Frozen shoulder :
Table of Contents
What’s frozen shoulder ?
Frozen shoulder is a common shoulder joint condition that affects millions of people worldwide. The cause of Frozen Shoulder is not known, but is generally thought to be due to the degeneration of the rotator cuff tendons and muscles. This condition can be painful and can affect many aspects of daily living. The exact cause and course of the disease is not fully understood, but is generally thought to be due to the degeneration of the rotator cuff tendons and muscles.
- It is also known as adhesive capsulitis.
- It is a condition which is characterized by stiffness and pain in the shoulder joint & shoulder becomes very hard to move.
- Signs and symptoms are begin gradually, then worsen over time and after resolve, usually within one to three years.
- Risk of developing frozen shoulder increases when recovering from a medical condition or procedure that prevents from the moving the arm — like as a stroke or a mastectomy and also addition and people who have diabetes
- Treatment of the frozen shoulder involve the ROM exercises & sometimes given to corticosteroids and numbing medications injected into the joint capsule.
- In a small % of cases, surgery [ arthroscopic ] is indicated to loose the joint capsule so that joint can move more freely.
- Usually for frozen shoulder is recur to in the same shoulder, but in some people frozen shoulder develop in the opposite shoulder.
- Physical therapy is focus on shoulder flexibility, it is the primary treatment of the frozen shoulder.
- In Frozen shoulder most commonly affected people between the ages of 40 and 60 & women are more affected than the men .
Anatomy of shoulder Joint :
Bones of the shoulder:
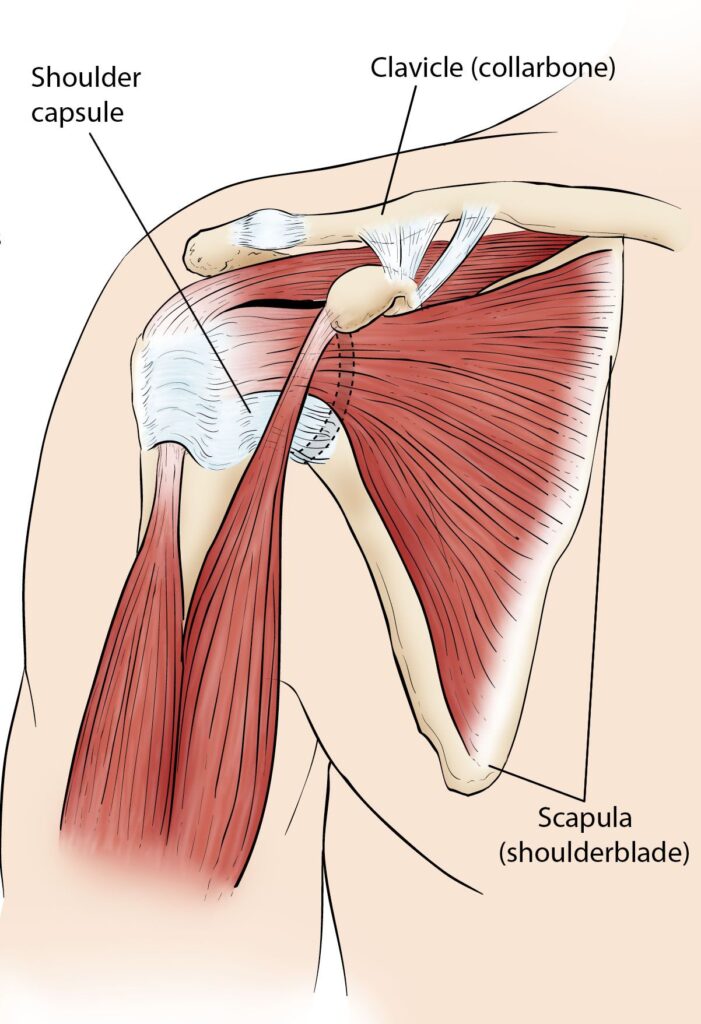
Upper arm bone = humerus it is the “ball” of the shoulder .
Scapula is a flat & triangular bone it is commonly called the shoulder blade.
Scapula are give to attachment points of many muscles and ligaments.
Glenoid is a shallow “socket” on the side of the scapula that is receives the ‘ball’ of the humerus.
Together to each other and form the “ball and socket” arrangement in the shoulder.
Clavicle is the collarbone & it is appears to be straight & it actually forms an S-shape .
Thorax or rib cage, give to attachment muscles and ligaments.
Bone junctions or joints of the shoulder :
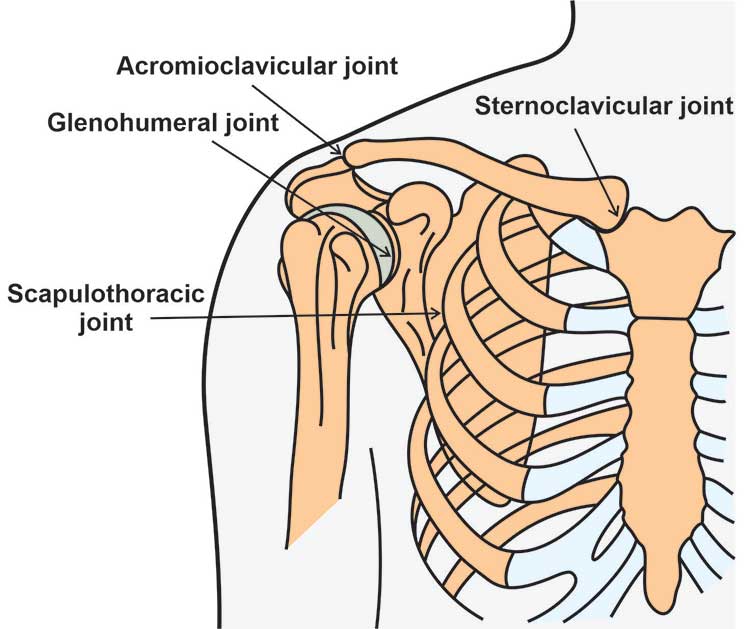
- There are 4 bone junctions around the shoulder .
Glenohumeral joint :
- It is the main joint of the shoulder.
- In the joint , the glenoid of the scapula and the head of the humerus come together.
- Flat socket of the glenoid is surrounded only 20% – 30% of the humeral head.
- Because of it is fit poorly,so that for support the joint relies heavily on surround soft tissue .
- lab-rum, it is a ring of fibro cartilage tissue which is attached to the glenoid and depend on the socket for encircle more of the humerus.
Acromioclavicular joint, or AC joint :
- It is the bony point of the top of the shoulder.
- It is stabilizes the scapula on the chest, by connecting the acromion on the scapula to clavicle [ collar bone ] .disk of fibrocartilage [ thick ] act to shock absorb between the bones.
- surrounding capsule and ligaments give the joint stability.
The Sternoclavicular joint, or SC joint :
- It is connect to the other end of the clavicle to the sternum [ “breastbone” ] . in joint contain a fibrocartilage disk which is help to the bone for achieve a better fit.
- It is also get the excellent support from the joint capsule and surrounding ligaments.
Scapulothoracic articulation :
- It is the area where the scapula, is embedded in muscle, glide over the thoracic rib cage.
- Surrounding muscles and ligaments are keep to the scapula in properly position so that arm move correctly.
Cartilage of the shoulder :
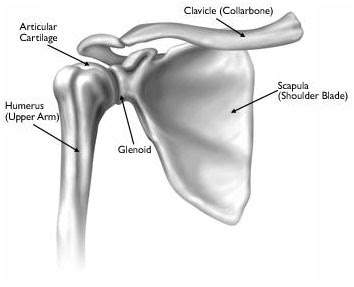
- Two types of cartilage in the shoulder joint :
Articular cartilage :
- It is the shiny white coating of cover the end of the humeral head & line the inside surface of the glenoid.
- Two purposes of the cartilage:
- To provide slick , smooth surface for easy movement .
- It is become to be a shock absorbed and protect the underlying bone .
Fibrocartilage :
- It is the thick tissue which is forms the disk of the AC , SC joints & the labrum, the ring is depend on the glenoid.
- Fibrocartilage has the three roles:
- Act as the cushion on shock absorption .
- Help to stabilize the joint by the improving to the fit of the bones .
- Act as a spacer and improve the contact between to articular cartilage surfaces .
Ligaments of the shoulder :

- Shoulder is relive heavily on the ligament for support.
- It is attached to bone to bone & provide static stability in the joint.
- It will be alternately become tight & loose with the normal motion.
- They will keep the joint within normal limits of the movement.
- Glenohumeral ligaments is attached in layer from the glenoid labrum to the joint capsule of the head of the humerus.
- Coracoacromial arch is the group of ligament which is that spans the coracoid process [ bony projections ] & the acromion.
- Coracoclavicular ligaments & acromioclavicular ligament provide most of the support for the AC joint.
Muscles and Tendons of the shoulder :

- Both are work together in the shoulder for provide to the “dynamic” stability of the shoulder.
- Four muscle groups are in the shoulder:
Rotator cuff muscles :
- In rotator cuff muscles including subscapularis, supraspinatus, infraspinatus, & teres minor.
- They are primary stabilizers which is hold the “ball” of the humerus in the glenoid “socket”.
- Socket is too shallow for offer to much security of the humerus.
- Those four muscles form a “cuff” which around the humeral head for securing it firmly in the socket.
- As per the name of muscle , this group of muscles are also rotaters of the arm.
- These muscles are protect the glenohumeral joint from dislocation & the allowing of the large muscles which that control to shoulder & give to power the arm with the great mobility.
Biceps tendon complex :
- These muscles are also help to keep the humeral head in the glenoid and help to raise the arm.
Scapulothoracic muscles :
- These are attach to the scapula and the thorax.
- Main function of the muscles are to stabilize the scapula for allow to proper shoulder motion.
Superficial muscles :
- These muscles of the shoulder are the large & outer powerful layer of muscles .
- These muscles are the important for the overall function of the shoulder.
- In This group includes the deltoid muscle, which that cover the rotator cuff muscles.
Bursa of the shoulder :

- Bursa is a pillow-like sac which is filled with a small amount of the fluid.
- Plural bursae is reduce the friction & allow the smooth glide between the two firm structures, such as bone and tendon or bone and muscle.
- In human body are 50 bursa in the 50 the largest is the subacromial bursa which is under the acromion of the shoulder.
- Subacromial bursa & subdeltoid bursa which is under the deltoid muscle are often considered as one structure.
- This bursa is separate the rotator cuff & the deltoid muscle, from the acromion.
Pathology of the Frozen shoulder :
- In this disease process affected the capsule of the anterior-superior joint , the coracohumeral ligament & axillary recess .
- In Patient have to small joint in which is the tight the anterior capsule , the loss of the axillary fold & synovitis [ mild or moderate] but not to actual adhesion.
- Rotator cuff Contracture is also been seen in the Frozen shoulder patients & give to contributes in the decreased range of motion .
- These are continued the disagreement about the underlying pathology such as the an inflammatory condition ,an goneurodystrophic process or fibrosing condition,
Causes of the Frozen shoulder :
- This is occurs when this capsule thickens and tightens around the shoulder joint which is restricted its movement.
- Also the capsule is become to inflamed and scarring develop and the scar formations are called adhesions.
- in Diabetes people Frozen shoulder are occur in people with diabetes.
- Other diseases such as Some additional medical problems which is associated with the frozen shoulder include
- Hypothyroidism , Parkinson’s disease, & cardiac disease.
- Other medical condition like a stroke, or surgery like a mastectomy .
Classification of the Frozen shoulder :

Primary
Secondary
Tertiary
Stages of the Frozen shoulder :

- Freezing stage.
- Any movement of the shoulder causes pain & range of motion of the shoulder starts to become limited.
- Frozen stage.
- Pain is may begin to diminish during this stage & become the shoulder stiff & use of shoulder is also becomes more difficult.
- Thawing stage.
- range of motion of the shoulder begins to improve.
- in this stage some people feel the pain worsens at night and also sometimes disrupting sleep
Symptoms of frozen shoulder :
- Shoulder Pain is usually dull or aching.
- It is typically worse in early morning .
- It is usually located over the outer shoulder area & sometimes the upper arm.
- Main symptoms of the frozen shoulder is pain and stiffness which is make it difficult or impossible to move the shoulder.
- Swelling are present in the frozen shoulder .
- Patient feel difficulty in the daily routine and also reduce the Range of Motion (ROM) of the shoulder.
- Sometimes Chest pain is also associated symptom’s
- High level of Sugar – Diabetes (Associated Symptom’s)
Diagnosis of frozen shoulder :
Physical Examination :
- After discuss the symptoms and medical history, the physiotherapist examine the shoulder.
- Physiotherapist will move the shoulder carefully in all directions to see of the shoulder movement ROM in frozen shoulder
- ROM is limited and patient feel pain during the motion .
- After active movement physiotherapist perform the passive movement [ means some stretch give to patient after their active ROM ]
- In frozen shoulder people have limited range of motion both actively and passively.
Imaging Tests :
- Other test are help to doctor for rule out other causes of stiffness and pain include:
- X-rays
- structures [ Dense ] such as bone .
- X-rays are show the other problems in the shoulder, like as arthritis.
- Ultrasound and Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI)
- These studies are create the better image of the soft tissues.
- It is not required for the diagnose of the frozen shoulder, but it is help to identify the other problems in the shoulder, such as a torn of the rotator cuff.
Risk factors of the frozen shoulder :
- Some factors is increase the risk of developing the frozen shoulder.
Age and sex :-
- In age Adults , between 40 and 60 years of the people .
- Particularly women are more affected than the men in the frozen shoulder.
Reduced mobility or Immobility :-
- Which People who have prolonged immobility or reduced mobility of the shoulder , it is the higher risk to develop the frozen shoulder.
- Recent shoulder injury
- Immobility is the result of the many factors such as including:
- Recovery from the surgery
- injury of the rotator cuff
- Broken arm
- Stroke
Systemic diseases :-
- Which People who have some diseases appear to develop frozen shoulder.
- Diseases that increase the risk are includes:
- Cardiovascular disease
- Diabetes
- hyperthyroidism
- hypothyroidism
- Parkinson’s disease
- Tuberculosis
- Shoulder injury such as direct impact, dislocation , FOOSH
- A vascular necrosis
- Metastatic disease
Treatment :
Frozen Shoulder treatment are mainly symptomatic Medical treatment and Physiotherapy treatment and exercise are helpful in recovering frozen Shoulder, if Medical and Physiotherapy treatment and exercise fails, Surgical treatment are the last option to select.
Before surgery under anesthesia joint mobilization is also preferred option.
Medical treatment :
- Non-steroidal anti-inflammatory medicine (NSAIDs)
- Drug such as the aspirin and ibuprofen
- It is used to for reduce pain and swelling.
- symptomatic other related medicine eg. Manage Diabetes and Chest pain if present.
- A corticosteroid injection :-
- It is give in the shoulder joint for reduce the pain and improve the range of motion.
- Joint distension
- In this treatment inject sterile water into the shoulder capsule for stretch it.
- It is help to move the shoulder easily.
Surgery of the frozen shoulder :
- Surgical treatment of a frozen shoulder is also known as the arthroscopic capsular release.
- In this surgery where the small camera is inserted into the shoulder joint.
- Through the small incisions of other , small instruments is also inserted to the treat problem.
- In the frozen shoulder, the problem is that thickened & tight capsule of the shoulder .
- So that the treatment is that to cut the tight capsule for allow to the joint for freedom of the mobility.
- Instruments is that inserted to release to capsule around the shoulder socket.
- In Sometimes patients will give to the arm special splint for keep to the capsule of the shoulder stretched.
- Most commonly physiotherapy will start immediately after the surgery for ensure to scar tissue not to start to re-form around the joint.
Alternatives to Arthroscopic Release :
Nonsurgical Treatment:
- Patients have to try the nonsurgical treatment for the frozen shoulder before consider any invasive treatments.
- Many patients is not realize the length of time of the frozen shoulder is persist, and the fact is that this treatment may take 12 to 18 months before symptoms resolve.
- So that most of surgeons is not consider to this treatments to fail to unless they have been try for the many months.
Manipulation Under Anesthesia:
- It is Perform to less common
- It is the passive stretching of the shoulder while the patient a sleep.
- Advantage = it is give to a much better stretch to joint capsule, but many complications.
- Pain is feel after that the procedure & when the pushed forcefully, it is possible to bones to break or tear to under excessive force.
Open Capsular Release:
- It is a much less common perform surgical procedure.
- This treatment is such as the arthroscopic procedure, the capsule of shoulder is divided, & the surgeon creating an open
- Incision to see inside the shoulder.
A corticosteroid injection :
It is give in the shoulder joint for reduce the pain and improve the range of motion.
- Joint distension :
- In this treatment inject sterile water into the shoulder capsule for stretch it.
- It is help to move the shoulder easily.
Acupuncture of the frozen shoulder :

- In this involve the inserting extremely fine needles in the skin at specific points on the body.
- This needles remain in place for 15 to 40 minutes.
- During the time needles to moved or manipulated.
- Because to needle is hair thin & flexible and insert superficially .
- Most of this treatment is relatively painless.
Massages for a frozen shoulder :
- Physiotherapist apply to appropriate massages and stretches to treat the shoulder.
- This massage is apply them correctly.
- If apply incorrectly, massages cause the further injury.
Foam roller underarm massage :-

- Place the foam roller under the underarm of the affected arm.
- Rest the arm on the floor.
- Lengthen the arm.
- Gently roll back over the foam roller.
- Continue for the up to 1 minute.
Foam roller shoulder massage :-

- Place the foam roller under the underarm of the affected arm.
- Lengthen the arm and keep the hand of the affect arm extended upward.
- Roll back and forth a few times.
- self-massage Simply .
- Use the opposite hand to massage the affected shoulder & arm.
- Focus on the any sensitive areas.
- Gently move the affected arm by massage on shoulder & arm.
Physiotherapy Treatment :
Physiotherapy treatment mainly pain relieving electrotherapy modalities and exercise to improve Range of motion and Stretching of Tight muscles around shoulder area and Strengthening of weak muscles.
Modalities for frozen shoulder :
- TENS = Trans-cutaneous Electrical Nerve Stimulation
- IFT = Inferential Therapy
- SWD = Shortwave Diathermy
- IR = Infrared radiation
- HOT PACK
- This modal its is applied to patient for the pain relief .
- In acute stage applied for pain relief.
- SWD and IR is also applied for the reduce the stiffness .
- All machine is applied to 10 minutes .
- All machine is applied before exercise .
- Hot pack is applied to after exercise for pain relief .
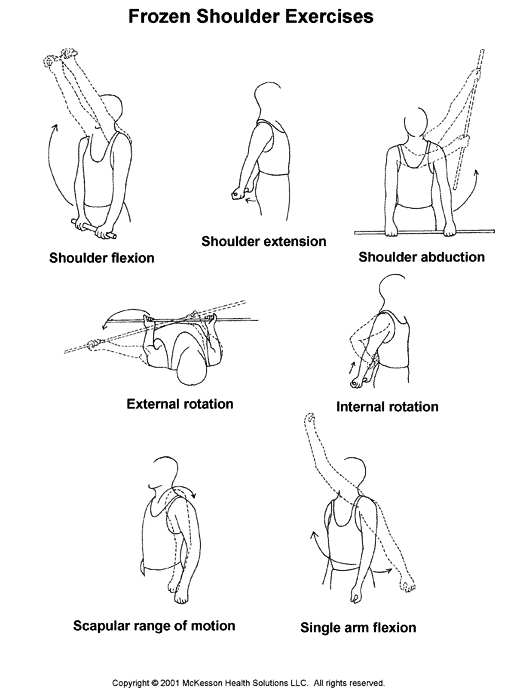
Stretching exercise of the frozen shoulder :
Pendulum stretch :-

- This exercise is doing first.
- Relax the shoulders .
- Stand or lean over slight and allow to affected arm to hang down.
- The arm Swing in the small circle — about the foot diameter.
- Perform the 10 repetition in each direction, once a day.
- When the improve in symptoms , increase the swing diameter, but not to force it.
- If the patient ready for more circle , then increase the stretch with hold light weight for the swinging arm.
Towel stretch :-
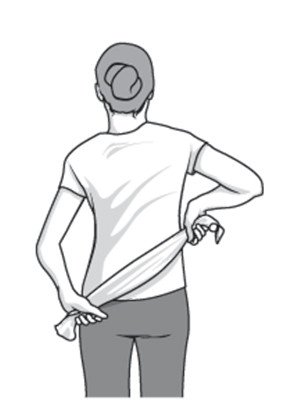
- Hold the three-foot-long towel in the one end of the behind the back and hold the opposite end with the other hand.
- The towel is hold in the position of horizontal .
- Use the good arm for pull the affected arm upward and stretch it.
- It is also perform in an advance version of the exercise with the towel drape over the good shoulder.
- The bottom of the towel is hold in the affected arm & pull the hand toward the lower back with the unaffected arm.
- This exercise is perform to 10 to 20 times per day.
Finger walk :-
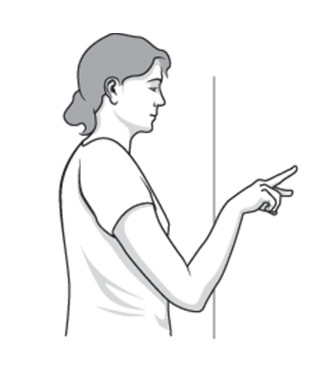
- Face the wall three-quarters of arm’s length .
- Reach out & touch the wall at side of the waist level with the fingertips of the affected arm.
- With the elbow slightly bent, slowly walk to fingers up the wall, like as spider, until the raised the arm as far as comfortable. the finger only the work, not the shoulder muscles.
- Slowly down the lower arm & repeat.
- Perform the exercise 10 to 20 times per day.
Cross-body St-reach Sit and stand :-
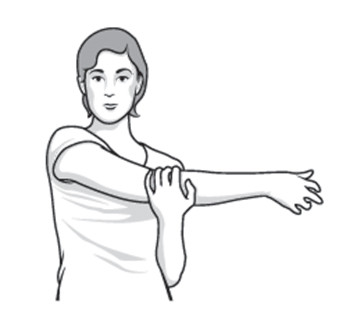
- Use the good arm for lift the affected arm at the elbow & bring the arm up and across the body,
- exerting gentle pressure for stretch the shoulder.
- this stretch is hold for 15 to 20 seconds.
- this exercise is repeat 10 to 20 times per day.
Armpit stretch :-

- Use the good arm, lift with the affected arm about breast-high.
- Gently bend the knees and open up the armpit.
- Dee pend the knee bend slightly, gently stretch armpit .
- With the each knee bend and stretch a little further, but not to force it.
- Do this exercise 10 to 20 times each day.
Outward rotation :-
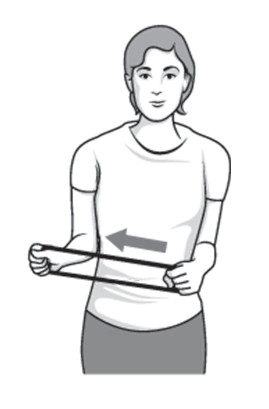
- Hold the rubber exercise band between the hands with the elbows at a angle of 90-degree close to the sides.
- Rotate to lower part of the affected arm for outward to two or three inches , hold for five seconds.
- Repeat this exercise 10 to 15 times, one time in day.
Inward rotation :-
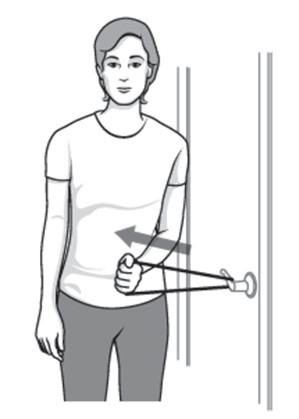
- Stand to the closed door and hook the one end of the rubber exercise band around to doorknob.
- Hold the other end in the hand of the affected arm, holding the elbow at a angle of 90-degree.
- Pull the band toward the body 2 or 3 inches and hold for 5 seconds.
- Repeat this exercise 10 to 15 times,one time in day.
Exercise of the frozen shoulder :
Shoulder Passive ROM Exercises :-
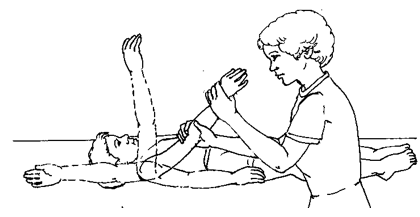
- This is used for the increase to ROM of shoulder .
- This exercise is perform with the help of other patient or therapist .
- This exercise perform in supine position .
- Do the movement of the shoulder [ flexion,exertion , abduction, addcation internal and external rotation ].
- End of the range apply gentle stretch to in every movement .
- Repeat this exercise for 10 times in one session and perform 3 times in a day .
Shoulder Active ROM Exercises :-

- This is used for the increase to ROM of shoulder and maintain the ROM .
- This exercise is perform patient on self .
- This exercise perform in supine or sitting position .
- Do the movement of the shoulder [ flexion, exertion , abduction, addcation ,internal and external rotation ]
- Repeat this exercise for 10 times in one session and perform 3 times in a day .
Isometric Shoulder Exercises :-

- This is used for the increase to ROM of shoulder and pain relief
- This exercise is perform with the help of other patient or therapist .
- This exercise perform in supine position .
- Do the movement of the shoulder [ flexion,exertion , abduction, addcution internal and external rotation ] And press in the every movement for not to low the movement .
- Repeat this exercise for 10 times in one session and perform 3 times in a day .
Scapular Stabilization Exercises :-
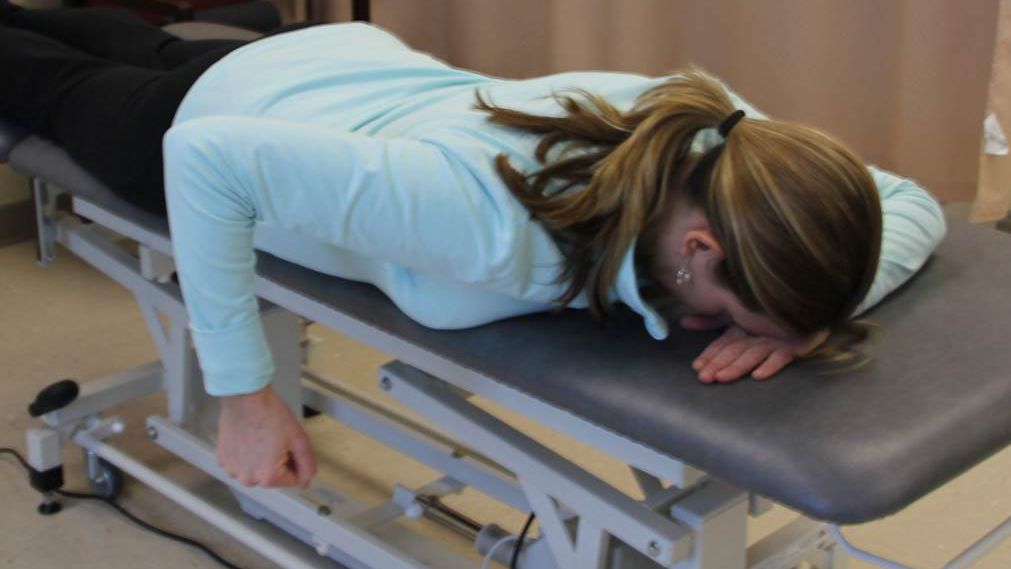
- This is used for scapula stabilization
- This exercise is perform with the help of other patient or therapist and also perform .
- This exercise perform in prone position .
- Exercise in I, T, and Y pattern .
- Repeat this exercise for 10 times in one session and perform 3 times in a day .
Wand exercise :-
- This is used for the increase to ROM of shoulder
- This is active assisted exercise
- This exercise is perform actively and with the help of stick .
- This exercise perform in supine , standing or sitting position .
- Do the movement of the shoulder [ flexion,exertion , abduction, addcution internal and external rotation ] with help of the both hand by stick .
- Repeat this exercise for 10 times in one session and perform 3 times in a day .
Pully exercise :-

- This is used for pain relief .
- This exercise is perform patient oneself .
- This exercise perform in sitting position .
- Hold the hook of the pully in both the hand .
- Do the movement in slowly like as pully .
- Repeat this exercise for 10 times in one session and perform 3 time in a day .
Frozen shoulder exercises video :
Yoga exercise of the frozen shoulder :
- Paschim Namaskarasana
- Ardha Matsyendrasana
- Bhujangasana
- Halasana
- Dhanurasana
- Garudasana
- Ustrasan
- Purvottanasana
Paschim Namaskarasana (Reverse Prayer Pose):-

- Start with the Tadasana [ keep hands straight hanging on either side. Relax the shoulders & bent down the knees a little. ]then , stretch the arms backward and join the palm together like in a prayer pose.
- When gradually inhaling press the palm of the inner surface towards the spine & hold this position for a the few seconds.
- Now the gradually exhale & move the palms downwards & come back to the starting pose.
- Repeat the exercise 4-5 times for better results.
Ardha Matsyendrasana (Sitting Half Spinal Twist):-

- Straight Sit with the legs stretched out & feet together.
- Bend the right leg & place to heel of the right foot beside the left hip.
- Then, take to left leg over the right knee.
- Place the right hand on the left foot & the left hand behind you.
- Twist to waist, shoulders, & neck to the left & look over to left side shoulder.
- Hold this position & continue breathing in and out gently.
- Come back to the original starting position Slowly
- Repeat this yoga in the same manner on the other side.
Bhujangasana (Cobra Pose):–

- Lie flat on the stomach & place the head on the ground.
- Keep both the hands on either side of the shoulders.
- Slowly, put pressure on the palm & lift the body from the torso while stretching the back & belly muscles.
- Straight out the arms and keep to shoulder blades pressed against the back.
- Fix the gaze at the point on ceiling & hold the position for 15-30 seconds .
- Then exhale and return to the starting position.
Halasana (Plow Pose):-

- Lying on the back, raise both legs above to stomach.
- Bend to body & try to extend the legs above to head and touch the ground with the toes.
- Hold the posture for 10-15 seconds, relax for a minute, and repeat this exercise.
Dhanurasana (Bow Pose):-

- Lie flat on stomach and raise both legs & torso backward.
- Extend the arms backward & grasp both to feet with the hands.
- Hold the position for as long as possible & do the inhaling normally.
- Return to starting position & repeat this exercise for 5-6 times.
Garudasana :-

Stretch to shoulders & upper back .
Loosen to shoulder & release to any tension in them .
Ustrasana :-

- Stretch & strengthening of the front the body .
- It Relieve to the body of lower backache .
Purvottanasana :-

- Stretch to the shoulder , chest & neck
- Strength to the shoulder, back, ankle & wrist





8 Comments