CERVICAL RIB: Extra Rib in Neck
Table of Contents
What is a Cervical Rib?
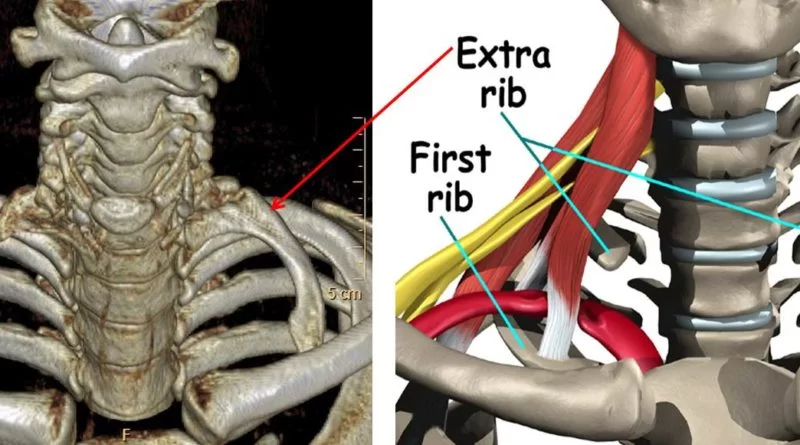
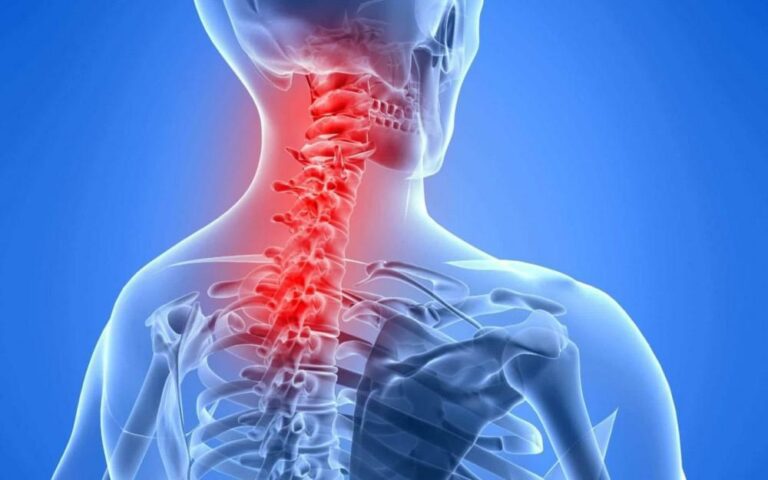
A cervical rib in humans is an extra rib that arises from the seventh cervical vertebra. Sometimes known as “neck ribs” their presence is a congenital abnormality located above the normal first rib. A cervical rib is estimated to occur in 0.2% (1 in 500 people) to 0.5% of the population. People may have a cervical rib on the right, left, or both sides. It may be a fully-formed bony rib or just a thin strand of tissue fibers.
Signs & Symptoms of Cervical Rib :
90% of cases of cervical ribs are not clinically relevant and do not have symptoms; cervical ribs are generally discovered incidentally. and it produces symptoms after the age of 30 years. A patient may present with the following symptoms:
(a) Neurological Symptoms:
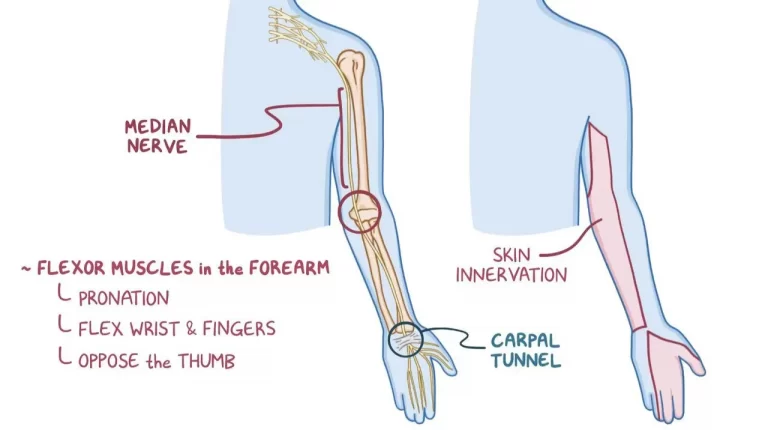
- Pain in your neck and shoulder, which spreads into your arm – this may be constant or come and go. This is commonly seen in thoracic outlet syndrome.
- Tingling and numbness, temporary loss of feeling in the affected arm and fingers(T1 dermatome). This is the most common complaint.
- Wasting of the hand muscle and temporary inability in the fine movement of the hand like buttoning
(b) Vascular Symptoms:
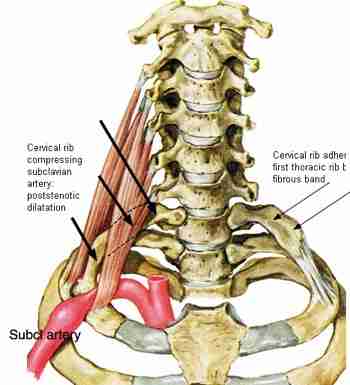
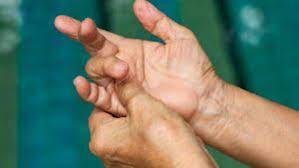
- An aneurysm in the subclavian artery which can affect the blood supply to the fingers leads to small red or black patches on the skin.

There may be present of Raynaud’s phenomenon – a condition that affects the blood supply to the fingers and toes, turning them white.
Radial pulse becomes feeble or may even be absent.
(c) Local Symptoms:
- Sometimes, patient may present with the tenderness in supraclavicular lump which, on palpation very hard and fixed.
- Swelling in the affected arm but, this is very rare.
Diagnosis:
(1) Generally it is diagnosed by the X-Ray examination to detect cervical rib, which could be easily palpable.
it is attached to the seventh cervical vertebra.
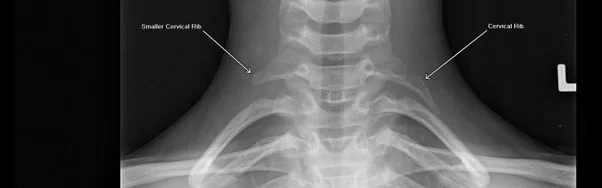
(2) Special test:
(a)Adson’s Test
Indications– Evaluation of Cervical Ribs/ Thoracic Outlet Syndrome.
Technique– Patient breathes deeply, Neck extended, Chin turned toward the affected side. The examiner lifts the arm away to the side to 90 degrees and performs external rotation of the shoulder, and notes whether the radial pulse disappears. However, there are many false positives, as the radial pulse may disappear in normal people as the head of the humerus (upper arm bone) compresses the brachial vessels when the arm is taken beyond 90 degrees. Repeat the test with the chin on the opposite side.
Interpretation– Positive test finding suggests interscalene compression, decreased Radial Pulse, and/or Distal extremity pain reproduced.
(b) Foraminal Compression Test/ Spurling’s Test
Spurling’s test is an orthopedic test used to diagnose nerve root compression primarily at the cervical level. It should not be used in instances in which vertebral instability is suspected.
(c) Shoulder Abduction Test

The shoulder Abduction Test is an orthopedic test used to help diagnose a cervical nerve root injury or cervical disc herniation. It is performed by having the patient abduct their shoulder and place their hand on top of their head. A positive test will involve a decrease in radiculopathy or pain.
Differential Diagnosis:
Patient with cervical rib is to be differentiated from patients present with radiating pain in the upper limb and the following are the causes:
1)Some of the more common conditions include herniated cervical disk, cervical spondylosis, and peripheral neuropathies.
2) Peripheral vascular disease like Raynaud’s disease.
3) Neurological conditions-like syringomyelia, polio, muscular dystrophy, and motor neuron disease.
Treatment of Cervical rib :
1. medical treatment:
Anti-inflammatory drugs and
analgesics mostly NSAIDs are prescribed by your doctors as a symptomatic line of treatment.
These two are given as conservative treatment.
2. surgical treatment in cervical rib:
surgery is essential in conditions of severe, progressive vascular and neurological signs and symptoms which are unbearable for the patients. It includes:
- Removal of the extra segment.
- Dividing the scalene group of muscles.
3. Physiotherapy Treatment:
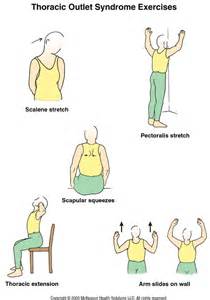
On the basis of the symptoms of the patient, the regime of physiotherapy is planned.
- For pain relief,- short wave diathermy, IFT, and TENS are used but it is contraindicated in case of sensory impairments.
- To improve distal circulation- gripping exercises like ball sqizing, and spring stretching.
- To improve tone, power, and endurance-Strengthening exercises of the whole arm particularly small muscles of the arm.
- For posture Correction -In this, the patient is guided to use a mirror to see that his shoulders are level, the head is straight, looking forward
- Specific exercises- To develop particular muscle groups for specific movements of the shoulder girdle like elevation, retraction, and raising the arm overhead as these movements bring spontaneous relief. The important exercises are:

1- Self resisted scapular elevation.
2- Self-resisted scapular adduction.
3- Endurance training exercise for the shoulder girdle muscles.
4-Progressive resistance exercises for shoulder girdle muscles with weight.
- Deep Tissue Massage for TOS ( thoracic Outlet Syndrome).

I have a cervical rib since 2 years and now i am suffering with unbarreble pain. What shoud i do? Plz guide me.