Dorsal Radioulnar Ligament
Table of Contents
Introduction
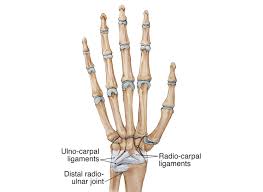
The dorsal radiocarpal ligament is a ligament located in the wrist joint that connects the radius bone to the carpal bones. It helps to stabilize the joint during movements such as wrist extension and flexion.
Injuries to this ligament can occur from sudden trauma or repetitive stress, leading to symptoms such as pain, swelling, and limited range of motion.
Treatment for dorsal radiocarpal ligament injuries may include rest, immobilization, physical therapy, or surgery depending on the severity of the injury. Proper technique and strengthening exercises can also help prevent these types of injuries.
Structure of the Dorsal Radioulnar Ligament
The dorsal radiocarpal ligament is a strong band of fibrous tissue that runs from the distal end of the radius bone to the proximal row of carpal bones in the wrist joint. It is one of the primary ligaments that helps to stabilize the joint during movements such as wrist extension and flexion.
The ligament is made up of several fibers that are arranged in a parallel fashion, running from the radius bone to the carpal bones. These fibers are tightly packed together and are anchored to the bone by small fibers called Sharpey’s fibers, which help to provide additional strength and stability to the ligament.
The dorsal radiocarpal ligament is divided into two parts: the superficial and deep portions. The superficial portion is located on the top surface of the wrist joint and is responsible for stabilizing the joint during wrist extension. The deep portion is located underneath the superficial portion and is responsible for stabilizing the joint during wrist flexion.
In addition to its primary role in stabilizing the wrist joint, the dorsal radiocarpal ligament also plays a role in transmitting forces between the radius bone and the carpal bones. This helps to distribute forces evenly throughout the joint, reducing the risk of injury.
Overall, the dorsal radiocarpal ligament is a crucial component of the wrist joint, providing stability and support during a wide range of movements. Injuries to this ligament can be painful and debilitating, making it important to seek prompt medical attention if you experience any symptoms of injury.
Functions of the Dorsal Radioulnar Ligament
The dorsal radiocarpal ligament has several important functions in the wrist joint. These include:
- Stabilization: The primary function of the dorsal radiocarpal ligament is to provide stability to the wrist joint. It helps to hold the radius bone in place and prevents it from moving too far away from the carpal bones. This is important during movements such as wrist extension and flexion, which can put a lot of stress on the joint.
- Force transmission: The dorsal radiocarpal ligament also plays a role in transmitting forces between the radius bone and the carpal bones. This helps to distribute the forces evenly throughout the joint, reducing the risk of injury.
- Joint alignment: The ligament helps to maintain proper alignment of the wrist joint. This is important for ensuring that the bones move smoothly against each other during movements, reducing the risk of wear and tear on the joint.
- Joint lubrication: The dorsal radiocarpal ligament also plays a role in lubricating the joint. It helps to distribute synovial fluid throughout the joint, which acts as a lubricant and reduces friction between the bones.
Overall, the dorsal radiocarpal ligament is a crucial component of the wrist joint. It helps to provide stability and support during a wide range of movements, while also helping to distribute forces evenly throughout the joint and maintain proper alignment. Injuries to this ligament can be painful and debilitating, making it important to seek prompt medical attention if you experience any symptoms of injury.
Blood supply of the Dorsal Radioulnar Ligament
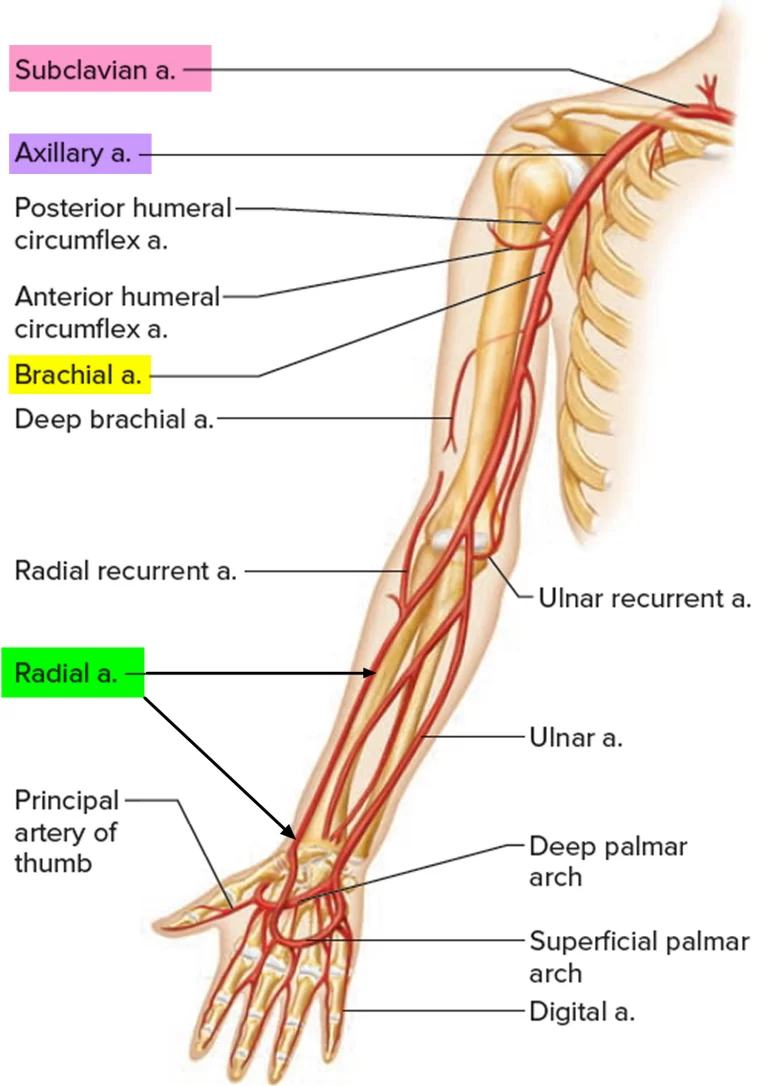
The dorsal radiocarpal ligament receives its blood supply from several sources. The main artery that supplies the wrist joint is the radial artery, which runs along the outside of the wrist. The radial artery gives off several branches that supply blood to the ligaments and other structures in the wrist, including the dorsal radiocarpal ligament.
In addition to the radial artery, the dorsal radiocarpal ligament also receives blood from the ulnar artery, which runs along the inside of the wrist. The ulnar artery gives off several branches that supply blood to the ligaments and other structures on the inside of the wrist, including the palmar radiocarpal ligament.
The blood supply to the dorsal radiocarpal ligament is important for maintaining its health and function. Without adequate blood flow, the ligament may become weakened or damaged, which can lead to instability or pain in the wrist joint. Injuries to the ligament may also disrupt the blood supply, which can further impair its ability to heal and recover.
Overall, the blood supply to the dorsal radiocarpal ligament is an important aspect of its function and health. Proper blood flow helps to ensure that the ligament remains strong and stable, reducing the risk of injury and promoting optimal joint function.
Injuries of the Dorsal Radioulnar Ligament
The dorsal radiocarpal ligament can be injured due to various activities that involve repetitive or sudden movements of the wrist joint. Some of the common activities that can cause injuries to this ligament include:
- Sports: Athletes who participate in sports such as tennis, basketball, and volleyball are at a higher risk of developing dorsal radiocarpal ligament injuries. These sports require repetitive movements of the wrist joint, which can strain the ligament and lead to overuse injuries.
- Manual labor: People who perform manual labor jobs such as construction workers, carpenters, and mechanics are also at a higher risk of developing dorsal radiocarpal ligament injuries. These jobs require repetitive use of the wrist joint, which can lead to overuse injuries.
- Falls: A fall onto an outstretched hand can cause a sudden and forceful movement of the wrist joint, which can result in a sprain or tear of the dorsal radiocarpal ligament.
- Car accidents: In a car accident, the wrist joint can be forcefully twisted or bent, leading to a sprain or tear of the dorsal radiocarpal ligament.
- Arthritis: Arthritis is a type of condition that causes inflammation and damage to the joints. Over time, arthritis can weaken the dorsal radiocarpal ligament and increase the risk of injury.
In conclusion, activities that involve repetitive or sudden movements of the wrist joint, falls, car accidents, and arthritis can all lead to injuries to the dorsal radiocarpal ligament. It is important to seek medical attention if you experience any symptoms such as pain, swelling, or instability in the wrist joint after engaging in these activities.
Symptoms of the Dorsal Radioulnar Ligament Injury
The symptoms of dorsal radiocarpal ligament injuries can vary depending on the severity of the injury. Some common symptoms include:
- Pain: Pain is the most common symptom of a dorsal radiocarpal ligament injury. The pain may be sharp or dull and can be felt in the wrist joint or the back of the hand.
- Swelling: Swelling is another common symptom of a dorsal radiocarpal ligament injury. The swelling may be mild or severe and can make it difficult to move the wrist joint.
- Stiffness: Stiffness in the wrist joint is another symptom of a dorsal radiocarpal ligament injury. The stiffness may make it difficult to move the wrist joint or perform daily activities.
- Instability: Instability in the wrist joint is a common symptom of a severe dorsal radiocarpal ligament injury. The instability may cause the wrist joint to feel loose or wobbly, and it may be difficult to grip or hold objects.
- Bruising: Bruising around the wrist joint may occur in some cases of dorsal radiocarpal ligament injuries. The bruising may be mild or severe and can last for several days.
- Numbness or tingling: In some cases, a dorsal radiocarpal ligament injury can cause numbness or tingling in the fingers or hand. This is due to pressure on the nerves that run through the wrist joint.
If you experience any of these symptoms after engaging in activities that can cause dorsal radiocarpal ligament injuries, it is important to seek medical attention. Early treatment can help prevent further damage to the ligament and promote faster healing.
Diagnosis of the Dorsal Radioulnar Ligament Injury
The dorsal radiocarpal ligament is a strong band of tissue that connects the radius bone in the forearm to the carpal bones in the wrist. It plays an important role in stabilizing the wrist joint and allowing for smooth movement of the hand and wrist.
Diagnosis of a dorsal radiocarpal ligament injury typically involves a physical examination, medical history review, and imaging tests. During the physical examination, a doctor will assess the wrist joint for pain, swelling, stiffness, and instability. They may also perform specific tests to evaluate the strength and range of motion of the wrist joint.
Medical history review involves discussing the patient’s symptoms, how the injury occurred, and any previous injuries or medical conditions that may be relevant.
Imaging tests such as X-rays, MRI, or CT scans may be ordered to confirm the diagnosis and assess the severity of the injury. These tests can also help identify any associated injuries such as fractures or dislocations.
Treatment of the Dorsal Radioulnar Ligament Injury
Conservative treatment
Conservative treatment of a dorsal radiocarpal ligament injury involves non-surgical methods to manage pain, reduce swelling, and promote healing. The goal of conservative treatment is to allow the ligament to heal naturally without the need for surgery.
The following are some of the conservative treatment options for a dorsal radiocarpal ligament injury:
- Rest: Resting the wrist joint is essential to allow the ligament to heal. The patient may be advised to avoid activities that put stress on the wrist joint, such as heavy lifting or repetitive motions.
- Ice: The application of ice to the injured area can help in reducing swelling and pain. The patient may be advised to apply ice packs for 15-20 minutes at a time, several times a day.
- Compression: Wrapping the wrist with an elastic bandage can help in reducing swelling and provide support to the joint.
- Elevation: Elevating the wrist above the heart level can also help reduce swelling.
- Pain relievers: Over-the-counter pain relievers such as acetaminophen or ibuprofen may be recommended to manage pain and inflammation.
- Physical therapy: A physical therapist can design an exercise program to help restore strength and mobility to the wrist joint. The exercises may involve range-of-motion exercises, strengthening, and stretching exercises.
- Immobilization: In some cases, the patient may need to wear a cast or splint to immobilize the wrist joint and allow the ligament to heal properly.
It is important to follow the doctor’s instructions carefully and attend all follow-up appointments to ensure proper healing of the ligament. If conservative treatment does not provide relief, surgical intervention may be necessary.
Physiotherapy treatment
Physiotherapy treatment of a dorsal radiocarpal ligament injury aims to restore the normal function of the wrist joint and promote the healing of the injured ligament. The treatment plan may vary depending on the severity of the injury and individual needs of the patient.
The following are some of the physiotherapy treatments that may be used for a dorsal radiocarpal ligament injury:
Range-of-motion exercises: These exercises use to improvise the flexibility and mobility of the wrist joint. The physiotherapist may guide the patient through various exercises, such as wrist circles, wrist flexion and extension, and wrist rotations.
Strengthening exercises: These exercises aim to improve the strength of the muscles that support the wrist joint. The physiotherapist may recommend exercises such as wrist curls, grip strengthening, and resistance band exercises.
Manual therapy: This involves hands-on techniques such as stretching, massage, and joint mobilization in order to help decrease pain and improve joint mobility.
Modalities: Various modalities such as heat therapy, cold therapy, ultrasound, and electrical stimulation may be used to reduce pain, swelling, and inflammation.
Functional training: This involves specific exercises that mimic the patient’s daily activities and help them regain their functional abilities.
Education: The physiotherapist may provide education on proper posture, ergonomics, and techniques to prevent further injury.
Home exercise program: The patient may be given a home exercise program to continue their rehabilitation outside of the physiotherapy sessions.
Overall, physiotherapy treatment can help reduce pain, restore function, and promote the healing of a dorsal radiocarpal ligament injury. It is important to follow the physiotherapist’s instructions carefully and attend all appointments to ensure optimal recovery.
Risk factors
The dorsal radiocarpal ligament (DRL) is a crucial structure that connects the radius bone of the forearm to the carpal bones of the wrist. It provides stability and support to the wrist joint during movement. Injuries to the DRL can occur due to various risk factors, including:
- Trauma: The most common cause of DRL injuries is trauma to the wrist, such as a fall or a direct blow to the wrist. The impact can cause the ligament to stretch or tear, leading to pain, swelling, and instability in the wrist joint.
- Sports activities: Athletes who participate in sports that involve repetitive wrist movements, such as tennis, golf, or gymnastics, are at an increased risk of developing DRL injuries. These activities can put excessive stress on the ligament, leading to overuse injuries.
- Age: As we age, our ligaments become weaker and less elastic, making them more prone to injury. Older adults are at an increased risk of developing DRL injuries due to age-related changes in their ligaments.
- Occupational hazards: People who perform manual labor or work in jobs that involve repetitive wrist movements, such as construction workers or assembly line workers, are at an increased risk of developing DRL injuries.
- Joint hypermobility: People with joint hypermobility syndrome have loose and unstable joints, making them more prone to ligament injuries. They may be more susceptible to DRL injuries due to their underlying condition.
- Genetics: Some people may have a genetic predisposition to ligament injuries, including DRL injuries. This may be due to inherited connective tissue disorders that affect the strength and elasticity of ligaments.
In conclusion, DRL injuries can occur due to various risk factors, including trauma, sports activities, age, occupational hazards, joint hypermobility, and genetics. Understanding these risk factors can help individuals take preventive measures and seek timely medical attention to prevent or treat DRL injuries.
How to prevent injuries of the Dorsal Radioulnar Ligament?
Preventing injuries of the dorsal radiocarpal ligament involves taking steps to reduce the risk factors that can lead to these injuries. Here are some strategies that may help prevent dorsal radiocarpal ligament injuries:
- Warm-up and stretching: Before engaging in activities that involve the wrist joint, it is important to warm up and stretch the muscles and ligaments in the area. This can help in improving flexibility and reducing the risk of injury.
- Proper technique: Using proper technique and mechanics during activities that involve the wrist joint can help reduce the stress placed on the ligaments. It is important to use good posture and maintain a neutral wrist position when performing tasks such as typing or lifting.
- Avoid overuse: Engaging in repetitive activities that place excessive strain on the wrist joint can increase the risk of injury. It is important to take breaks and vary activities to avoid overuse.
- Wear protective gear: If participating in sports or other activities that involve impact or falls, wearing protective gear such as wrist guards can help reduce the risk of injury.
- Maintain good overall health: Maintaining good overall health through regular exercise, a balanced diet, and adequate sleep can help improve joint health and reduce the risk of injury.
- Take medical attention for pain or discomfort: If experiencing pain or discomfort in the wrist joint, it is important to seek medical attention and avoid activities that exacerbate the symptoms. Ignoring pain or discomfort can lead to further injury and complications.
By following these strategies, individuals may be able to reduce their risk of dorsal radiocarpal ligament injuries. It is important to consult with a healthcare provider for personalized advice on injury prevention.
FAQ
The dorsal radiocarpal ligament is a strong band of connective tissue that connects the radius bone of the forearm to the carpal bones of the wrist on the backside (dorsal) of the wrist joint.
The dorsal radiocarpal ligament helps to stabilize the wrist joint and prevent excessive backward (extension) movement of the wrist.
Symptoms of a dorsal radiocarpal ligament injury may include pain, swelling, stiffness, weakness, and limited range of motion in the wrist joint.
A dorsal radiocarpal ligament injury can be diagnosed through a physical examination, imaging tests such as X-rays or MRI, and possibly an arthroscopy procedure.
Treatment for a dorsal radiocarpal ligament injury may include rest, ice, compression, elevation, immobilization with a splint or cast, physical therapy, and in severe cases, surgery.
The healing time for a dorsal radiocarpal ligament injury depends on the severity of the injury and the treatment approach. It may take some weeks to some months for a total recovery.
A dorsal radiocarpal ligament injury can be prevented by maintaining proper form and technique during activities that involve repetitive wrist movements, wearing protective gear during high-risk activities, and performing wrist-strengthening exercises.