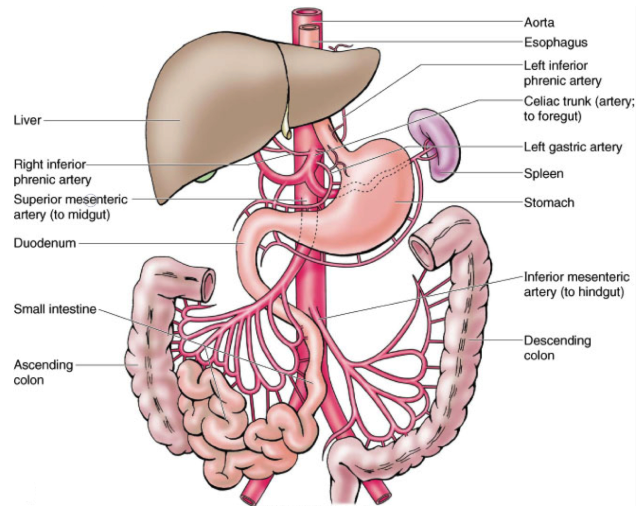
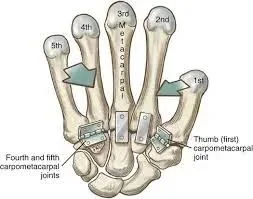
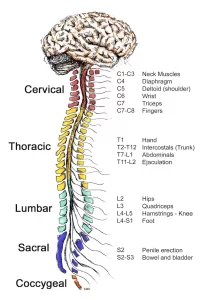
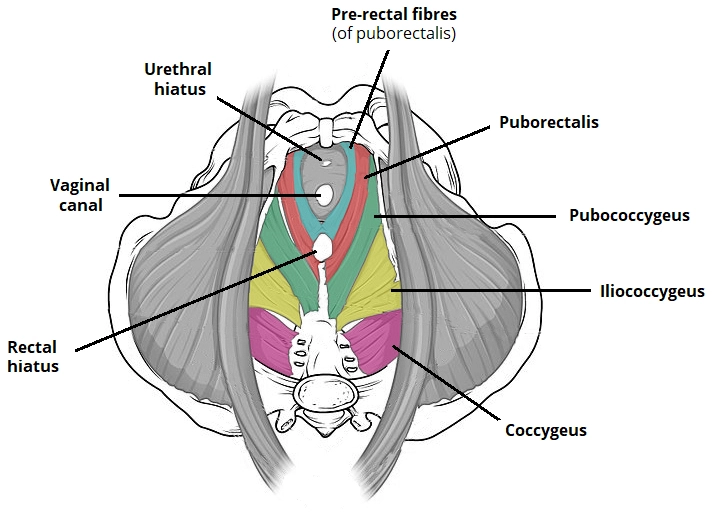
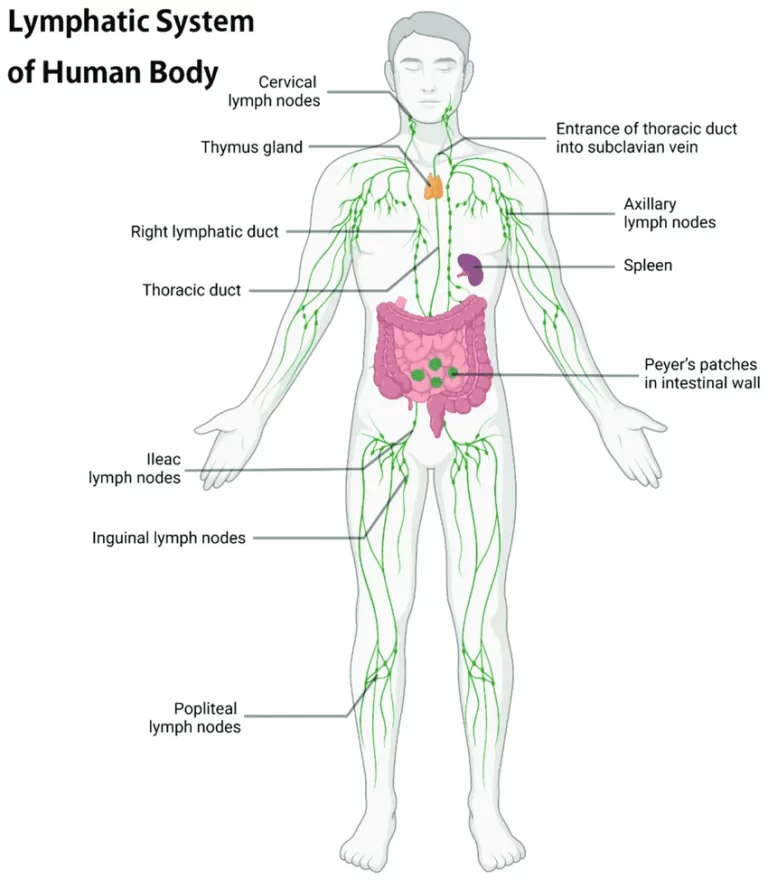
Superior Mesenteric Artery
Introduction The superior mesenteric artery (SMA) is a major blood vessel in the human body, arising from the abdominal aorta just below the celiac artery at the level of the first lumbar vertebra It begins at the level of the L1 vertebrae on the anterior surface of the aorta, about 1 centimetre below the celiac…