Extensor Pollicis Brevis Muscle
Table of Contents
Description
The extensor pollicis brevis muscle is a skeletal muscle situated in the hand that is responsible for extending the thumb at the carpometacarpal joint (base of the thumb). It arise from the distal 3rd of the posterior surface of the ulna bone and the interosseous membrane and inserts into the base of the proximal phalanx of the thumb.
The extensor pollicis brevis is a short, tiny muscle that joins the thumb’s proximal phalanx to the posterior surface of the radius. It is in the forearm’s posterior compartment. It is one of the deep extensors of the hand, along with the supinator, abductor pollicis longus, extensor pollicis longus, and extensor indicis muscles.
The primary function of this muscle, along with that of its long counterpart, the extensor pollicis longus muscle is to develop the thumb at the metacarpophalangeal and carpometacarpal joints.
Origin of Extensor Pollicis Brevis Muscle
- The lower third of the posterior part of the ulna bone and the interosseous membrane act as the extensor pollicis brevis muscle’s origin.
- Particularly, it arises from the posterior level of the body of the ulna bone, the adjacent interosseous membrane, and the dorsal border of the radius bone.
Insertion
- The extensor pollicis brevis muscle runs into the base of the proximal phalanx of the toe.
- More particularly, it fix to the base of the distal phalanx of the thumb through a tendon that travels through a groove on the dorsum of the radial styloid process, crosses the wrist joint, and passes via the extensor retinaculum.
- Finally, the extensor pollicis brevis tendon connected to the base of the proximal phalanx of the thumb, helping to thumb extension and abduction at the carpometacarpal joint.
Relations
- The extensor pollicis brevis, or deep thumb extensor, is very near to the extensor digitorum muscle.
- It is situated posterolateral to the extensor pollicis longus muscle and continues to move forward within the abductor pollicis longus muscle.
- The outer border of the triangular depression on the lateral part of the wrist, known as the anatomical snuffbox, is generated by the tendon of the extensor pollicis brevis and the tendon of the abductor pollicis longus.
- The tendon of the extensor pollicis longus and the styloid process of the radius, both create the medial lines and proximal lines of this space.
- The radial artery goes via the snuffbox among other structures. due to this being the most usual location for palpating the radial pulse, it is an important clinical point.
Innervation
The posterior interosseous nerve, which prolongs a profound radial nerve branch with root values C7 and C8, innervates the extensor pollicis brevis.
Blood supply
- The extensor pollicis brevis gets their blood via the posterior interosseous artery and the foremost interosseous artery’s perforating segment, which are portions of the normal interosseous artery.
- The typical interosseous artery quickly emerges under the ulnar artery’s tuberosity.
The function of EPB Muscle
- Both the extensor pollicis brevis and the extensor pollicis longus are responsible for controlling the thumb’s extension in the first metacarpophalangeal joint.
- Additionally, it allows the CMP joint to straighten the thumb.
- Due to the reason that it allows the letting go of an object, this motion is essential to the anatomy of the grasp.
- Additionally, when the extensor pollicis brevis is across the wrist, it contributes to the joint’s extension and abduction.
Clinical relevance
- The tendons of the EPB and APL are protected in a normal sheath at the dorsum of the wrist.
- The friction in the middle of the thumb and wrist may be improved by powerful or repetitive movement, which in turn may cause inflammation in the joint tendon.
- De Quervain’s Tenosynovitis is a condition that causes pain and then goes to the forearm’s proximal side from the wrist’s radial aspect.
Assessment
- De Quervain’s Tenosynovitis may be diagnosed using the Finkelstein Test:
- The therapist holds the patient’s thumb with one hand and holds the patient’s forearm in an equal position with the other.
- The examiner then stretches the longitudinally on the patient’s thumb, making a minor ulnar deviation at the wrist.
- A positive test indicates expanded torment at the spiral styloid process.
Extensor pollicis brevis stretching
Thumb stretch
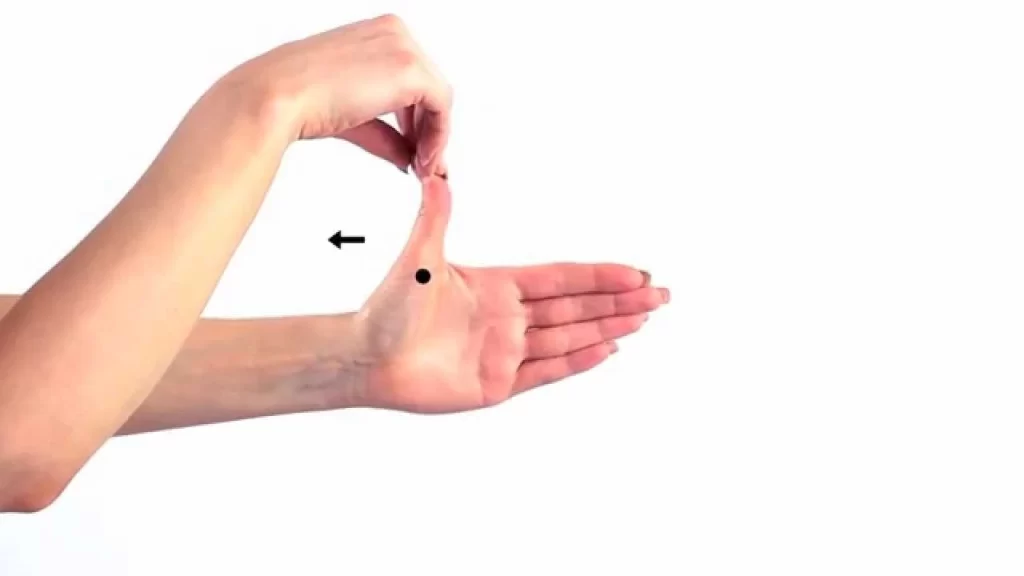
- To stretch the extensor pollicis brevis starting with the thumbs facing upward, close the fist around the thumb.
- By tilting the fist downward, gently enter the ulnar deviation in a pain-free range.
- Keep stretching for up to 30 seconds.
Extensor pollicis brevis strengthening exercise
Thumb isometrics

- This exercise may assist to strengthen the thumb muscles in many various ways.
- To get started, use the other hand to apply pressure in both directions while making a fist with the thumb.
- Keeping up an upstanding thumb to oppose the tension, and hold for 10 to 15 seconds.
Finger extension with band
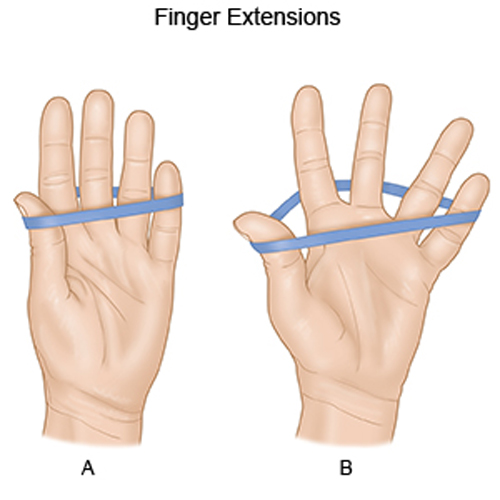
- This is an exercise for reinforcing the finger extensors.
- Usually, at the level of the 3rd knuckle, circle a hair or adaptable band surrounding the back of the fingers.
- To stretch the band, extend the fingers and hold them there for up to 10 seconds.
- Back to neutral after each repetition to complete it.
Finger yoga
- This is an exercise for reinforcing the finger extensors.
- Place the palm on a table, work surface, or another level place to get everything moving.
- Elevate the tiny, middle, and thumb off the bottom while keeping up the planted position of the other 2 fingers.
- Stand firm on this footing for as long as 10 seconds as a person attempts to raise the raised fingers as high as might be expected.
- To back to nonpartisan and substitute positions, raise the 2nd and 4th fingers as high as possible while remaining down.
- Hold 10 seconds once more.
- To complete the repetition, back to neutral and recount as crucial.
FAQ
Extensor pollicis longus straighten the terminal phalanx of the thumb. The abductor pollicis brevis and adductor pollicis both affixes to the extensor pollicis longus tendon and may straighten the thumb’s interphalangeal joint to the neutral position.
This muscle straightens the thumb at the metacarpophalangeal and carpometacarpal joints. It is also a minor abductor of the thumb.
Put a finger from the other hand on the back of the thumb in the middle of the knuckle and the end joint of the thumb. Try to move the thumb away from you towards the outside, using the other hand to resist the movement. Try to hold this position without any kind of movement, making sure that you keep the tip of the thumb bent.
Although the isolated extensor pollicis longus (EPL) rupture is induced by fractures and chronic tendonitis rupture of the extensor pollicis brevis (EPB) tendon is very infrequent.
The EPL may be tested by putting the patient’s hand flat on a table and telling the patient to lift the thumb toward the 2nd metacarpal; the EPL may be palpated toward the ulnar side of the snuffbox if it is present. The intent of this article is to describe an alternative method to assess for EPL rupture. might be expected. To back to nonpartisan and substitute positions, raise the 2nd and 4th fingers as high as possible while remaining down. Remain steadfast on this foundation for just 10 seconds once.