Corrugator supercilii muscle Origin, Insertion, Function, Exercise
Table of Contents
Introduction
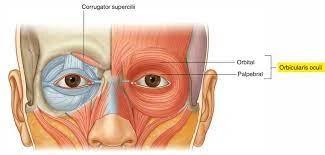
- Corrugator supercilii is a small, pyramidal muscle that belongs to the circumorbital & palpebral group of facial muscles, along with the levator palpebrae superioris & orbicularis oculi muscles. Like other facial muscles, corrugator supercilii is supplied by branches of the facial nerve.
- The corrugator supercilii is a paired muscle located deep to the medial end of each eyebrow. Upon contraction, these muscles draw the 2 eyebrows together medially & inferiorly, thereby producing vertical wrinkles over the glabella & an expression of frowning.
Origin of Corrugator Supercilli:
- The corrugator supercilii originates on the medial orbital rim, near the lacrimal bone. It originates from the medial end of the superciliary arch; & its fibers pass upward & laterally, between the palpebral & orbital portions of the orbicularis oculi muscle, & are attached to the deep surface of the skin, above the middle of the orbital arch.
Insertion of Corrugator Supercilli :
- It inserts on the medial side of the bony orbit, inferior to the corrugator supercilii. In some specimens, it exhibits 2 heads & in others, only one.
Structure & Function
- The corrugator supercilii muscles exist as a pair of small pyramidal muscles that are located deep in the frontal part of the occipitofrontalis & the orbicularis oculi muscles. They originated from the medial supraorbital ridge of the frontal bone. From the medial end of the eyebrow, the corrugator supercilii muscles run laterally and above the orbital rim to become more superficial. They then attach to the dermis of the medial aspect of the eyebrow above the supraorbital margin. The paired corrugator supercilii muscles have2 heads: a transverse head & an oblique head.
- The transverse head originates from the superomedial part of the orbital rim that serves to pull the brows medially while the smaller oblique head travel parallel to the depressor supercilii and serves to depress the medial brow.
- These functions lead to the vertical wrinkling of the supranasal skin of the forehead. Along with the glabellar muscles & procerus, the corrugator supercilii muscles also act as accessory protractors of the upper eyelid that aid to reduce glare under bright sunlight. Additionally, the corrugator supercilii muscles serve as mimetic muscles that contract when one is angered or perplexed & form a major component of the superficial musculoaponeurotic system (SMAS) of the upper part of the face.
- A previous study exhibited that participants who categorized surprised facial expressions as negative exhibited greater corrugator supercilii muscle activity compared to those who viewed them as positive facial expressions. Therefore, corrugator supercilii muscle activity can assist evaluate differences in positivity-negativity bias among different participants.
Relations
- Corrugator supercilii is situated superior to the orbit, extending diagonally over the supraorbital margin & the medial end of the eyebrow. As corrugator supercilii extends superolateral, it is located deep to the orbicularis oculi muscle & the frontal belly of occipitofrontalis, partially blending with both. At its origin point, corrugator supercilii is situated laterally adjacent to the procerus muscle.
Nerve supply :
Facial Nerve (7th Cranial nerve)
- A plexus important from the inferior ramus partly from the middle ramus of the temporal branch of the facial nerve enters the corrugator supercilii muscle in the supraorbital area.
Blood Supply & Lymphatics
- The corrugator supercilii muscles collect blood supply from the supraorbital & supratrochlear arteries of the ophthalmic artery, which is a branch of the internal carotid artery.
- On the right side of the body, the common carotid arteries arise from the brachiocephalic trunk, & on the left side of the body, they come from the aortic arch. In the neck, at the upper margin of the thyroid cartilage, each common carotid artery passes within the carotid sheath & bifurcates into the internal & external carotid arteries.
- In the temporal bone, the internal carotid artery enters the skull through the carotid canal & divides into the ophthalmic artery, which travels through the orbit through the optic canal. Inside the orbit, the ophthalmic artery split into more branches, adding the supraorbital artery, supratrochlear artery, lacrimal artery, central retinal artery, ethmoidal arteries, ciliary arteries, & the inferior and superior muscular arteries. The supraorbital & supratrochlear arteries of the ophthalmic artery provide the corrugator supercilii muscles. The supratrochlear artery, which 1st traverses underneath the frontalis & corrugator supercilii muscles, gradually appears more superficial. The supratrochlear neuromuscular bundle passes through the corrugator supercilii muscles & supply sensation & vascularity to the forehead.
Clinical importance
- As a significant part of the glabellar complex, the corrugator supercilii muscles play an important role in maintaining the position of the brow. Total resection of the corrugator supercilii muscles has been a recommendation for forehead rejuvenation. Incomplete corrugator supercilii muscle resection can have harmful therefore, such as forehead asymmetries, skin dimpling, & recurrence of glabellar furrows & frown lines. One previous study suggested the amount of corrugator supercilii muscles resection can differ turn on the surgical technique used, with as much as 1/3rd of the transverse corrugator supercilii muscles head remaining after the corrugator supercilii muscles removed using transpalpebral methods. Therefore, familiarity with the anatomy of the corrugator supercilii muscles with regard to fixed bony landmarks is necessary for a more systematic approach to precise resection of the corrugator supercilii muscles.
- Total resection of the corrugator supercilii muscles has also been a suggested approach for the treatment of migraine headaches. There have been suggestions that migraine headaches are associated with peripheral nerve trigger points & the supraorbital nerve/supratrochlear nerve. Chemodenervation of the corrugator supercilii muscles by botulinum toxin type A has been exhibited to improve migraine headaches by decompressing the supraorbital nerve & the supratrochlear nerve & relaxing the nearby musculature. Patients who have complete corrugator supercilii muscle myectomy have also been manifested to have long-term success.
- Patients with thyroid eye disease with upper eyelid retraction also have overactivity of the accessory muscles that play a role in eyelid closure& the glabellar muscles. They may have a staring facial expression with proptosis, upper lid retraction, & a glabellar frown. The frown may have vertical glabellar furrowing & an altered eyebrow contour, with medial brow ptosis & a deep horizontal line over the nasal bridge. These facial lines mainly arise from a chronic contraction of the corrugator supercilii muscles & the procerus pulling on the skin. Botulinum A chemodenervation has been manifested to flatten the glabellar region & enhance the medial eyebrow contour in patients with thyroid eye disease.
- Among patients with abnormal Parkinson’s disease, the “procerus sign” is a clinical sign that is also observed, particularly in patients with progressive supranuclear palsy (PSP). PSP may suffer misdiagnosis as the more well-known Parkinson’s disease. The procerus sign involves having vertical wrinkles on the forehead & a staring, astonished look with eyelid retraction & infrequent blinking. It is also believed the procerus sign is secondary to dystonia of the procerus muscle. However, the term may be misleading as the corrugator supercilii muscles seem to be the main muscles to produce the frown or vertical creases. Nevertheless, the generation of vertical creases on the forehead is a complex phenomenon, & the procerus sign might be prominent in early PSP.
Strengthening Exercise of Corrugator Supercilli:
- Initiate by placing the tip of the middle fingers in the center of each of your eyebrows.
- Tug them apart while simultaneously keeping a frown.
- Hold the position then release, Now re-position the fingertips at the center of your brow, but instead push the brows together (inward) while raising the brows.
- Once again, hold & then relax.
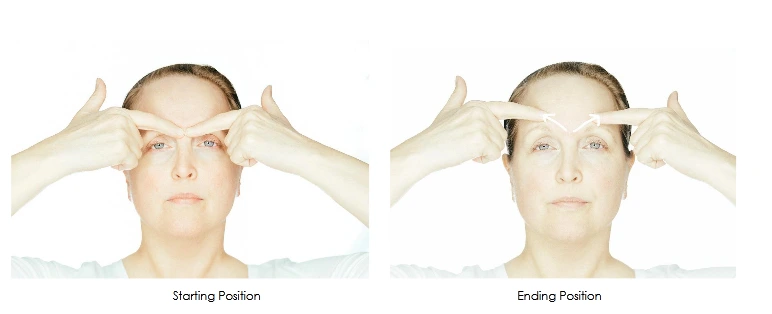
Stretching Exercise of Corrugator Supercilli:
- corrugator Supercilli stretch is great for relaxing the corrugator supercilii muscle. This stretch assists to counter the vertical furrows & lines that can be found at the bridge of the nose & between the eyebrows.
- Maintain your face in a neutral position & place both of your index fingers on the bridge of your nose.
- With moderate pressure, glide the fingers firmly from the root of the nose diagonally upward to just above the middle of each eyebrow.
- Move through the stretch & hold for 5 seconds. Rest and repeat.
- Initiate with 5 reps per day & work up to 10 repetitions per day by increasing the number of repitation each week.
- This is a simple motion that can be done at any time
FAQ
Exercising the corrugator supercilii is mainly in the strengthening of the muscle & decreasing stress lines of your forehead. Start by placing the tip of your middle fingers in the center of each of your eyebrows. Tug them apart while simultaneously maintaining a frown. pause the position for 6 seconds then release
Action. The corrugator supercilii muscle draws the eyebrow downward & medially, producing the vertical wrinkles of the forehead. It is the “frowning” muscle & may be considered the principal muscle in the expression of suffering.
As a significant component of the glabellar complex, the corrugator supercilii muscles play a main role in maintaining the position of the brow. total resection of the corrugator supercilii muscles has been a recommendation for forehead rejuvenation.
Use your fingers to slowly lift your eyebrows upwards, just a tiny bit. Again, use the mirror to make sure the eyebrows are level as you do this move. maintain the fingers in place to provide a bit of tension, and close the eyes. Hold here for about ten seconds.
Corrugator Supercilii is strained by habitual frowning. This frowning function can compress the supratrochlear nerve (branch of the trigeminal nerve.) This can cause deep aching frontal headaches. This muscle is certain times surgically severed or injected with Botox as a preventive treatment for some types of migraines.
The massage around the eyes assists to increase circulation by stimulating the deeper layers of the skin, This helps the removal of toxin build-up around the eye area, which in time balances & improves skin texture and tone.”
The corrugator supercilii is a paired muscle that lies deep to the medial end of each eyebrow. Upon contraction, these muscles draw the two eyebrows together medially and inferiorly, thereby producing vertical wrinkles over the glabella & an expression of frowning.
the facial nerve
A plexus important from the inferior ramus partly from the middle ramus of the temporal branch of the facial nerve runs the corrugator supercilii muscle in the supraorbital area.
A more lasting solution is to surgically “disrupt” (cut & resect) the corrugator muscle. The surgical approach can either be done endoscopically (no scar) or as a portion of a conventional forehead lifts or brow lift procedure.

One Comment