, which is located in the midfoot. The navicular bone is a small bone situated on the inside of the foot, just above the arch.
Fractures of the navicular bone are most generally the cause of either high-impact injury or overstress, with the after having a greater incidence in more youthful people and sportsmen. Tarsal navicular stress fractures account for up to one-third of all stress fractures, despite the fact that midfoot fractures are rather infrequent. These fractures are a more significant threat of nonunion and osteonecrosis owing to the navicular bone’s tenuous blood circulation as well as the inherent complexity of the joint. These fractures usually need surgical attention, though they can occasionally be managed conservatively.
The talus, calcaneus, three cuneiform bones, and cuboid all articulate with the navicular, shaped like wedges bone. The base and apex of the bone can be found dorsolaterally and plantar medially, respectively, with the central oblique axis between the lateromedial and dorsoplantar.
The navicular articulates with the head of the talus posteriorly via a biconcave surface. Anteriorly, the navicular has plantar concavity, with three articular surfaces existing. The largest of these surfaces is located medially, articulating with the medial cuneiform, and exhibits a convex physical appearance. The navicular tuberosity, found medially, is the insertion place for the posterior tibial tendon. Considering the more significant number of articulations seen on several surfaces of the navicular, a more significant part of the bone is covered in articular cartilage.
The posterior surface of the navicular takes vascular circulation by the medial tarsal branches of the dorsalis pedis artery, along with branches of the lateral tarsal artery. Providing the medial plantar surface of the navicular is a branch of the tibialis posterior artery. Some literature recommends a zone of avascularity from the central third to the distal cortex of the navicular, which can contribute to the avascular necrosis occasionally related to these fractures.
The Chopart joint, which also includes the talonavicular and calcaneocuboid joints, includes the tarsal navicular as a key component. Both of these joints are crucial for the inversion and eversion movement of the foot.
Epidemiology
Midfoot fractures just describe a little part of all foot trauma, though stress fractures include roughly one-third of all stress fractures of the foot.
In the condition of traumatic navicular trauma, the extensive prevalence is caused by road traffic accidents, next by falls and sharp trauma. Stress fractures are most typical in youthful people with great functional demands for example competitive athletes.
Causes of Navicular Fracture
While the biomechanics behind stress fractures of the tarsal navicular is slightly poorly understood, those of traumatic trauma are more broadly explained. It is recognized, still, that stress fractures are a chronic overuse injury related to microfractures of the bone Traumatic trauma can result in a diversity of navicular fracture types, as well as avulsion fractures, tuberosity fractures, and body fractures.
Depending on the force applied to the midfoot, avulsion fractures of the navicular can occur dorsally, medially, or in a plantar direction. In the condition of foot posterior avulsion, fractures cause by undue plantar flexion cause unnecessary stress on the deltoid and posterior capsules. Exaggerated pull from the dorsal tibialis tendon can cause medial and tuberosity fractures, and plantar avulsion fractures are secondary to ligamentous sprain.
Navicular body fractures can be the result of either a direct hit or an indirect impact. The Sangeorzen type, devised in 1989, is the greatest system for grading tarsal navicular body fractures. This system types tarsal navicular body fractures depending upto the direction of the fracture line, the degree of disruption of nearby joints, and the direction of foot displacement. In this type,
- Type-1 injury is one that happens in the coronal plane, with no angulation of the forefoot.
- Type-2 injury is one that features a medial displacement of the main segment and forefoots together with a dorsolateral to the plantar-medial fracture line.
- Type-3 injury is defined by a comminuted fracture in the sagittal plane of the bone with lateral forefoot displacement. There are various other hypotheses on the forces resulting in navicular body fractures, though all are because of axial forces on a foot in plantar flexion.
Symptoms in Navicular Fracture
Patients with recent fractures of the navicular generally present with:
- Pain over the posterior or dorsomedial foot next to injury.
- Localized swelling and tenderness over the navicular.
- Problem with weight-bearing
- Increased pain and incapacity to walk on or push off (ie, plantarflex while weight-loading) with their toes.
- Other symptoms may possess tenderness in the middle of your foot, bruising, or pain that reduces while resting
Evaluation
In a patient with a supposed tarsal navicular fracture, the earlier radiographic evaluation is the three-view radiograph of the foot; this contains a non-weight bearing anteroposterior, lateral, and diagonal X-ray. Regardless, patients with supposed ligamentous sprain or minor trauma can need a weight-loading radiograph. An exterior diagonal radiograph of the foot is helpful in the evaluation of a supposed tuberosity fracture. In considering radiographs, the clinician must be mindful of the possibility of the formation of an accessory navicular, which is identifiable with a radiograph of the contralateral foot.
The help of computed tomography (CT) can be useful in high-impact trauma, as it can more specifically delineate complex fracture type, and the geometry of the talonavicular joint, and can help in preoperative planning. Further, CT can be utilized to create three-dimensional reconstructions of the navicular.
Differential Diagnosis
In the event of a predicted navicular fracture, several cases that may have identical symptoms and representations involved tendinopathy of the posterior tibialis owing to its insertion on the navicular tuberosity, sprain of the spring ligament, or split of an accessory navicular- a fairly standard anatomic variant. An MRI can discriminate between a tarsal navicular fracture and one of these situations. Regardless, it is usually not required in the earlier administration as radiographs, and CT scans easily diagnose many tarsal navicular fractures.
Prognosis
Patients who have experienced a navicular stress fracture generally have a clear prognosis if managed immediately and properly. A current analysis confirmed that fifty-seven out of their sixty-two-patient section had been capable to return to activity at their preinjury status, indicating an optimal clinical result In an illustration study of 10 patients with comminuted tarsal navicular fractures, all surgically treated patients were able to achieve union, with no patient needing an arthrodesis at a mean follow-up of 20 months.
Treatment of Navicular Fracture
Tarsal navicular fractures can be treated either nonoperative or operative, relying on the respective fracture features, for example, the extent, how far the displacement happened, the site, comminution, as well as the circumstances and virtue of the soft tissues of the foot, the existence of accessory damages on the same side of the foot, comorbidities, and general functional situation.
In the condition of navicular stress fractures, immobilization, and secure weight loading for a period of six to eight weeks are indicated. Regardless, patients with great functional requirements, for example, athletes can be operated on for operative intervention rather. In the event of operative intervention, these fractures can undergo repair with open reduction and internal fixation.
The treatment of traumatic navicular fractures can also be treated with operative or non-operative intervention. slight avulsion fractures, tuberosity fractures, and undisplaced body fractures can be treated nonoperatively, with the help of a weight-loading short-leg splint and finally, a walking boot is used.
Displaced navicular body fractures generally need operative intervention, with the help of open reduction and internal fixation. The purposes of surgical intervention are anatomic fracture reduction, repair of the length of the inner aspect, and the result of a rigid osseous construct which would permit an initial range of movement.
Recovery time for a navicular fracture can vary depending on the individual and the specific fracture. It may take several weeks or even months for the bone to heal completely. During the recovery period, weight-bearing activities are typically restricted, and physical therapy may be recommended to restore strength, flexibility, and function to the foot.
Physiotherapy Treatment
In many circumstances of a navicular stress fracture, management with a time of non-weight-loading in a cast is the management of preference. An operative is even a treatment alternative. Pursuing your earlier treatment, your physical therapist will be capable to create an advanced protocol of exercises for your return to activities of daily living. During your rehabilitation, your physical therapist will take into account the circumstances around how you came across a stress fracture in your navicular.
Other treatment includes:
Orthotics
Orthotic devices are used externally to a joint or limb and are prepared to help and fix anomalies and correct function next to trauma, injury, or illness.
The usage of orthotic devices is frequently an essential part of individual rehabilitation. Individuals with neurological problems will be able to better manage their condition and increase their independence with daily activities thanks to orthotic devices.
Few people may help from orthotic devices for example splints. The usefulness of orthotics may possess:
- Lessening contractures
- Assisting walking
- Improving the joint position
- Stretching tight muscles
- preventing overuse injuries and supporting weakened joints, muscles, and ligaments
- Reducing pain and stress
- encouraging independence and practicality at home
- Enhancing security with everyday tasks and minimizing injury
- There are a considerable variety of devices available depending on the diagnosis and physical necessities of the person.
Electrotherapy
Electrotherapy involves applying an electric current to the area of the body that is injured in order to hasten healing and lessen pain and swelling.
Electrotherapy is operated by our trained physiotherapists to treat a type of condition. Our physiotherapists use various types of electrotherapy comprising :
- Electrical Muscle Stimulation (EMS)
- Functional Electrical Stimulation (FES)
- Interferential Therapy
- LASER
- Low-Intensity Pulsed Ultrasound (LIPUS)
- Pulsed Shortwave Diathermy (PSWD)
- Transcutaneous Electrical Nerve Stimulation (TENS)
- Ultrasound
Taping
Physiotherapists use taping or strapping as a technique for injury prevention or recovery. Depending on your treatment goals, specialized physiotherapists are fully qualified to perform effective taping. In order to restart using the tape, physiotherapists can also teach you how to use it yourself.
The advantages of taping will be based on your injury. Your physiotherapists will purpose to promote some of the next usefulness:
- Protection of wounded soft tissue structures (like ligaments, tendons, skin, and fascia)
- Injury prevention
- Encourage normal movement
- Quicker return to sport or work
- Pain reduction
- Improves the stability of a joint
- Reduces the risk of re-injury
- Reduces swelling
Hydrotherapy
Hydrotherapy applies taking out exercises and thorough physiotherapy methods in warm water to assist reduce pain, relax and strengthen muscles, increase circulation, and subsequently enhance function. Hydrotherapy also permits adults and children who have little mobility to maximize their mobility within the water.
Complications
The navicular fracture is accompanied by a number of possible hazards and problems, as is the case with most periarticular regions. Osteonecrosis, malunion, nonunion, prolonged stiffness, and discomfort are some of these side effects. Depending on the severity of the deformity, patients with nonunions may have a deformity that can be treated surgically or with an orthosis. However, osteonecrosis can cause severe deformity and is usually treated with the main objective of restoring length and alignment, which is frequently accomplished through the fusion of the talonavicular or naviculocuneiform joints.
FAQ
These fractures are in significant danger of nonunion and osteonecrosis owing to the navicular bone’s fragile blood circulation as well as the intrinsic complexity of the joint. These fractures usually need operative intervention, though they can be managed conservatively in a few conditions.
You will keep to be in a cast or a “removable cast” and not bear a load for several weeks. You can remain non-weight loading by operating walking aids like crutches or a “knee walker” like the one at Privilege. Many patients spend about six to eight weeks in an immobilized cast, but some patients can require to be in one prolonged.
Physiotherapy can relieve symptoms of navicular fracture and help to prevent re-occurrence in the hereafter life. Treatment can possess:
Immobilization of the foot by a splint or boot to rest the difficulty and permit the inflammation to diminish
Stretching exercises
Strengthening exercises
Orthotics (insoles) to correct the position of the foot to relieve stress on the affected region
First-line treatment of the symptomatic navicular fracture is non-surgical. For consequential symptoms, immobilize in a CAM boot for six weeks; for mild symptoms, the goal is to reduce stress by preventing narrow footwear or footwear modification and assume a period of short-term activity modification.
Due to it having no cure, prevention is ideal. Keeping a routine trimming or shoeing plan with a skilled farrier maintains the horse’s hoof in the right ratio. The most effective way to avoid it, according to Turner, is to keep a farrier who is capable of fitting the horse with its ideal foot.
The objective of non-operative treatment for a navicular fracture is to reduce the symptoms. The following may be used: Immobilization. Positioning the foot in a cast or removable walking boot permits the involved parts to rest and lessens inflammation.
You will keep to be in an immobilized cast or a “removable cast” and not take the load for several weeks. You can remain non-weight loading by utilizing walking aids crutches or a “knee walker” like the one at right. Many individuals spend approximately six weeks in a cast, but few patients can require to be in one extended.