Vitamin C Deficiency
This vitamin is cannot be produced by the human body. It is required for the health & repair of different tissues in the body, involving skin, bone, teeth & cartilage. A persistent shortage of vitamin C in the diet can cause a condition called scurvy. Symptoms of scurvy have easy bruising, bleeding, and pain in muscles and joints. Vitamin C insufficiency can be treated with a diet rich in vitamin C and supplements of vitamin C.
Table of Contents
What is Vitamin C Deficiency?
Lack or deficiency, of vitamin C in the body occurs because of a lack of adequate amounts of vitamin C in the diet. A lack of vitamin C suggests that new collagen cannot be formed. This causes different tissues in the body to start to break down & the health & repair of the body become affected. Chronic vitamin C deficiency, generally over 3 months or more, can induce an illness known as scurvy.
What is vitamin C?
This vitamin is also known as ascorbic acid, and these vitamins are a group of essences required in small amounts by the body to sustain health. It cannot be produced by the human body & so is an important element of the diet. Vitamin C is required to have a substance called collagen which is needed for the health & restoration of various tissues in the body, involving:
- Skin
- Bone
- Cartilage
- Ligaments & tendons
- Blood vessel walls
- Teeth
Various foods are rich in vitamin C, including:
- Citrus fruits such as oranges, grapefruit, limes & lemons.
- Berries like blackcurrants, strawberries, raspberries, blueberries & cranberries.
- Cantaloupe melon & watermelon.
- Kiwi fruit.
- Vegetables like spinach, green & red peppers, tomatoes, cauliflower, cabbage, broccoli, Brussels sprouts & potatoes.
Specific foods like cereals are reinforced with vitamin C, which indicates that they have vitamin C added to them. Vitamin C is also
encountered in fresh milk, fish & offal like liver & kidney. Vitamin C in the human diet is from fruit & vegetables. Boiling vegetables and fruits decreases the vitamin C content by around a third. The suggested everyday intake of vitamin C in the diet relies on age & sex. Advice may differ in various countries. Pregnant & breastfeeding women also require higher amounts of vitamin C in their diet.
- Children aged 1 to 10 years require 30 mg of vitamin C/ day.
- Children aged 11 to 14 years require 35 mg of vitamin C / day.
- Children over the age of 15 years & adults require 40 mg/day.
How common is vitamin C deficiency?
Scurvy due to vitamin C deficiency is infrequent in the UK.
Specific groups of people are more at threat of vitamin C deficiency.
They include:
- People dependent on medications or alcohol may not have a healthy, balanced diet.
- People who go on extremely restrictive diets.
- People living on a lower income tend not to purchase foods with a high vitamin C content.
- People with a medical illness that involves the body’s ability to digest & absorb food, like Crohn’s disease & ulcerative colitis.
- Older people may eat a less varied diet.
- Smoker: Smoking involves the absorption of vitamin C from foods & also vitamin C is used up in the body faster in those who smoke.
- Pregnant & breastfeeding women because they require higher quantities of vitamin C.
Cause Vitamin C Deficiency
The preceding cause of vitamin C deficiency is an imbalanced diet. This is because the human body does not inherently synthesize vitamin C, & it has to be delivered through external sources. This especially concerns food intake, including vegetables, fruits, & fortified foods.
This is why most reasons for deficiency of vitamin C affect an improper diet. Some of these are as follows:
- A diet lacking vitamin C-rich refreshed vegetables & fruits
- Mental health problems & other conditions such as anorexia
- Old age
- A restrictive diet due to health disorders such as a weak digestive system, allergies, etc.
Besides, there can be many other causes for the lack of vitamin C. These contain treatments, health requirements, & habits that limit the body’s capacity to absorb nutrients. Some of them are as follows:
- Ulcerative colitis
- Intake of illegal medicines & high amounts of alcohol
- Chemotherapy
- Crohn’s condition
- Smoking
- Hyperthyroidism
- Pregnancy
- Prolonged diarrhea
- Surgery
Etiology
Most animals need no exogenous vitamin C. For humans, vitamin C is an important vitamin. Humans lack the enzyme L-gluconolactone oxidase, & people must drink it. Therefore, vitamin C insufficiency & its manifestations have mostly been a product of inadequate dietary intake. Vitamin C is inherently found in fresh fruits & vegetables:
- Grapefruits
- Oranges
- Lemons
- Limes
- potatoes
- Spinach
- Broccoli
- Red peppers
- Tomatoes
Up to 90% of vitamin C is ingested in the form of vegetables & fruits. Deficiency of exposure to these foods has been the most frequent reason for the deficiency. Vitamin C is heat-sensitive, & boiling or cooking vegetables has released their nutritional worth. While a small part of vitamin C is found within leukocytes, adrenal glands, or the pituitary, there is extremely little storage of vitamin C in the body, & therefore, plasma concentration is mostly connected to current intake. Body storage of vitamin C is 1500 mg, & symptoms such as weakness appear after that level is decreased to less than 350 mg.
Risk factors for Vitamin C deficiency include:
- Alcoholism
- Babies only fed cow’s milk
- Seniors only consuming tea & toast diet
- Poor people who are not able to afford fruits & vegetables
- Smokers
- People with eating disorders
- Type 1 diabetes who have high vitamin C needs
- Individuals with disorders of the GI tract like inflammatory bowel disorder.
- People with iron overload, which cause the wasting of vitamin C by the kidneys.
- People with restrictive diets, and food allergies.
How Much Do You Need Vitamin D Deficiency?
If eating a level diet, it’s pretty easy to get sufficient vitamins. Adult women, who aren’t pregnant or breastfeeding require 75 milligrams of vitamin C per day: for men, 90 milligrams. A half cup of natural red bell pepper & 3/4 cup of orange juice will do it, while a half cup of cooked broccoli brings you slightly midway there. Your body doesn’t make or accumulate vitamin C, so you have to eat it every day.
Signs and symptoms of Vitamin C Deficiency
Unchecked early signs of deficiency of vitamin C can contain some of the following ongoing health issues:
- Bleeding from nose & gums
- Subperiosteal hemorrhage or bleeding between joints
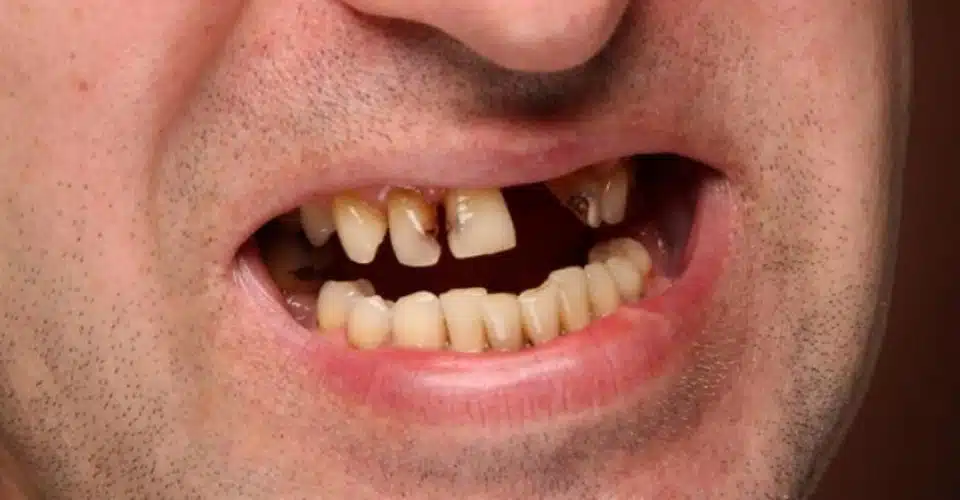
- Loose teeth
- Improper & delayed wound healing
- Weak bones
Other severe persistent signs due to insufficiency of vitamin C contain fever, nerve problems, shortness of breath, & convulsions.
People suffering from the same might not be capable to identify these as a result of a typical nutrient deficiency. However, a deficiency of vitamin C can cause severe diseases.
Who’s Falling Short?
The most likely people have those with an overall poor diet, with kidney disorders who get dialysis, heavy drinkers, & smokers. Require an extra 35 milligrams of vitamin C per day to help improve the damage caused by free radicals that form when you smoke.
Slow Wound Healing
When you get injured, vitamin C plays an important role in recovery. The body requires it to produce collagen, a protein that recreates an essential role in each stage of improving the skin. Vitamin C allows neutrophils, a type of white blood cell that fights off the infection, to work well.
Bleeding Gums, Nosebleeds, Bruises
Vitamin C keeps the blood vessels healthy, & it helps the blood clot. Collagen is also important for healthy teeth & gums. One study discovered that people with gum disorder who ate grapefruit for 2 weeks saw their gums didn’t bleed as much.
Weight Gain
Early investigation has discovered a connection between low levels of vitamin C & higher parts of body fat, specifically stomach fat. This vitamin may also play an important role in how well the body burns fat for energy.
Dry, Wrinkled Skin
People who eat a nutritious diet with plenty of vitamin C may have smoother, softer skin. One possible reason; Is that vitamin C is an antioxidant, it can assist protect the skin from free radicals. These radicals break down oils, proteins, & DNA.
Tired and Cranky
In an analysis, 6 of the 7 males who had low levels of vitamin C communicated they felt fatigued & cranky. That means a connection, though other things could be recreating a role. Other examinations of 141 office employees discovered that giving them vitamin C created them sense less tired within 2 hours, particularly if their level was lower to start with.
Weak Immunity
Since vitamin C has many jobs related to the immune system, it shouldn’t shock to learn that more likely to get sick & may have a harder time healing. There’s some proof that vitamin C can help save you from illnesses like pneumonia & bladder infections. It may even lower the odds of heart conditions & some types of cancer.
Vision Loss
If have age-related macular degeneration (AMD), it may get more impaired faster without vitamin C & other antioxidants & certain minerals. Getting adequate vitamin C from foods might help prevent cataracts, but we require more research to understand that relationship better.
Scurvy
Before the 1700s, this potentially fatal condition used to be a huge problem for sailors. Today, it’s fairly rare but possible if get only 10 mg/day of vitamin C or less. People with scurvy have issues like loose teeth, broken fingernails, joint pain, breakable bones, & corkscrew body hair. When increasing vitamin C, signs start gaining better in a day, & generally, it’s repaired within 3 months.
Rough, Bumpy Skin
Vitamin C plays a crucial role in the exposition of collagen, and a protein that is fruitful in connective tissues like skin, hair, joints, bones, & blood vessels.
When vitamin C levels are low, a skin disease known as keratosis pilaris can grow. In this situation, bumpy “chicken skin” begins on the back of the upper arms, thighs, or buttocks due to a buildup of keratin protein inside the pores.
However, there are numerous other potential reasons for keratosis pilaris, so its presence alone is not sufficient to diagnose a deficiency.
Corkscrew-Shaped Body Hair
Vitamin C insufficiency can also affect hair to grow in bent or spiral shapes due to faults that develop in the protein form of hair as it grows.
Corkscrew-shaped hair is one of the hallmark symptoms of vitamin C deficiency but may not be exact, as these ruined hairs are more likely to break off or fall out.
Hair anomalies usually resolve within one month of treatment with sufficient amounts of vitamin C
Bright Red Hair Follicles
Hair follicles on the surface of the skin have many small blood vessels that supply blood & nutrients to the place.
When the body is lacking in vitamin C, these small blood vessels become fragile & break easily, generating small, bright red spots to occur around the hair follicles.
This is learned as perifollicular hemorrhage & a well-documented symptom of severe vitamin C deficiency.
Taking vitamin C supplements generally resolves this symptom within 2 weeks.
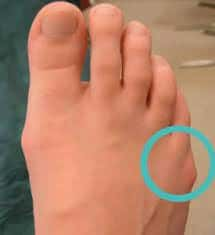
Spoon-Shaped Fingernails With Red Spots or Lines
Spoon-shaped nails are indicated by their concave shape & are usually thin & brittle.
More generally associated with iron deficiency anemia but has also been attached to vitamin C deficiency.
Red areas and vertical lines in the nail bed are known as fragment hemorrhage. It happens during vitamin C insufficiency due to weakened blood vessels that rupture efficiently.
While the observable shape of fingernails & toenails may help determine the likelihood of vitamin C deficiency, information that it’s not considered diagnostic.
Painful, Swollen Joints
Since joints have a lot of collagen-rich connective tissue, they can also be influenced by vitamin C deficiency.
Many recorded cases of joint pain associated with vitamin C deficiency, are usually extremely sufficient to cause limping and problems in walking.
Bleeding within the joints can also happen in people who are lacking in vitamin C, inducing swelling & additional pain.
Both symptoms can minister with vitamin C supplements, And it can be commonly determined within one week.
Weak Bones
Vitamin C insufficiency can also impact bone health. Low intake has been connected to an increased risk of fracture & osteoporosis.
The research discovered that vitamin C plays an essential role in bone formation, so a deficiency can increase the rate of bone loss.
Children’s skeletons may be significantly impacted by vitamin C deficiency, as they are still growing & developing.
Persistent Iron Deficiency Anemia
Vitamin C & iron insufficiency anemia usually occur together.
Symptoms of iron deficiency anemia contain paleness, fatigue, trouble breathing during exercise, dry skin & hair, headache & spoon-shaped fingernail.
Low levels of vitamin C may contribute to iron deficiency anemia by decreasing the absorption of iron from plant-based foods & negatively affecting iron metabolism.
Vitamin C deficiency raises the risk of extreme bleeding, which can contribute to anemia.
Chronic Inflammation and Oxidative Stress
Vitamin C is one of the body’s essential water-soluble antioxidants.
It assists prevent cellular damage by neutralizing free extremists that can induce oxidative stress & inflammation in the body.
Oxidative stress & inflammation have been connected to many chronic illnesses, including heart disease & diabetes, so reducing levels is likely helpful.
Low intakes of vitamin C have been connected to higher levels of inflammation & oxidative stress, as well as an improved risk of heart conditions.
One study discovered that grown-ups with the lowest blood levels of vitamin C were nearly 40% more likely to conceive heart failure within 15 years than those with the most elevated blood levels, even though they were not lacking in vitamin C.
Diagnosis of Vitamin C Deficiency
The vitamin C deficiency diagnosis is generally caused clinically in a patient who has skin and gingival signs. And it is in danger of vitamin C deficiency.
Laboratory: Laboratory verification may be available, and the complete blood count is done, usually detecting anemia. Bleeding, coagulation, & prothrombin times are normal. Laboratory diagnosis, which needs measuring blood ascorbic acid. It is sometimes done at academic centers.
Levels of less than 0.6 mg/dL [ less than 34 mcmol/L ] are considered borderline: levels of less than 0.2 mg/dL [ less than 11 mcmol/L ] indicate vitamin C deficiency.
X-rays: Skeletal X-rays can help analyze childhood but not adult scurvy. Differences are most evident in the lots of long bones, particularly at the knee. Early changes correspond to atrophy. Loss of trabeculae results in a ground-glass formation.
The rough cartilage, cortex thins, and line of calcified, means a white line of Fraenkel may be observable at the metaphysis. A zone of rarefaction or a linear fracture proximal & parallel to the white line may be observable as only a triangular imperfection at the bone’s lateral margin but is precise. The epiphysis compressed, and healing subperiosteal bleedings may promote & petrify the periosteum.
Dimensions of ascorbic acid levels in the white blood cell and platelet layer of centrifuged blood are not available.
In adults, scurvy must be determined from arthritis, hemorrhagic disorders, gingivitis, & protein-energy undernutrition. Hyperkeratotic hair bristles with surrounding hyperemia & bleeding are pathognomonic.
Bleeding gums, conjunctival bleedings, petechiae, & ecchymoses are nonspecific.
Differential Diagnosis
Differential diagnosis contains many cutaneous purpuric pathologies, including:
- Resistant thrombocytopenic purpura
- Henoch-Schonlein purpura
- Transmitted intravascular coagulation
- Rocky Mountain spotted fever
- Meningococcemia
- Hypersensitivity vasculitis
Mucosal involvement may mimic necrotizing gingivitis. Other vitamin deficiencies, including:
Niacin
Biotin
Zinc
It may present with skin changes; however, a symmetric, hyperpigmented inflammation on sun-exposed sites with the former & alopecia and deficiency of petechial & follicular findings in the latter 2 easily differentiate them from scurvy.
Treatment of Vitamin D deficiency
Replacement of vitamin C is normal, with up to 300 mg every day for children & 500 mg to 1000 mg daily for adults. The endpoint of relief is one month or upon resolution of clinical sequelae. Alternative treatment regimens for adults contain one to 2 g for up to 3 days observed by 500 mg daily for a week followed by 100 mg every day for up to 3 months. In addition to direct supplementation, educate the patient on lifestyle changes to ensure adequate intake & recommend cessation of alcohol & tobacco use.
In the absence of a vitamin, daily needs are up to 45 mg per day in children, 90 mg per day for males, 75 mg per day for females, & up to 120 mg per day for lactating females.
The key is to treat the immediate condition causing scurvy.
Complications
Vitamin C has extremely little storage in the body: however, especially, toxicity from over-supplementation can occur. As vitamin C is eliminated in the urine, its impact on other urinary metabolites has been studied. Notably, vitamin C has been demonstrated to increase renal oxalate excretion & ensuing calcium oxalate crystals & stone formations.
Prevention & Overcome Vitamin C Deficiency
The best method to prevent vitamin C insufficiency is to provide a diet rich in vitamin C. Some of the most prominent food origins of this nutrient are as follows:

Fruits:
- Kiwi fruit
- Lemons
- Strawberries
- Papaya
- Blackberries
- Guava
- Oranges
Vegetables:
- Carrots
- Spinach
- Bell Pepper
- Tomatoes
- Broccoli
- Cabbage
- Potatoes
Other eatables:
- Oysters
- Paprika
Vitamin C can deteriorate under the impact of heat during storage. This is why it is advisable to swallow raw & fresh fruits & vegetables as much as possible.
On the other hand, if have already been analyzed with a vitamin C deficiency, will require to consult a dietician who might recommend the following treatment methods:
- Oral vitamin C supplements
- Vitamin C injections
The healthcare professional will advise the ideal dosage, counting on the deficiency level. He or she will also specify a diet chart to speed up the healing process.
How Long Does it Take to Fix Vitamin C Deficiency?
Vitamin C insufficiency patients can observe considerable improvement in their health situation after starting to replenish the nutrient.
If wondering precisely how long it will take to fix vitamin C deficiency, here is a list of the signs & the possible time they might take to disappear.
- 24 hours: Pain, brainiac fog, fatigue, anorexia, & inactivity.
- 1-2 weeks: Intense weakness, bleeding, & bruising.
- 3 months: Complete healing.
This timeline may differ across people, depending on the extent of deficiency & other health disorders.
However, permanent injuries like extreme tooth deformation or loss of teeth are irreversible. This is should prioritize bringing good care of health to prevent vitamin C imperfection before it is too late.
FAQ
In adults, symptoms of vitamin C insufficiency develop after weeks to months of vitamin C shortage. Lassitude, weakness, irritability, weight loss, & vague myalgias, and arthralgias may produce. Symptoms of scurvy are related to deficiencies in connective tissues which form after a few months of deficiency.
Not eating sufficiently fresh fruits & vegetables can lead to deficiency. People feel exhausted, weak, and irritable, Extreme deficiency, named scurvy, leads to bruising, gum & dental problems, dry hair & skin, & anemia. The diagnosis is established on symptoms & sometimes blood tests.
Time-release vitamin C is usually the best choice since vitamin C has better bioavailability when taken in fewer doses throughout the day. A time-release procedure strives to solve this problem without taking multiple tablets, by removing the vitamin C gradually throughout the day.
Kakadu plums: The Kakadu plum is an Australian aboriginal superfood having 100 times more vitamin C than oranges. It has the highest available concentration of vitamin C, including up to 2,907 mg/ 100 grams.
Guava has the highest gram of vitamin C which is a lot higher than any further fruit. Yield on amazing guava recipes & add the distinction of guava to the diet.
Scurvy happens when there is a deficiency of vitamin C also means ascorbic acid. The shortage of vitamins causes symptoms of weakness, anemia, gum disease, & skin issues. This is because vitamin C is required to make collagen, an essential part of connective tissues.