Iliotibial Band Syndrome (IT Band Syndrome) :
Table of Contents
What is iliotibial band syndrome ?
It is also known as iliotibial band friction syndrome or It Band Syndrome.
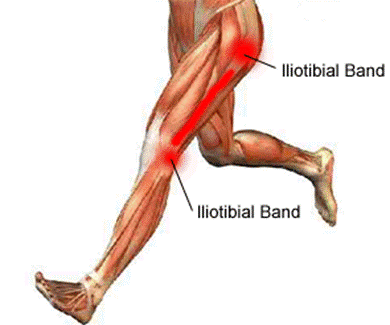
Iliotibial band syndrome (ITBS or IT band syndrome) is an overuse injury of the connective tissues that are located on the lateral or outer part of thigh and knee. It causes pain and tenderness in those areas, especially just above the knee joint. Iliotibial band syndrome is the most common cause of lateral knee pain in runners and bicyclists.
The iliotibial band is a thick band of fascia (tissue) that begins at the iliac crest in the pelvis, runs down the lateral or outside part of the thigh, and crosses the knee to attach into the top part of the tibia or shinbone. It forms from the tensor fascia lata and two of the gluteal muscles (gluteus medius and gluteus minimus) in the buttock and then stretches across the knee. The iliotibial (IT) band helps stabilize the outside part of the knee through its range of motion
What causes iliotibial band syndrome ?
The problem is friction where the IT band crosses over your knee. A fluid-filled sac called a bursa normally helps the IT band glide smoothly over your knee as you bend and straighten your leg.
But if your IT band is too tight, such as when you skip stretching before exercising, bending your knee creates friction. Your IT band and the bursa can both start to swell, which leads to the pain of IT band syndrome.
When the knee is positioned in extension the iliotibial band lies anterior to the lateral femoral epicondyle. When the knee is positioned in 30° of flexion the band moves posteriorly to the lateral femoral epicondyle. Friction can therefore occur between the posterior edge of the iliotibial band and the underlying lateral femoral epicondyle.
Certain physical conditions raise the chances of getting IT band syndrome :
- Bowed legs
- Knee osteoarthritis
- One leg that’s longer than the other
- Rotating your foot or ankle inward when you walk or run
- Rotating your whole leg inward when you walk or run
- Weakness in your abs, glutes, or hip muscles
What are the symptoms of iliotibial band syndrome ?
A stinging sensation just above the knee and outside of the knee (lateral side of the knee) joint, to swelling or thickening of the tissue in the area where the band moves over the femur.
The stinging sensation just above the knee joint is felt on the outside of the knee or along the entire length of the iliotibial band. Pain may not occur immediately during activity, but may intensify over time.
Pain is most commonly felt when the foot strikes the ground, and pain might persist after activity. Pain may also be present above and below the knee, where the ITB attaches to the tibia.
Other symptoms include :
- Aching, burning, or tenderness on the outside of your knee
- Feeling a click, pop, or snap on the outside of your knee
- Pain up and down your leg
- Warmth and redness on the outside of your knee
Examination Test for IT Band Syndrome :
1.Noble compression test :
This test starts in supine position and a knee flexion of 90 degrees. As the patient extends the knee applies pressure to the lateral femoral epicondyle. If this induces pain over the lateral femoral epicondyle near 30-40 degrees of flexion, the test is considered positive.
2.Ober Test :
the person lies on their pain-free side with the bottom knee and hip at a 90-degree angle. The physiotherapist will steady the pelvis and then lift the affected leg. They then bring the hip back toward the ground.
A person tests positive for IT band syndrome when there is less than a 10-degree angle from the natural horizontal position
Physiotherapy Treatment :
* rest : rest period depends on the severity of the condition and the reproduction of pain during clinical examination.
* Electrotherapy Modalities to provide pain relief eg. Interferential Therapy(IFT), TENS, Ultrasound Therapy and ice (cryotherapy) or heat
* If no improvement of symptoms occurs and inflammation persists, the following other treatment techniques might be considered:
> ultrasound therapy, providing thermal or non-thermal treatment of the injured tissue at a frequency range of 0.75 to 3 MHz (depending on the depth of the soft tissue to be treated)
> Iontophoresis or phonophoresis, techniques in which medication is administered into the injured tissue through ion distribution driven by an electric field or passed through the skin using ultrasound waves, respectively.
Iontophoresis with dexamethasone may be useful as an anti-inflammatory modality.
Exercises for iliotibial band syndrome :
1. SIDE LEG RAISE :
Lie on your right side with both legs straight. Slowly raise your left leg about 45 degrees, then lower. Repeat on both sides. To make this move more challenging, use an exercise band around your ankles to increase resistance. Reps: 20–30 on each side
2.Gluteal stretch :

Lie on your back with your knees bent and feet on the bed or floor. Place one ankle on the opposite thigh. Pull your knee towards the opposite shoulder.
The stretch should be felt on the back and lateral side of your hip. Hold for 30 seconds, 2 times
3.Hip Thrust :
Lie on your back with your weight on your upper back between the shoulder blades and your feet. Keep your arms at your sides or cross them over your chest. Lower your butt almost to the ground and thrust upward by activating your glutes and driving your heels into the ground. A more advanced version is the Single Leg Hip Thrust.
Lift one leg so your weight is all on one leg and your back. Repeat the same movement, making sure you drive your heel into the ground and keep a stable pelvis. Perform 20-30 reps.
4.Side Hip Bridge :
Lie on your side with your feet propped on an elevated surface about 1-2 feet off the ground. Push your bottom foot down and lift your torso using your hip muscles while keeping a stable spine. Return to the starting position. Perform 10-30 reps.
5.Side Shuffle :
With your knees slightly bent in a squat-like position, take ten steps to one side. While still facing the same direction, take another 10 steps back to your starting position. This is one set. A more advanced version includes a Thera-band or loop of rubber tubing around your ankles. It should be tight enough so it provides constant resistance during the entire movement. Perform 3-5 sets.
6. Pistol Squat :
Standing on one leg, squat down so your thigh is almost parallel to the ground. Keep your spine in a neutral position and keep the motion slow and controlled, ensuring your knee does not collapse inward. Perform 5-15 reps.
7.side lying it band stretching exercise :
Lie on your side with your affected knee on top.Bend your top knee and grab your ankle. You should feel a tightness in your quadriceps muscle with this.Pull back a bit, and then place your bottom foot on the side of your top knee.
Gently pull the foot on your knee down towards the floor, elongating the outside part of your top thigh.You should feel a stretch in the side of your knee where the IT band crosses the knee.
Hold the stretch for 15 to 20 seconds, and then release.Repeat 3 to 5 times.
8.Knee to Opposite Shoulder Stretch :
Lie on your back.Bend the knee of the involved (hurting) leg.
Grasp behind the bent leg’s knee with both hands and pull the involved leg toward the opposite shoulder.
Hold for 30 seconds.Relax your leg.Repeat four more times.






12 Comments