Apprehension test
Table of Contents
What exactly is the apprehension test?
- Most of the time, this test is used to check the stability of the glenohumeral joint capsule or to look for anterior glenohumeral instability in conditions related to shoulder dislocation.
- The crank test is another name for it.
What does a positive Dread test do?
- If your test comes back positive, your shoulder may have a labral or bony lesion at the anterior inferior rim of the glenoid.
The goal of this test is
- The glenohumeral instability in the anterior direction and the integrity of the glenohumeral joint capsule are typically the purposes of this test.
- Additionally, it is used to check for shoulder dislocation.
- A portion of this exam:
- Part of this test- There is four parts to this test:
- Normal crank test Anterior translations signify fulcrum test Relocation test Posterior translations signify surprise test How does the test work?
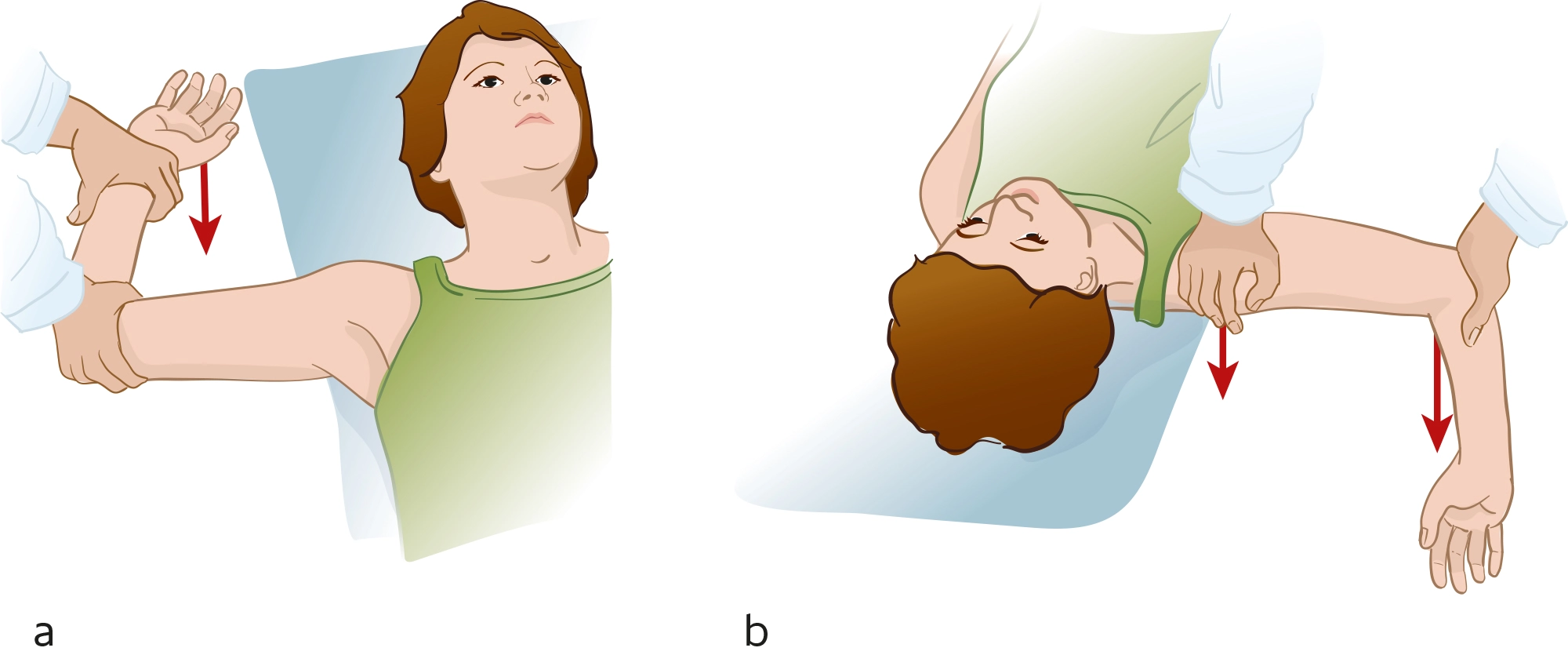
- The supine position is the test position.
- The therapist is abducting the patient’s shoulder and flexing the patient’s elbow up to 90 degrees while maintaining a neutral rotation.
- The examiner then carefully monitors the patient while slowly applying external rotation force to the arm at 90 degrees.
- If the patient is apprehensive about the procedure or does not feel any pain, the test is considered positive.
- Pain in relation to the maneuver but not to the fear; may indicate a pathology other than instability, such as posterior rotator cuff impingement, among other possibilities.
The Cluster’s Test Item
- When the test comes back positive, it is used in conjunction with the Jobes Relocation test.
- The fowler sign is the name given to this test for moving jobs.
- Supine is the test position.
- The edge of the examination table provides support for the scapula when the patient is supine.
- The arm is then positioned for 90 degrees of abduction and external rotation.
- After that, the examiner shifts to the external rotation and monitors the patient’s anxiety.
- The test can also be taken while seated.
- After establishing this position, the examiner places the hand known as the fulcrum on the humerus and applies the anterior translation force using the thumb on the posterity of the humerus.
- If the patient is apprehensive about the pain, the test for posterior instability is positive.
- The examiner then tries to move the joint by applying posterior translations or stress to the humeral head.
- If the pain or anxiety also decreases, the test for shoulder dislocation will be positive.
- In the last stage when the analyst leaves the back pressure, the patient is given an ordinary position and produces the wrench sound/return of aggravation and fear.
- The surprise test or anterior release test is the name given to this section of the test.
Evidence of the test
- The test’s sensitivity is 0.53
- Its specificity is 0.99.
- The likelihood ratio [+LR] is 53.0,
- The negative likelihood ratio [-LR] is 0.47.
Importance of the Apprehension test
- Patients who suffer from instability in their shoulders are more likely to suffer shoulder dislocation and injury.
- The instability of the shoulder can be traumatic, genetic, or microtrauma-tic.
- Patients experience muscle length discrepancies, other connective tissue issues, and joint capsule lengthening as the injury mechanism.
- The Bankart lesion is the most common injury, mostly due to anterior apprehension.
- Because dislocated shoulder causes damage to the surrounding nerves and vascular supply, this test is important for the apprehension sign.
FAQs
Typically, a labral or bony lesion at the anterior inferior rim of the glenoid is associated with a positive test result. The Posterior Impingement Sign, a variation of the Apprehension test, is described by Meister (2000). The shoulder is in the late cocking position as a result of this.
an apprehension that something undesirable will occur: a sense of unease regarding the future noncount] The idea of moving to a new city makes me nervous.
If the long axis force causes an increased sense of apprehension and muscle guarding to prevent posterior shoulder dislocation, the test is positive. Accuracy of the diagnosis: Unknown. Relevance of the Test: Neer and Foster defined multidirectional instability (MDI) at the shoulder for the first time in 1980.
The act of seizing, capturing, or otherwise arresting someone and preventing them from moving around is known as apprehension.
Trepidation There is a growing fear that fighting will resume.
He was a little nervous as he watched the election results.
The concern is expressed regarding the children’s safety.
Their fear made them tremble.
She discussed the anxieties and fears she had as a child.