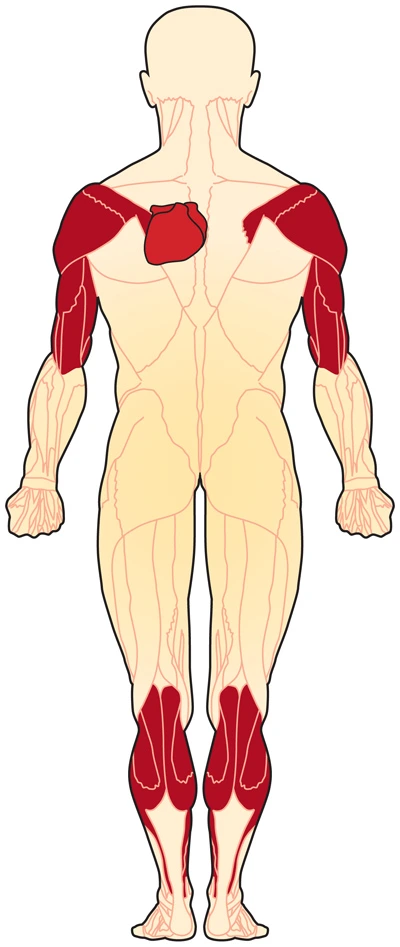
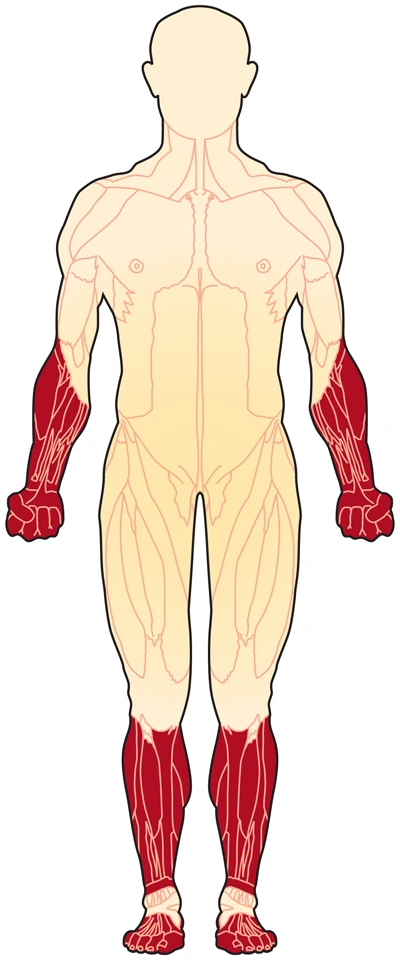
Musculocutaneous nerve injury:
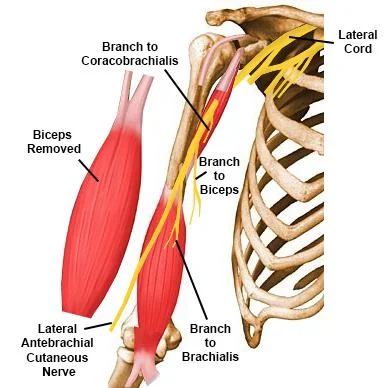
Overview: The musculocutaneous nerve originates from- C5-C6 nerve roots and the terminal branch of the lateral cord of the brachial plexus. it has both motor and sensory fibers. It supplies the muscles of the front of the arm and the skin of the lateral side of the forearm. The nerve passes through the coracobrachialis muscle…