De Quervain Tenosynovitis: Cause, Symptoms, Diagnosis, Treatment
Table of Contents
What is a De Quervain’s tenosynovitis?
De Quervain’s tenosynovitis occurs when the 2 tendons around the base of your thumb become swollen.
The swelling causes the sheaths covering the tendons to become inflamed.
This puts pressure on nearby nerves, causing pain and numbness.
Related Anatomy
DQ syndrome affects the extensor pollicis brevis (EPB) tendon and the abductor pollicis longus (APL) tendon. These muscles are located on the back side of the forearm and run to the lateral side of the thumb from a fibrous-osseous tunnel. These tendons are protected by a slippery and thin soft-tissue layer called synovium sheath. This also provides nutrients to the tendons and allows them to slide easily through the sheath that covers them.
The tendons of the abductor pollicis longus and the extensor pollicis brevis are tightly secured against the radial styloid by the overlying extensor retinaculum.
Any thickening of the tendons from acute or repetitive trauma restrains the gliding of the tendons through the sheath.
Efforts at thumb motion, especially when combined with radial or ulnar deviation of the wrist that cause pain and perpetuate the inflammation and swelling.
What are the causes of De Quervain’s tenosynovitis?
hobby or job involves repetitive hand and wrist motions. This is a very common cause of de Quervain’s tenosynovitis.
injury to the wrist.
Scar tissue can restrict the movement of your tendons.
In pregnancy. The hormonal changes that occur during pregnancy can cause de Quervain’s tenosynovitis.
It is also commonly seen with rheumatoid arthritis.
arthritis.
It is most commonly seen in the age group of the 40s to 50s with seen mostly in women as compared to men.
Which Signs and symptoms are seen in De Quervain’s tenosynovitis?
Symptoms are:
- pain at the radial side of the wrist
- Muscle spasms
- tenderness at the base of the thumb
- occasional burning sensation in the hand
- swelling over the thumb side of the wrist
- difficulty gripping with the affected side of the hand.
- The onset is often gradual.
- Pain is made worse by movement of the thumb and wrist, and may radiate to the thumb or the forearm.
Symptoms and pain mostly start suddenly or it may be seen initially with mild pain and gradually worse.
Differential Diagnosis
- Osteoarthritis of the first carpometacarpal joint
- Trigger thumb
- Rheumatoid arthritis
- Wartenberg’s syndrome (superficial radial nerve neuritis)
- Scaphoid or radial styloid fractures
- Intersection syndrome
- Carpal tunnel syndrome
Diagnosis:
Diagnostic test in De’quiveran’s Tenosynovitis:
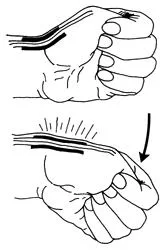
Finkelstein test:
First, you bend your thumb so it rests across your palm. Then you make a fist, closing your fingers over your thumb.
Last, you bend your wrist toward your little finger.
If you have tenderness or pain at the base of your thumb, you probably have de Quervain’s tenosynovitis.
When to contact a doctor?
Contact your Physio or doctor if you are suffering from pain. It mostly recovers with medical and Physiotherapy treatment. If you are not taking proper treatment, it can affect your movement or cause the tendon sheath to burst. Once you recover, you also work on how to prevent it from happening again.
Treatment of DQ tenosynovitis:
NSAIDs (Non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs) are mostly prescribed by your Doctor such as Aceclefenac, and ibuprofen. This helps to relieve pain, swelling, and muscle spasms.
Rest – Avoid activities that are painful and use alternate activities.
Corticosteroid injection is the second option in which injection into the tendon sheath can be effective in relieving the condition by reducing pain, inflammation, and swelling. Mostly one or two injections have been effective in 50 to 80% of patients.
Physiotherapy treatment in De Quervain’s tenosynovitis:
Immobilizing your thumb and wrist, keeping them straight with a splint or brace to help rest your tendons.
Thumb-Spica Splint.

Use a splint 24 hours a day for 4 to 6 weeks.
Apply heat or ice pack to the affected area.
Use of Ultrasound and TENS also helps to relieve pain, swelling, and tenderness over the thumb region.
Deep tissue massage at the thenar muscles can help relax tight muscles that cause pain.
Pain-free gradual strengthening and stretching exercise of the extensor pollicis brevis (EPB) and the abductor pollicis longus (APL).
Avoiding pinching with your thumb when moving your wrist from side to side
NSAID-non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs, such as ibuprofen.
Avoid that activities which cause pain and swelling, especially repetitive hand and wrist motions.
Taping in DQ:
Objective: Inhibit/support
Rest/unload.
Clinical implications :
Dequiveran’s Disease
RSI
Preparation for sport.
Application in DQ’s:
Measure and cut a “I” strip.
Position: Wrist in ulnar deviation and slight flexion.
Thumb in flexion and adduction.
Anchor the long “i” strip over the tip of the thumb and apply the tape along the dorsum of the thumb, continuing along the lateral aspect of the forearm to the course of the muscles.
Surgical Treatment
Surgery is the last option if your symptoms are severe or do not improve with conservative treatment. The aim of surgery is to release the swollen tendon sheath to make more space. The surgeon made a small cut in the sheath near the swollen tendons. This helps to create a space for the tendons to move. This can help to relieve the symptoms of DQ tenosynovitis without affecting the hand/wrist function.
After surgery, you will be required to do physiotherapy treatment and exercise to strengthen your wrist and thumb. This will help for a permanent solution. Once the area has correctly healed and achieve full strength and flexibility of your wrist, you can use your hand and wrist normally without any pain.
FAQs
With proper treatment, you will fully recover from tenosynovitis within 3 to 6 weeks. If you are not treated properly, you are at risk of having the affected joint becoming stiff and having the tendon become permanently restricted. Avoiding painful repetitive movements can also help to relieve tenosynovitis.
DQ surgery is also famously called “De Quervain’s release.” In this surgery, you’ll apply a local anesthetic to numb both your hand and your wrist. The surgeon will release the tendon sheath wrapped around the base of your thumb to relieve both painful friction and pressure.
DQ tenosynovitis is a condition where the wrist muscles tendons and their sheath in your wrist near your thumb get painful, inflamed, and swollen. It is most commonly seen in people doing jobs where repetitive tasks like typing, certain sports, or repeated lifting activity is required.
When you applying a Hot pack can increase blood flow, which may help promote the healing of the tendon. Hot packs also relieve muscle spasms, which can relieve pain and inflammation. It is a natural pain reliever and easy to do at home.




How DQ splint is comes under physiotherapy treatment?