Abdominal muscle spasm
Table of Contents
What is abdominal muscle spasm?
Abdominal muscle spasm are contractions of the abdominal muscles (abs), stomach, or intestines. Depending on which part of the body is spasming & how badly, it might feel like either a slight muscle twitch or stomach cramps.
In many cases, abdominal muscle spasms themselves are harmless, but they could be a symptom of an underlying condition sometimes.
What are the abdominal muscles ?
The abdominal muscles are the muscles forming the abdominal walls & the abdomen being the portion of the trunk connecting the thorax & pelvis. An abdominal wall is formed of skin, fascia, & muscle & encases the abdominal cavity & viscera.
The abdominal muscles support the trunk, allow movement, hold organs in place & are distensible (being able accommodate dynamic changes in the volume of abdominal contents).
There are five main muscles in the abdomen:
External obliques.
Internal obliques.
Pyramidalis.
Rectus abdominis.
Transversus abdominis.
Where are the abdominal muscles located ?
There are five main muscles in the abdomen. Two are vertical (up & down) muscles located toward the middle of the body. Three are flat muscles stacked on top of the each other, located toward the sides of the trunk.
The two vertical muscles are:
Pyramidalis: This vertical muscle is small & shaped like a triangle. It’s located very low, in the pelvis. It helps maintain internal pressure in the abdomen.
Rectus abdominis: This pair of muscles goes down the middle of the abdomen from the ribs to the front of the pelvis. The muscles hold the internal organs in place & keep the body stable during movement. The rectus abdominis may form bumps sometimes called a “six-pack”ab when someone has a trim, fit abdomen.
The three flat muscles are:
External obliques: The external oblique muscle are a pair of muscles, one on each side of the rectus abdominis. They are the largest of the flat muscles & at the bottom of the stack. They run from the sides of the body toward the middle. The external obliques allow the trunk movement to twist side to side.
Internal obliques: The internal obliques are a pair of muscles on top of the external obliques, just inside the hip bones. Like the external obliques, they are on the sides of the rectus abdominis, running from the sides of the trunk toward the middle. They work with the external oblique muscles to allow the trunk to twist & turn.
Transversus abdominis: The transversus abdominis is located at the bottom of the stack. This is the deepest pair of muscles of the flat muscles. They stabilize the trunk & help to maintain internal abdominal pressure.
What are the functions of an abdominal muscles ?
The abdominal muscles have several important functions:
It helps with essential bodily functions, including urinating, defecating, coughing, sneezing, vomiting. They help also in increase the intra-abdominal pressure facilitating during child birth.
Hold the internal organs in place & protect them (including your stomach, intestines, pancreas, liver & gallbladder).
Maintain consistent internal pressure in the abdomen.
Maintain posture & provide core support.
Support your spine & body during sitting, standing, bending over, twisting, exercising & singing.
Causes of abdominal muscle spasm:
1.Abdominal Muscle strain-
Overusing the abdominal muscles could cause them to spasm. Spasm because of muscle strain are most likely to occur in people who do strenuous & frequent exercise, especially crunches & sit ups.
Strains can involve tiny, minor tears in the muscle fibers to the severe pulls that can even detach the muscle.
This type of injury is more common in sports that require twisting, such as tennis, football, baseball & golf.
Difficulty in moving.
2.Dehydration-
Losing electrolytes from dehydration caused by sweating, vomiting, & diarrhea can result in muscle spasms throughout the body, including the stomach. This happens because muscles need electrolytes such as calcium, potassium, & magnesium to work properly. When they don’t have these electrolytes, the muscles may start working abnormally & seizing up. Learn more about identifying & treating an electrolyte imbalance.
Other symptoms of dehydration include:
extreme thirst
headaches
dizziness
dark yellow urine
3.Gas-
A buildup of gas in the stomach can cause the intestinal muscles to spasm as the body tries to release the gas.
If you have gas, you might also have:
distended stomach or bloating
sharp stomach pain
a feeling of fullness
an urge to pass gas or burp
4.Inflammatory bowel disease-
These diseases, such as Crohn’s disease & ulcerative colitis (UC), are chronic inflammatory conditions. Crohn’s disease can be affecting any part of the gastrointestinal tract, while UC only affects the colon. In both conditions, inflammation can cause bowel spasms.
Other symptoms of inflammatory bowel diseases are:
diarrhea
weight loss
abdominal cramps & pain
fatigue
night sweats
constipation
feels like urgently need to go to the bathroom
5.Irritable bowel syndrome–
Irritable bowel syndrome (IBS) is a chronic condition which affects the large intestine. It does not cause bowel tissue changes like inflammatory bowel disease, but symptoms are similar, including:
stomach pain or cramping
bloated feeling
constipation
diarrhea (sometimes constipation and diarrhea will alternate)
gas
6.Gastritis & gastroenteritis-
Gastritis & gastroenteritis are both stomach inflammation, but in gastroenteritis, the intestines are also inflamed. Infections, like as from Helicobacter pylori, Norwalk virus & rota virus, usually cause these conditions.
Other symptoms of gastritis & gastroenteritis include:
nausea & vomiting
diarrhea (gastroenteritis only)
stomach pain
bloating
7.Infectious colitis-
Colitis can cause abdominal cramping due to irritation & inflammation of the colon, which causes it to spasm. Some bacteria which can cause colitis include Clostridium, Salmonella, & E. coli. Parasites such as Giardia can cause colitis too.
8.Ischemic enteritis and colitis-
Sometimes colitis is caused by lack of blood supply to the small bowel & colon. Spasm can also occur in this type of colitis as well.
9.Constipation-
The bowels may cramp when you experience constipation as they distend in response to increased pressure inside them.
10.Ileus-
An ileus is when the bowels become lazy or sleepy. This can occur for a many of reasons including infection, inflammation ,recent surgery (especially in the abdomen), narcotic use, severe illness, & lack of physical activity. An ileus causes the bowels to fill with air & fluid, resulting in distention & pain.
11.Gastroparesis-
Gastroparesis is basically an ileus involving the stomach. It most commonly occurs in those with diabetes & can cause stomach cramping especially after eating.
Other common causes of abdominal muscle spasm:
Overstretching of the muscles.
Overuse of the abs.
Quick, violent twisting of the trunk.
Muscle spasms in the abdomen & core.
Trunk pain while exercising, laughing, coughing or sneezing.
Swelling or bruising.
Trouble breathing in severe cases.
A pulled stomach muscle is the often an overuse injury. Repetitive movements, usually in sports or any other physical activity, cause the muscle to stretch or tear.
Accidents, such as falls or motor vehicle wrecks.
Chronic coughing or sneezing.
Intense or excessive exercise.
Lifting heavy objects.
Poor form when playing sports or exercising.
Sudden twisting.
Diastasis Rectus is a stretching of an linea alba with abnormal widening of the gap between the 2 medial sides of the rectus abdominis muscle, which is often seen during pregnancy, or post-menopausal women.
A hernia occurs when there is an weakness or hole in the muscular wall that usually keeps the abdominal organs in place.
Symptoms of abdominal muscle spasm:
tenderness or pain in the abs
pain that gets worse with movement
Dehydration include:
extreme thirst
headaches
dizziness
dark yellow urine
bloating of abdominal.
sharp abdominal pain.
a feeling of fullness.
an urge to pass gas or burp.
pain in your mid to upper abdomen, sharp & sudden or that comes & goes
pain that radiates to your back or shoulder
pain that worsens when you eat greasy & spicy food and food high in fat
cramping
stomach twitching
stomach flutters
burning sensation in the stomach the throat
fever
chills
nausea
vomiting
diarrhea
feeling like food is getting stuck in the throat when you eat
blood in stool
black stools
yellowing of the eyes and skin
shortness of breath
How is the abdominal spasm diagnosed?
The cause of abdominal spasm is diagnosed based on the symptom history, a physical examination, & testing, if needed. The doctor is likely to ask you questions about the characteristics of the pain, & whether you have any underlying physical or mental health conditions that could be contributing to the abdominal pain.
Questions may address by the following aspects of the abdominal spasm:
Where it’s located
How intense it is
Whether it’s cramping pain
Whether it comes & goes
When you experience or notice it most
Whether it radiates outward to other areas of the body
How long you’ve had it
Whether any activities or the actions seem to make it worse or better
The doctor may also ask about the overall health history, any recent injuries, & whether you might be pregnant.
If the doctor suspects a serious health condition that may need treatment, any of the following tests may be used to help diagnose the cause of the abdominal pain:
Blood, urine, or stool tests
X-ray of the abdomen
Ultrasound of the abdomen
Computerized tomography (CT) scan of the abdomen
Barium enema (colon X-ray)
Endoscopic procedures (inserting a tube with a tiny camera through your mouth or rectum to view areas inside the digestive tract)
Electrocardiogram
When to seek an doctor?
Most abdominal spasms are harmless & go away without further treatment. If the abdominal spasms are painful or happen often, they could be an symptom of an more serious medical issue. Seek to an doctor if you have any of these symptoms in addition to abdominal spasms:
vomiting
blood in your bowel movements
severe pain, especially chest pain
long-lasting or recurring stomach spasms
fever
shortness of breath
You should also see the doctor if the stomach spasms are interfering with the daily life or causing you distress.
Treatment of Abdominal muscle spasm:
Abdominal muscles spasm causes include overstretching, improper technique while playing sports that require running, turning, & jumping, lifting heavy objects, laughing, coughing, or sneezing, etc.
Treatment of an abdominal muscle spasm is difficult. There’s no way to splint the abdomen & it’s nearly impossible to fully rest these muscles.
The below are basic things to advice the person who suffer it:
Avoid exercise to allow the injured muscle for healing.
Avoid activities which cause pain or spasm of the abdominal muscles.
Practice gentle stretching. It should not be painful or an excessive, as this may slow the process of healing.
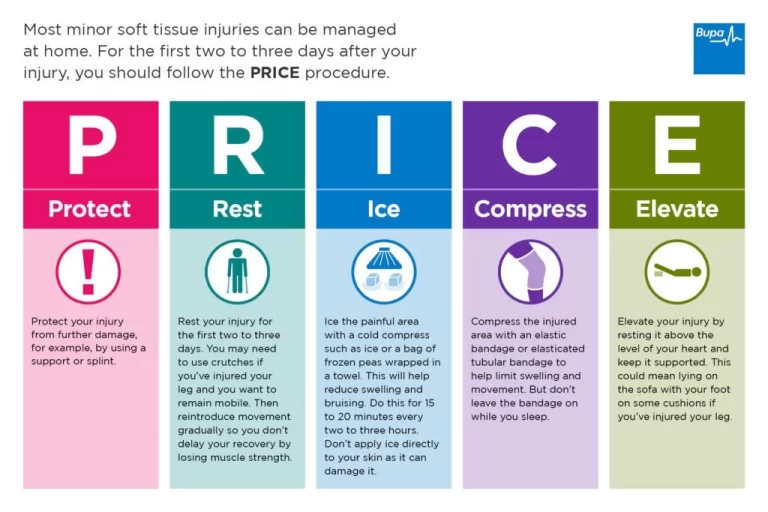
Apply ice to an injured area in the acute phase, or during the first 48 hours after an injury. It’s also helpful to apply ice after activities.
Apply heat before activities to loosen the muscle.
Take proper medications if necessary or required.
Home remedies for immediate relief of Abdominal muscle spasm:
If the abdominal spasms are bothering you, there are ways you can get immediate relief or treat them at home. Some at-home treatments will treat the underlying cause of muscle spasms, while others relax the abdominal muscles so that they stop spasming.
Heat-
Heat can help to relax the abdominal muscles. This is particularly helpful if muscle strain or overuse is causing the spasms.
Massage-
Massaging the stomach muscles can help to relax them.
Chamomile tea-
Chamomile can be used to calm an upset stomach & could help manage spasms. It’s also considered a home remedy for gas.
Find a great selection of chamomile tea here.
Electrolytes-
If the stomach spasms are caused by dehydration, replenishing the electrolytes may help. Try drinking a sports drink like Gatorade or eating a banana.
Use caution, however, if you have an history of kidney failure because some electrolytes, particularly potassium can rise to hazardous levels with supplements.
Also, if you develop dizziness or you pass out because of dehydration, you have lost a significant amount of body fluid. Seek immediate treatment in the nearest emergency room for intravenous fluid replacement to prevent the body from going into shock & to prevent damage to the heart, liver, brain, and kidneys.
Pain relievers-
If the abdominal spasms are painful, an over-the-counter (OTC) pain reliever such as ibuprofen (Advil, Motrin) or acetaminophen (Tylenol) can help.
You must be cautious with OTC pain medications. Ibuprofen & similar drugs can cause gastric ulcers & kidney damage if taken in excessive amounts. Acetaminophen in large amounts can cause liver damage & even liver failure. If you feel that you need to take more of these medications than the prescribed dosage on the bottle, you should consult with a doctor.
Antacids-
Stomach acid can cause gastritis, which in turn can cause abdominal spasms. In these cases, antacids or OTC proton pump inhibitors can help the spasms by reducing stomach acid.
Rest-
If the spasms are caused by muscle strain, cutting back on exercise & resting the stomach muscles will help stop the spasming.
Other treatments-
Abdominal spasms caused by conditions such as gas, dehydration, & muscle strain can usually be treated at home. Other conditions or severe abdominal spasms usually require treatment from a doctor.
This are the some preventive ways to cure abdominal spasm:
Exercise correctly. Working the muscles hard can be good for the health, but working them too hard or incorrectly can lead to injuries. Always make sure you use proper form & rest if you need to. By doing regular abdominal & core stretching & strengthening exercise one can live an proper healthy life.
Stay hydrated. A loss of electrolytes due to dehydration can cause abdominal spasms. Making sure you stay hydrated, therefore, can help reduce spasms.
Changing the diet may help prevent abdominal spasms caused by gas, gastritis, & inflammatory bowel disorders.
If gas is causing the stomach spasms, limiting fiber intake might help. Eating fiber can help people having constipation caused by inflammatory bowel syndrome & gastritis.
Limit the alcohol consumption.
Limit spicy foods, which can irritate the stomach & make spasms worse.
Fatty foods can also increase symptoms in these conditions & should be limited.
If you have an inflammatory bowel disease, work with the doctor to find the safest foods for you to eat.
While doing any abdominal stretching & strengthening exercise, make sure as this exercise are doing in proper way and in under control manner. Do not try to overdoing an these exercise as sometimes by doing over exercise it might increase the spasms or injuries to the abdominals. So proper care should be taken.
Abdominal muscles stretching:
When it comes to an daily stretching exercises, the abdominal muscles are often overlooked. However, stretching the abs is good for the posture & overall flexibility. Try static stretches, such as cobra, cow, & cat poses. You can also perform dynamic stretches, like glute bridges & side bends. If you have an exercise ball, perform full-body extensions to stretch the abs. To avoid injury, warm-up before stretching, breathe while you stretch, & avoid deep stretching the same muscle group two days in a row.
A strong core is an important component of the overall fitness, athletic performance, & daily life.
Warming up with dynamic stretches before you start an exercise & cooling down with static stretches after you finish the exercise can help.
Types of abs stretch,
There are some various types to stretch abs :
1.Cobra Pose abdominal stretch
2.Cat-Cow Stretch
3.Seated side-straddle stretch
4.Chest opener on an exercise ball
5.Ab Side Stretch
6.Supine Stretch
7.Slow Cyclone For Abs
8.Locust Pose
9.Leaning Lifting Crunch
10.Kneeling Spinal Wave
11.Seated Rotation
12.Bow Pose
13.Twisting Shoulder Bridge

1.Cobra Pose abdominal stretch:
How to do: Lay down face on the ground or on an exercise mat. This is the beginning position.
Place both hands near the shoulder, elbows are bent.
With the hips flat on the floor, push the torso upward, while gazing straight ahead.
This will stretch the abdominal muscles.
Hold this cobra pose for 20 secs, then back to the starting position.
Repeat 2- 4 times.
2.Cat-Cow Stretch:

How to do: Get all four limbs in position, & draw the head down as you arch the back, same as a cat does.
Stretch the neck all the way upwards, & sink the belly all the way downwards, stretching the abdominal muscles.
Hold this abs stretch for 20 secs, then back to the starting position.
Repeat 2- 4 times.
3.Seated side-straddle stretch:

How to do: Sit upright on the ground with the legs apart.
Lift the arms to the side with the elbows flexed & fingers pointing upward.
Use the abdominal muscles & slowly bend sideways to the left, bringing the left elbow towards the floor.
Don’t flex forward or rotate. You can feel the stretch through the obliques.
Hold this abs stretch for 20 to 30 secs, then back to the starting position.
Repeat on the right side & hold for 20 to 30 seconds.
Repeat 2 to 3 times on both sides.
4.Chest opener on an exercise ball:

How to do: Take a lying position on the exercise ball.
The scapulae, neck, & head should be on the top of the ball, with the back extended, feet flat on the ground, & knees bent at 90-degrees.
Start the stretch by opening up the arms & letting them drop to the side of the ball.
Make sure you should looking up at the roof.
Hold this stretch for 20-30 secs.
Repeat 3-4 times.
5.Ab Side Stretch:
How to do: Stand tall with the feet shoulder-width apart with the arms on either side.
Raise the left arm in the air, keeping the right arm by the side.
Slowly lean over to the right, sliding the right arm down the side.
In this pose, you should feel a stretch through the obliques.
Slowly back to the original position & place both of the hands on either side.
Repeat the ab stretch, this time raising the right arm in the air.
Pause 8-10 secs per side.
6.Supine Stretch:
How to do: Take a lying position on a mat.
Then lift the arms & reach it over the head with the fingers pointing away from the body.
Stretch by the spine & move away from the head.
Hold this supine stretch for 8 – 10 secs.
7.Slow Cyclone For Abs:
How to do: This is an dynamic ab stretching. Then, stand tall with the feet shoulder width apart & keep a mild bend in the knees to keep them soft.
Stand upright & lift both of the arms in the air.
Circle the torso from the hips upwards so that the trunk moves in a round motion.
As you perform this, keep the arms parallel with the trunk & do the stretch in a continuous motion.
The duration of the stretch is 15 secs.

8.Locust Pose:
How to do: Begin by lying in a prone position with the arms at the side, positioned against the side of the legs.
Raise the chest & the legs making a boat shape, so you have an inward curved back.
Release & come back lower to the ground.
Hold this boat pose for 10 secs.
9.Leaning Lifting Crunch:
How to do: Take a standing position shoulder-width apart, & make a prayer pose by holding the palms together.
Lift the arms above the head, imitating the upper half of the tree pose.
Lean over to the right until to feel a stretch in the obliques.
Next, move the torso by leaning to the left, this time kicking the lift leg out to the side at the same time.
Repeat on one side for 20-30 secs then switch to the other side & repeat.
The holding period of this abs stretch is 30 secs on each side, with rest in between.
10.Kneeling Spinal Wave:
How to do: Begin on the hands & knees. obtain the balance & get comfortable on a mat.
Push back so the arms are flat in front of you & the head is lower.
In this pose, you should be seated on the knees with a straight back.
From this position, push up into a ‘cat’ position before returning into a ‘cow’ position
Then, push forward into a cobra pose, with the feet soles upward, legs extended & the chest & torso upright.
Push back into an‘cat’ pose & repeat the motion.
The duration of this stretch is 30 secs.
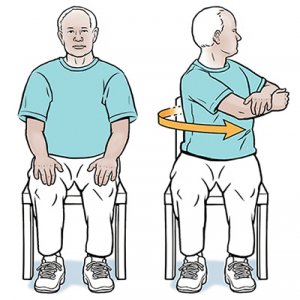
11.Seated Rotation:
How to do: Take a sit on a chair with the spine neutral.
Rotate the body to the right side & pause the position.
Then turn on the left side & pause.
Hold this rotation for 20-30 secs.
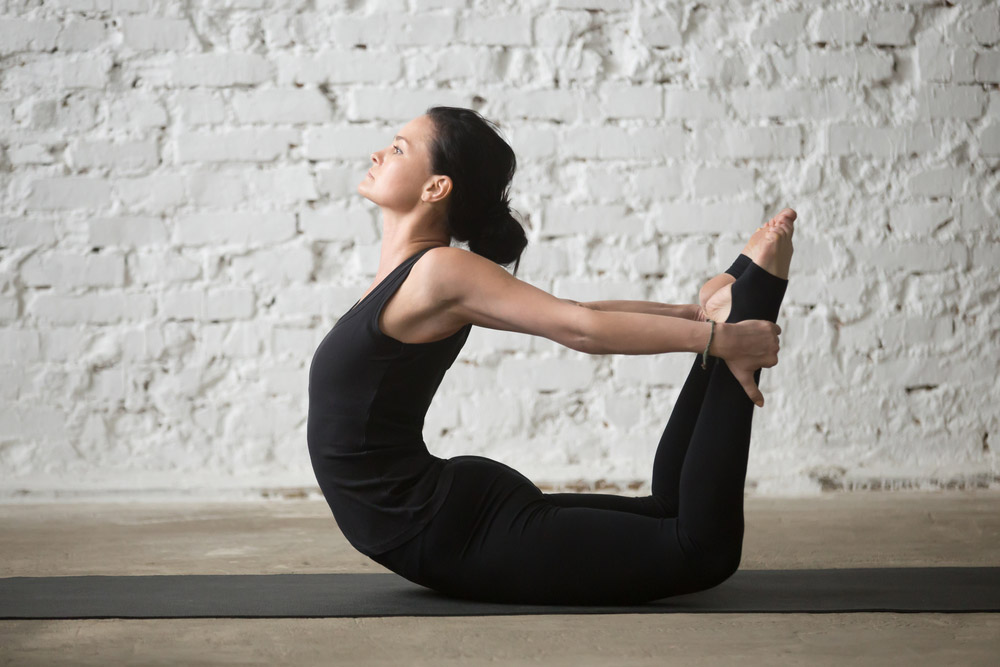

12.Bow Pose:
How to do: Begin the stretch by lying on the stomach with the knees together & flexing at a 90-degree angle.
Lift the chest & stomach off the ground while keeping the pelvis & thighs on the ground.
Move the arms backward & grab the ankles as you pull the legs up & push the chest out.
Keep the neck stable with the spine by looking at the wall in front of you during the whole stretch.
Hold this abs stretch for 30 secs & then slow down the upper body & legs to the ground.
13.Twisting Shoulder Bridge:
How to do: Lie supine on a floor.
Bend the both knees & drag the heels towards the hips. The arms by the sides.
Now thrust the hips up towards the sky, the feet touching the ground.
Keeping the left arm on the ground, reach for the left heel.
Then, rolling over onto the left shoulder, reach the right arm back & over the head.
Switch to the other side & repeat.
What are the common mistakes to avoid during the abs stretch ?
There are some mistakes you should not do during the abs stretch :
Overstretching: Overstretching during this abdominal stretch could raise the risk of injury & even the pulling a muscle, most likely in the obliques. You have to stretch the muscle enough that you may feel the stretch only & nothing more, but you should stop stretching the muscle as earlier as you feel any pain.
Overarching the back: Overarching the back puts extra stress on the muscles in the trunk, as well as the thighs & hamstrings.
Bending the knees too much: By over bending the knees, you will put extra pressure on the legs, particularly the knees, which could cause pains & aches. Standing in the wrong position could also make the stretch unnecessarily difficult, the amount of time that you can experience it & as a result, make it less effective.
Leaning too far over laterally: Leaning too far during abs stretch causes an increase in the risk of the injuries by giving extra strain to the obliques. Instead of move in an comfortable yet stretching in circular movement.
Going too slow: It was one of the ab stretches that needs to be done at a moderate speed. The crunching action should be a slow & controlled motion as moving too fast would put a strain on the obliques.
Putting the head on the ball: You do not need to overextend the back & have the lower back on the floor as this could cause backache & strain. Instead, assure you have the shoulders & lower back raised onto the ball for optimal support.
Pushing from the toes: Pushing from the toes can be dangerous & give strain to the legs & back.
Moving too quickly: Stretching is slow-motion, & rushing won’t allow you to feel the full advantages of ab workout stretches. So avoid rushing through this movement, take it slow & assure that you feel the muscles stretching.
Bending the knees: In standing abs stretch, You have to stand up with the knees straight when doing this ab stretch. Bending the knees will risk the stretch & ultimately give unnecessary pressure on the legs & knees.
Abdominal strengthening exercise:
Abdominal exercises need to be gradually progressed from how to activate muscles & maintain contraction to integrate them with functional movement.
Health benefits by doing abdominal muscles strengthening exercise:
Helps to supports better posture.
Helps to improve balance.
Helps to support better running form “core strength allows the hips, pelvis & lower back to work together more smoothly with less rocking & less excess energy using.
This exercises improve stability if you have a weak core, you instantly heighten the risk of muscle injuries, lower back pain, & poor posture.
Helps to protects the Organs.
This exercises makes the life easier: like bending down to pick something off from the ground, long time standing or performing household chores. This is the reason why many core exercises fall under the umbrella of functional fitness: They can help you go about the day with more easiness, seriously it makes you more functional.
This exercises can reduced or prevent a low back Pain.
This exercises boosts the power.
This exercise supports strength training.
This exercise helps you age well: It stabilizes the whole body & gives you better balance & posture, all of which can help you prevent falls, prevent back pain, & keep you mobile as you get older.
Helps to improve spine mobility.
However, abdominal exercises can help to tone the belly somewhat by defining the abdominal muscles & once you lose the tummy fat, you will likely to discover that you have that 6 pack hiding underneath.
Many people desire to gain stronger, leaner abdominal muscles (or abs). The abdominals are the muscles surround the tummy & belly button & are often referred to as a “six-pack.” If you are interested in burning belly fat & getting a leaner midsection, here are a,
A few key factors to consider:
Strong abdominal muscles: Focusing on exercises that develop core strength & stability can help develop toned abs.
Genetics: Numerous people are genetically predisposed to abdominal fat. While it doesn’t necessarily mean you will always have it, you may have to step up the workouts to get the results you are hoping to achieve.
Belly fat: You won’t be able to see the strong core muscles from the surface if there is a layer of body fat around you midsection. However, you can still have a strong abdominal & have a bit belly fat & still be considered healthy, especially if you are exercising regularly & following a well-balanced diet.

Types of Exercises to strengthen the abdominal muscles:
1.Abdominal Crunches:
How to do it:
This is a great exercise to do this will not place too much stress on the lower back & spine.
For this exercise, you have to Lie on the back & flex the knees to a comfortable position, lock the hands behind the head or cross the arms in front of the chest now curl the head, shoulders, & upper back off the ground.
The lower back should be in contact with the ground; you should only rise a 2 to 3 inches exhale as you rise.
Hold this position for three to ten seconds.
Slowly return to the initial position. Repeat 10 more times.

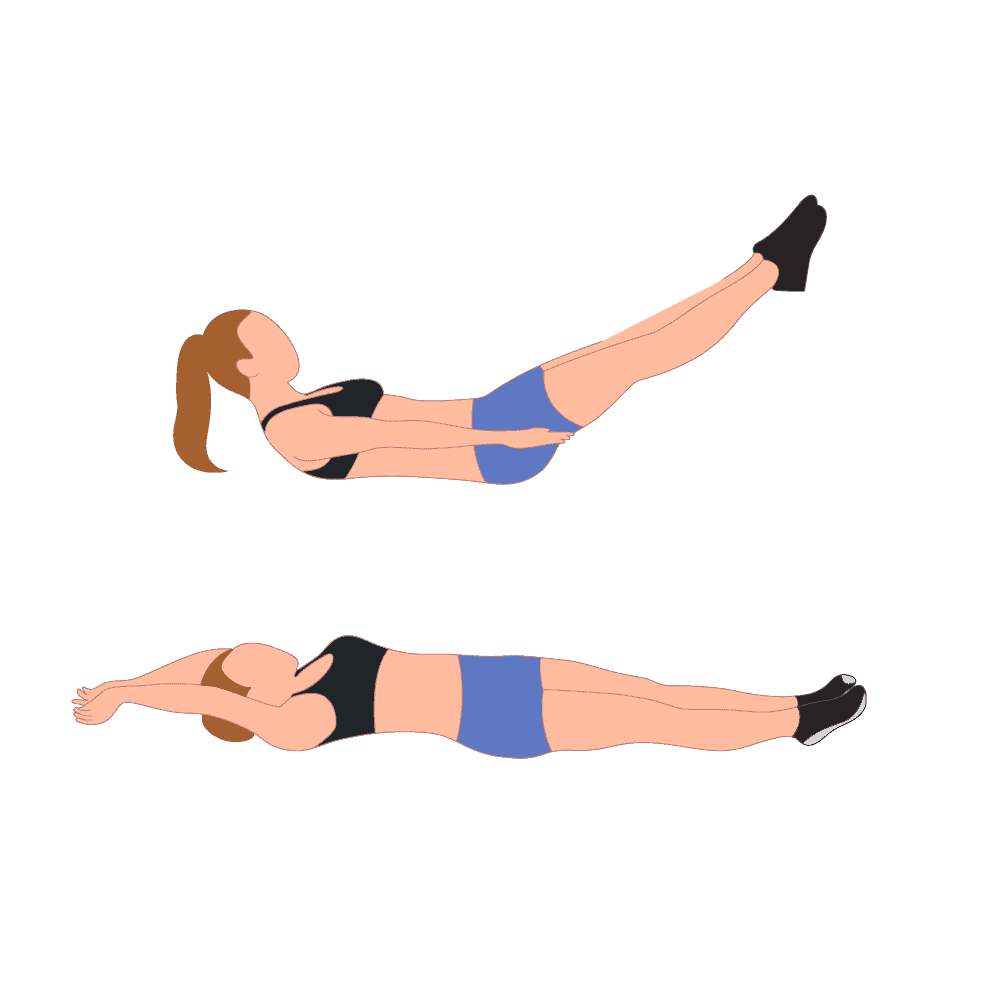
2.Low Ab Leg Raises:
How to do it?
For this exercise, you have to Lie on the back & flex the knees to a comfortable position
Then extend the legs. Contract the abdominal muscles to lift the feet off the ground in an arc-like motion
Lift the feet about ten inches up.Slowly (in the same arc- like motion) return the legs/feet to the ground.
Repeat 10 more times for 2 to 3 set.
3.Twisting Sit-Ups:
How to do it?
This is a great exercise to get the obliques into action & work properly. For this exercise you have to Lie on the back. Flexed the knees to a comfortable position. Lock the hands behind the head.
Curl the head, shoulders, upper & lower back off the floor & angle the left elbow toward the right knee exhale as you lift.
Hold this position for 5 secs .Slowly return to the initial position.
Curl the head, shoulders, upper & lower back off the ground & angle the left elbow toward the right knee .Hold this position for 5 secs.
Again, exhale as you lift slowly return to the starting position .
Repeat 10 more times alternating the twisting motion. Keeping the abdominals working properly is the best way to stay in shape, & by regularly exercising & maintaining proper posture for the back, you may be able to stave off any attacks of back pain or sciatica.
4.Pilates:
How to it?
Lay on the back & lift the shoulders off the floor while placing the hands next to the hip. Lift the feet up & hold.
Make sure the back touches the floor. If the back bows then raise the legs higher for a rounder back. Keep the legs straight.Hold for 10-20 secs.
5.Bicycle crunch:
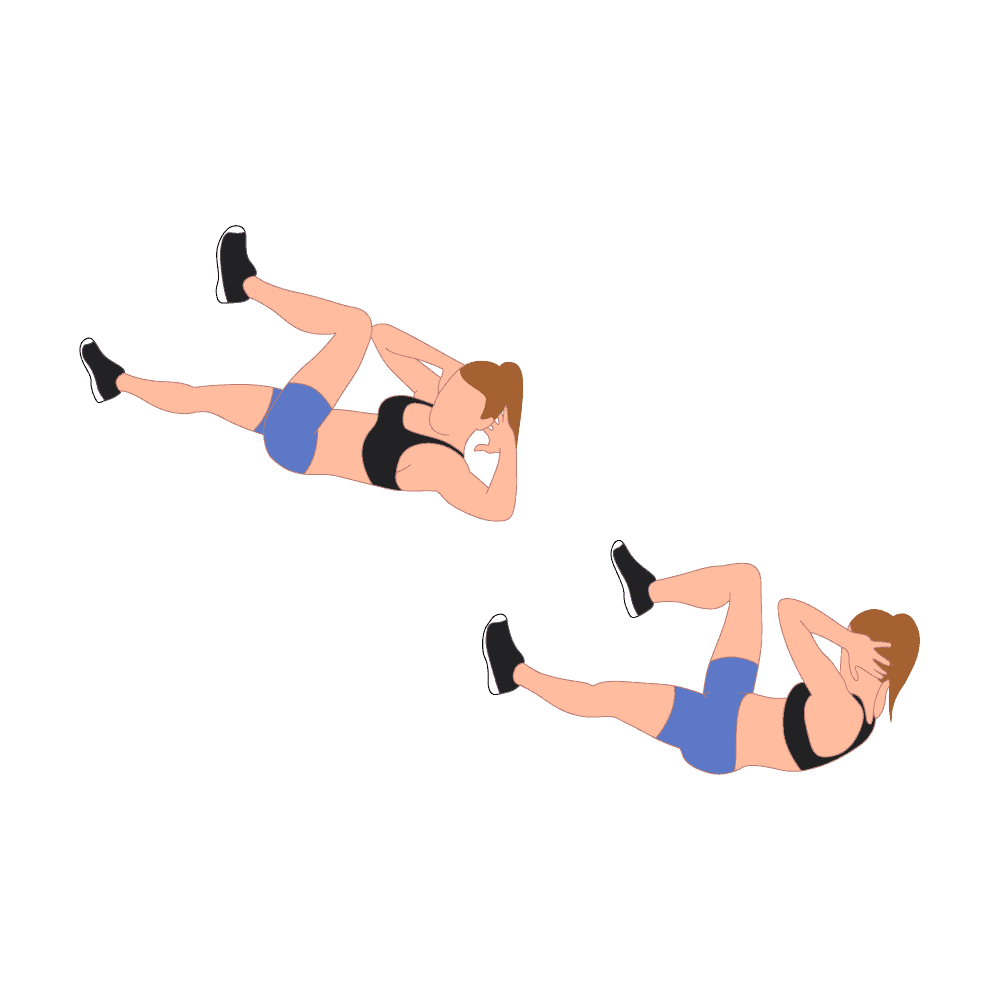
How to do it?
This floor exercise is one of the best exercises to strengthen the rectus abdominis muscle.
For this exercise, you have to supine lying on the ground. Press the lower back into the ground & flexed the knees while keeping the feet flat on the ground. Put the hands behind the head, interlacing fingers if preferred.
Elbows wide & gently cradle the head in the hands. Bring the knees up, with shins parallel to the ground, as you lift the shoulder blades off the ground. (Be careful not to strain or pull on the neck.) As you straighten your right leg out at about a 45 degree angle, turn the upper limb to the left, bringing the right elbow toward the left knee. Return to the starting position, with both knees flexed & elbows wide.
Repeat on the other side extend the left leg to a 45 degree angle & turn the upper body to the right, bringing the left elbow toward left knee. Return to the initial position to complete 1 repetition.
Complete 2 to 3 sets of 15–20 repetitions, resting for 30 seconds to 1 minute after each set.
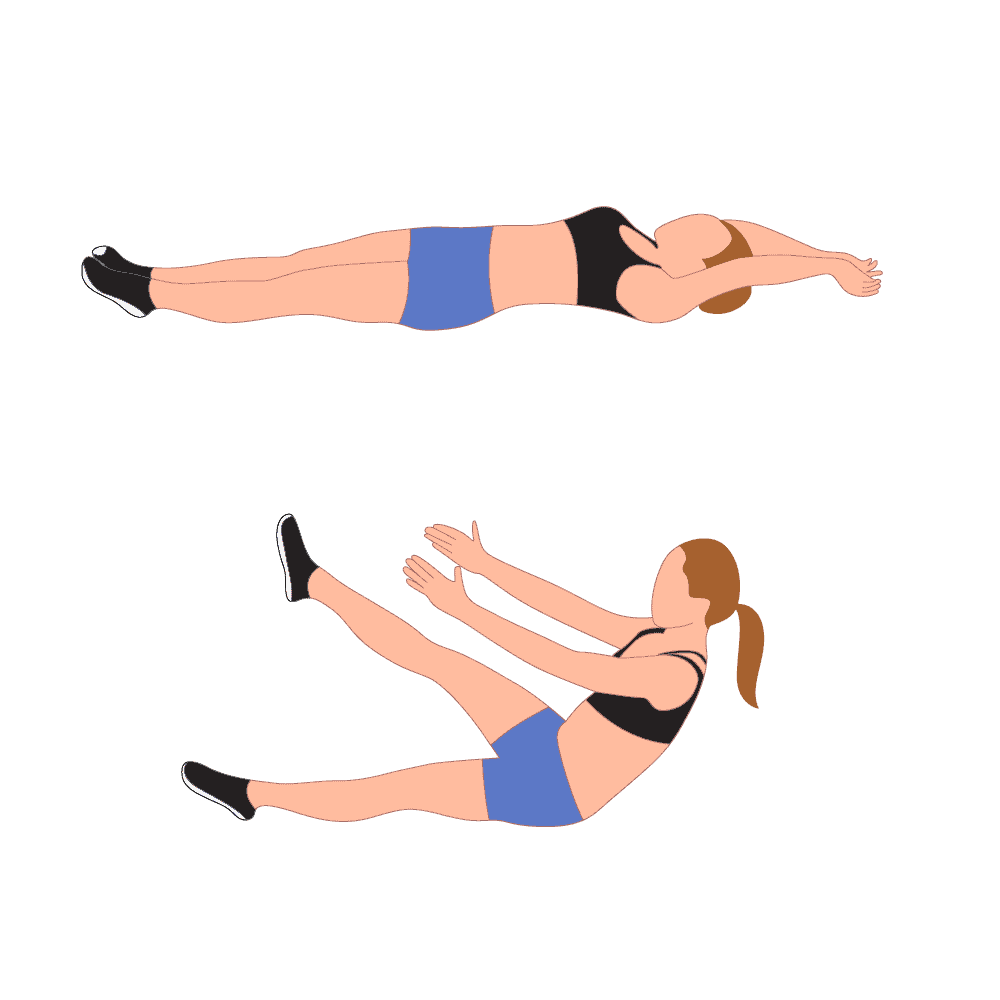
6.Single-Leg Jack Knife:
How to do it?
Lie on your back & stretch the arms above the head. Then lift one leg up & reach the hands toward the foot at the same time.Make sure legs & arms stay straight & your upper body is completely lifted off the floor then slowly lower the body back down to the starting position then switch the legs.
Hold for 10-20 secs. 15–20 repetitions ,2 to3 sets each.

7.Plank:
How to do it?
Start on your toes & hands or elbows & keep the body straight like a board. Your feet should be hip width apart & the hands or elbow shoulder width.
Hold this position. Make sure the hips is not drop too low or rise too high.
Hold for 20-30 secs.
8.Fitness ball rollout:
How to do it?
Use an exercise ball for this exercise. this exercise targets the rectus abdominis muscle.
To perform the exercise you have to kneel on the ground with a stability ball in front of you or you can use a yoga mat to kneel on for extra cushioning. The ball should be within arm’s reach.
Put the hands in a loose fist & place them on the ball. The forearms will also rest on the ball. Make sure the elbows are flexed up to 90 degrees. Keep the body in a straight line with the back flat. Roll the ball forward with the hands as the arms & body straighten out. This motion needs to be slow & controlled. Keep the gaze looking straight ahead. Extend out as far as you can go. The chest will touch the ball. Hold this position for a 2 to 3 seconds.
Slowly reverse the movement by bending the elbows to roll the ball back to the starting position. Keep your core tight, so the hips don’t drop.
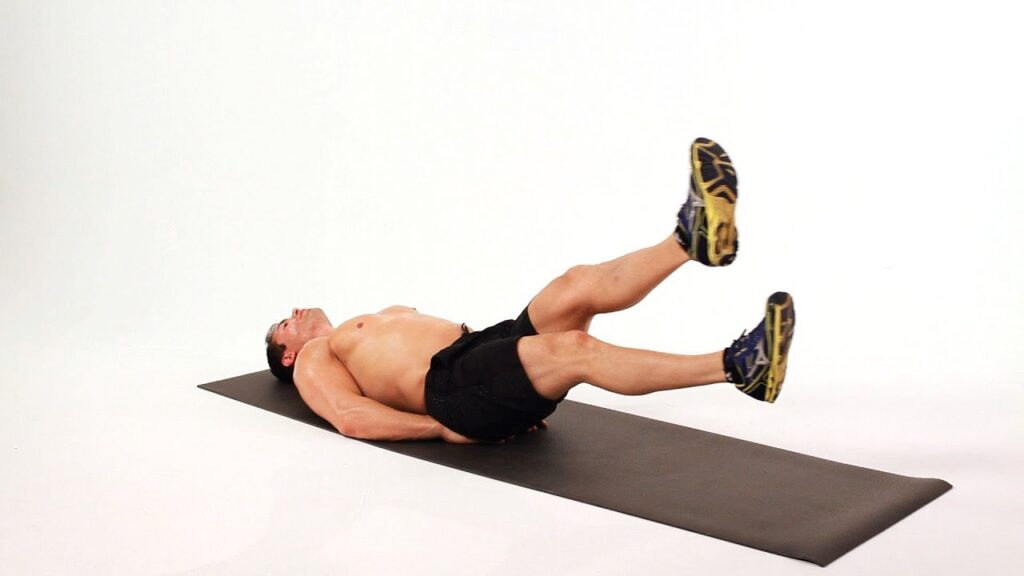

9.Flutter-Kicks:
How to do it?
Lie on your back & place the arms next to the body (straight). Lift both legs & keep them straight while moving them upwards & down the opposite way.
If there is a gap between the floor & the back, raise the upper body to round out the back. You can then lean on the elbow & place them next to the body to holding the weight.
20 seconds or 20 reps, 10 each side.
10.Sit-ups:
How to do it?
Do sit-ups the right way to keep them safe. Rather than placing the hands behind the head, cross them in front of you or slide them along the thighs to the knee. flexed the knees at a 45 degree angle. For this exercise, you have to Lie on the back with flexed knees & the feet anchored. Tuck the chin towards the chest to lengthen the back of the neck. Interlace the fingers at the base of the skull, cross the arms with the hands on opposite shoulders, or place the palms down alongside your body.
Breath out as you lift the upper limb toward the thighs. Breath in as you slowly lower by self back down to the ground.
11.Squats:

How to do it?
There have a lot of variations in squatting. Mix them up in the routines to challenge the body in new ways.
For this exercise, you have to stand with shoulder-feet width apart & toes facing front.
Move the hips back—flexed the knees & ankles & press the knees slightly open as you.
Now flexed the knees until the thighs are parallel to the ground.
Press into the heels & straighten the legs to return to the initial upright position.




i have stomach spasm two days ago, I have visited physician and also found this article online, really informative, that I discussed with my Doctor also.