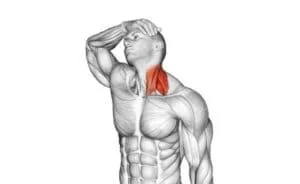
Trapezius Muscle
Table of Contents
What is Trapezius Muscle?
- The trapezius muscle is a large, triangular, paired muscle situated on the posterior aspect of the neck & thorax. When viewed combined, these pairs create a diamond or trapezoid shape, what its name says. The trapezius has many joining points, extending from the skull & vertebral column to the shoulder joint girdle.
- The trapezius relates to the superficial layer of the extrinsic muscles of the back, together with the latissimus dorsi, rhomboid major & minor, & levator scapulae muscles. The trapezius is largely included in actions of the shoulder girdle & is therefore functionally considered as a muscle of the upper extremity rather than of the back.
- The human trapezius muscle has a starting point that is more extensive than that of any other body muscle.
- The muscle is differentiated into 3 parts: descending (superior), ascending (inferior), & middle. The muscle assists in scapulohumeral rhythm via its joining on the clavicle & scapula, & to head balance through muscular control of the cervical spine.
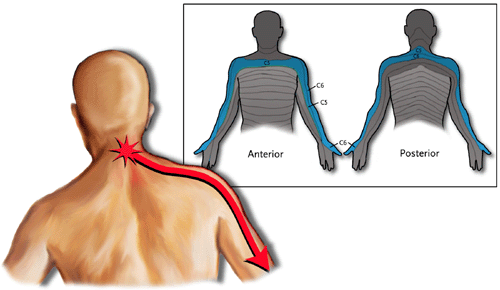
- In persons who are chronically stressed & anxious, the trapezius suffers. Hunching the shoulders & holding tension in the shoulders & neck, puts a continuous strain on the trapezius. Hence the trapezius is an important source of headache pain, usually a tension headache.
- Tearing & straining the trapezius is rare, usually only occurring in bodybuilders lifting very heavy a weight.
Relations of Trapezius Muscle
- According to their joining, course & location discussed earlier, we can differentiate the trapezius into 3 functional parts.
- The parts of the trapezius include:
- The descending (upper) part, made up of superior fibers
- The transverse (middle) part, made up of middle fibers
- The ascending (lower) part, made up of inferior fibers
- Together with the latissimus dorsi, the trapezius is the more superficial of the superficial extrinsic back muscles. It crosses the remaining muscles of this group, namely the rhomboids & levator scapulae. Deeper into the trapezius muscle, we can also find the serratus posterior superior, which relates to the intermediate layer of extrinsic muscles of the back.
- Furthermore, the trapezius covers many muscles of the superficial layer of the intrinsic muscle group, such as the splenius capitis, splenius cervicis, spinalis, longissimus, and iliocostalis muscles. The upper portion of the trapezius also overlies the suboccipital region.
- The anterior margin of the trapezius muscle creates the posterior border up to the posterior triangle of the neck. Moreover, its free inferior margin creates the medial boundary of the triangle of auscultation, an area of the chest wall not obscured by the scapula & only surfaced by the thin layer of muscle.
Origin of trapezius muscle
The trapezius muscle has different starting points along the midline of the posterior neck & back.
- The superior fibers join to the medial third of the superior nuchal line & the external occipital protuberance of the occipital bone. These fibers have a descending course near their ending point, hence why this part of the trapezius is termed the descending part.
- The middle fibers start from the nuchal ligament, which is joined to the spinous processes of the C1 to C6 vertebrae, as well as the spinous processes of C7 to T3 vertebrae & their intervening supraspinous ligaments. These fibers are directed horizontally and run laterally near the shoulder. Thus, these fibers present the transverse part of the trapezius.
- The inferior fibers arise from the spinous processes of the T4 to T12 vertebrae & their respective supraspinous ligaments. These fibers course superiorly & laterally towards their ending point & hence presents the ascending part of the trapezius.
Insertion of trapezius muscle
- Together with their course, all fibers of the trapezius diverge laterally on the superior angle of the scapula to join to their respective ending points.
- The superior fibers end on the posterior border of the lateral 3rd of the clavicle.
- The middle fibers end in the medial margin of the acromion of the scapula, as well as in the superior crest of the scapular spine.
- The inferior fibers end through an aponeurosis on a tubercule at the external apex of the medial end of the scapular spine.
Nerve Supply
- The trapezius muscle is the only muscle of the upper limb that does not collect its nerve supply from the brachial plexus. Instead, the motor nerve supply to the trapezius is transmitted by the accessory nerve (CN 11) as well as the anterior rami of the C3 & C4 spinal nerves, which also include proprioceptive/sensory fibers from the muscle.
Blood Supply
The vascular supply to the trapezius varies depending on the level.
- The descending (upper) part of the muscle is conveyed by transverse muscular branches starting from the occipital artery (branch of the external carotid), which crosses along the deeper surface of the muscle.
- The transverse (middle) part of the muscle is transmitted by the superficial cervical artery, or by a branch from the transverse cervical artery.
- The ascending (lower) part is transmitted by muscular branches of the dorsal scapular artery, which starts from the subclavian artery.
Action of trapezius muscle
- Descending part: it raises the pectoral girdle
- Middle part: it works to retract the scapula
- Ascending part: it works to depress shoulders
- Descending & ascending together: it helps the rotates scapula upside
- Bilateral contraction: it works to extend the neck
- Unilateral contraction:
- It works for Ipsilateral side flexion of the neck
- Middle part: it helps with ipsilateral side flexion & contralateral axial rotation of the upper thoracic area
The function of the Trapezius Muscle
- The trapezius muscle is active, together with the deltoid muscle & the rotator cuff muscles. In addition, the trapezius is also included in the movements of the head & neck.
- The motion of the trapezius muscle is broadly dependent on the direction of the fibers that are squeezing.
Descending (upper) fibers
- Synonyms: Flexio lateralis cervicis
- The descending (upper) fibers work with the levator scapulae muscle to generate an elevation of the scapula at the scapulothoracic joint. In the same manner, they also engage the level of the shoulders against gravity e.g. when weight is being held in the hand.
- When the muscle is working unilaterally, the descending fibers create an ipsilateral lateral flexion of the head & neck by working on the atlanto-occipital joint & upper cervical vertebrae, respectively. Unilateral contraction might also result in opposite side rotation of the head at the atlantoaxial joint. Bilateral contraction of the descending part of the trapezius (i.e. when both right & left muscles contract) causes an extension of the head & neck.
Ascending (lower) fibers
- The ascending (lower) fibers are done for the depression of the medial part of the scapula, thus lowering the shoulder. This action work is especially necessary for activities in which the shoulders are lower down against resistance, for example when using the hands to assist ownself up from a seated position.
- Combined with the descending part, the ascending fibers also create a rotation of the scapula around an axis that passes anteroposteriorly via the base of the scapular spine.
Transverse (middle) fibers
- The transverse (middle) fibers work combine with the rhomboids to create a retraction of the scapula, by pulling it towards the midline. The trapezius muscle is also used for the upward rotation of the scapula, together with the serratus anterior muscle. This allows us to raise our arms above our heads above the level of the shoulder.
Clinical Significance of the Trapezius Muscle
- Dysfunction of the trapezius can occur in the winged scapula, occasionally further specified as “lateral winging”abnormal mobility & function of the scapula (scapular dyskinesia). There are many causes of trapezius dysfunction.
Palsy
- Trapezius palsy which occurs due to damage to the spinal accessory nerve is symptomized by difficulty with arm adduction or abduction or is associated with a drooping shoulder, or shoulder or neck pain. Intractable trapezius palsy will be surgically managed with an Eden-Lange procedure.
Facioscapulohumeral muscular dystrophy
- The trapezius muscle is 1 of the commonly affected muscles in facioscapulohumeral muscular dystrophy (FSHD). The lower or middle fibers are affected initially, or the upper fibers are commonly preserved until later wards in the disease.
Underdevelopment of Trapezius Muscle
- Although occasionally, underdevelopment and absence of the trapezius have been seen to correlate to neck pain or poor scapular control that are not responsive to physical therapy. The absence of the trapezius has been seen in association with the Poland syndrome.
Injuries that affect how the traps works include:
- Trapezius Muscle strains: Due to an accident, rigorous exercise, and overuse, the trap muscle can be stretched too far, or a tear occurring. This common injury will lead to muscle cramps and muscle spasms. Back strains or back spasms can affect the trap muscles and any muscles in the lower back.
- Nerve damage: If the nerve that powered the trapezius gets injured, the trapezius muscle will not work as it should do previously. Though rare, this type of injury will result from neck surgery (such as surgery to excise a tumor). Nerve damage might cause muscle weakness. In chronic cases, the entire trap muscle will be paralyzed.
- Tightness or pain: Poor posture, such as sitting at a desk with hunched shoulders for prolonged periods of time, can be causing tightness in the traps. People who are sitting at a computer for several hours a day have a higher risk of severe pain in the neck or shoulders. Headaches will result from tension in the shoulders, especially if the tight muscles gave pressure on the nerve that holds the trapezius.
Stretching Exercise For Trapezius Muscle
Trapezius Self Stretching:
- This is a good method to stretch the trapezius muscle.
- How to do – Took a sitting or standing position. Place the ipsilateral hand on the back & touch the other side of the back.
- Now flex the head on another side. If you want to stretch on the right side then flex the head on the left side.
- When you felt stretched then stop there. Hold that position for 30 secs and then do it on the other side.
- Do it two to three times.
Shoulder stretch:
- You are extended one arm outwards in front of you.
- With the other arm, pull the elbow joint of the outstretched arm toward the chest.
- Hold this stretching position for about 30 secs.
- Repeat this stretching exercise ten times in one session & repeat this session three times per day.
Extended Child’s Pose on Fingertips stretch:
- The patient is Kneeling on the floor.
- Try to Touch the big toes together & the patient is sitting on the heels.
- Next, separate the knee joint about as wide as the hip joint.
- Then Bend the forward from the hip joint & walk the hands out as far in front of them as possible.
- With the arms extended palms are facing down then come up onto the fingertips as if the ball underneath the palms & melts the chest toward the floor.
Ear to shoulder stretch:
- You are sitting with a straight spine & tilt your head toward your right shoulder joint.
- Then Go as far as you can without straining & lifting your left shoulder joint.
- For Deepen the stretch by using your right hand to gently pull your head down.
- Hold this stretching position for 30 seconds.
- Repeat this stretching exercise 3 times in 1 session & 3 sessions per day.
Cross arm stretch:
- Start with your left arm across the front of your body at about chest height.
- For Support use your left arm with the elbow joint crease of your right arm.
- Then use your right hand to hold your left arm.
- Stretch out your shoulder joint & continue to face forward.
- Hold this stretching for 30 seconds.
- Repeat this stretching exercise 3 times in 1 session & 3 sessions per day.
Thread the needle stretch:
- This exercise starts with all fours with your hands directly under your shoulders & your knee joint underneath your hip joint.
- Lift your right hand & slowly bring it over to the left with your palm facing up.
- Rest your body on your right shoulder & turn your head to face to the left.
- Make sure you are not sinking onto your shoulder joint.
- Hold this exercise position for 30 seconds.
- Slowly release & come back to the original position.
- Repeat this stretching exercise 3 times in 1 session & 3 sessions per day.
Across-the-chest stretch:
- Start this exercise with your right arm across your chest.
- Place the arm in the crease of your left elbow joint & use your left hand to support your arm.
- Hold this stretching position for up to 1 minute.
- Then Repeat on the opposite side.
- Do this stretching each side 3–5 times.
- To deepen the stretch, lift your arm at shoulder height.
- Repeat this stretching 3 times in 1 session & 3 sessions per day.
Doorway trapezius stretch:
- You are standing in a doorway with your elbow joint & arms forming a 90-degree angle.
- Then Step your right foot forward as you press your palms into the sides of the door frame.
- Lean forward & engage your core muscle.
- Hold this stretching position for up to 30 seconds.
- Repeat the stretching with your left foot forward.
- Repeat this stretching exercise 3 times in 1 session & 3 sessions per day.
Pendulum stretch:
- You are standing with the feet hip-width apart.
- Lean forward & look at the ground.
- Then Place the right hand on a table & chair for support.
- Let the left arm hang down.
- then Swing the left arm gently in small circular motions & letting gravity do most of the work.
- Continue this stretching for 30 seconds to 1 minute.
- Then Change the direction of the motion.
- Repeat this stretching exercise 3 times in 1 session & 3 sessions per day.
Cross-body trapezius stretch:
- You are standing with the feet hip-width apart.
- Then try to Stretch the right arm out straight.
- Start the right arm across the body, so that place the hand points to the floor on the other side of the left leg.
- Bend the left arm at the elbow joint.
- Then Hook the left forearm under the right arm & for support use the right arm above the elbow joint.
- Use the left forearm to pull the right arm further in & across the body & try to stretch the back of the right shoulder.
- Hold this stretching for 30 seconds, then repeat this stretching on the other side.
- Repeat this stretching exercise 3 times in 1 session & 3 sessions per day.
Eagle arm stretch:

- You are standing with your feet hip-width apart.
- During Inhale & lift the arms to the sides.
- During Exhale & swing the arms in toward the body.
- Then Allow the right arm to cross under the left arm.
- Cradle the left elbow joint in the crook of the right elbow joint.
- Start the palms together so that they reach for each other.
- When the palms are not touching & hold the backs of the hands together.
- Then take three or four deep breaths.
- Release the stretch & repeat it on the other side with the left arm crossed under the right.
- Repeat this stretching exercise 3 times in 1 session & 3 sessions per day.
Standing wall trap stretch:

- First Place both hands on a wall from a 90-degree angle to your body.
- Then Walk your feet back till your arms are straight & bow, hinging forward at the hip joint.
- But take care of this thing Don’t push on the wall & don’t allow your arms to raise too high to avoid shoulder impingement.
- Must be Keep your shoulder blades set back & avoid scrunching your shoulder joint around your neck.
- Repeat this stretching exercise 3 times in 1 session & 3 sessions per day.
Strengthening Exercise For Trapezius Muscle
Trapezius Strengthening exercise:
- First, place the knee joint on a bench or chair.
- Try to lean forward so that the hand is reached the bench and also help to support the weight.
- The other hand is placed at the side and palm facing the body.
- Try to raise the arm and rotate the hand to the thumbs-up position.
- Stop this exercise when the hand is at shoulder height and the arm is parallel to the floor.
- Slowly lower the arm to the original position for a count of five.
- Do this exercise two to three times per day.
- Do the exercise by pressing on the side of the head. Repeat eight times, then on other sides.
Prone Rows Exercise
- Lie on the stomach with the arms dangling off the side of the bed (try angling the body so your head is facing the corner of the bed).
- Use a pillow under the stomach for comfort. Begin by pulling arms back while bending elbows & squeezing shoulders blades combine then slowly back to starting position.
- Do not lift the head up while pulling the arms back.
- Repeat twenty times. Perform two times a day.
Shoulder blade squeeze exercise
- Sit or stand up high with good posture.
- Keep your shoulders relaxed and down,
- slowly squeeze your shoulder blades together and hold for 3 seconds. then relax.
- Repeat 10 to 12 times.
- for progression do this exercise with theraband
External Rotation exercise
- Attach theraband to a fixed object at waist level
- Rotate shoulders back and down and maintain this position
- Place towel between elbow and side
- Slowly rotate the hand down from the abdomen
- Hold 3 sec. Repeat 12-15 times
Prone rowing exercise

- lies prone on your bed with the arm hanging freely off of the side.
- While holding on the shoulder blade ‘set’,
- raise the arm against the floor while bending at the elbow.
- The elbow should be raised and the side of the body until the hands touch the lower ribs.
- Always return slowly to the start position.
- Perform 2 sets of 10-15 repetition
Angel Wings exercise
- Stand with your head, shoulders, upper back, and butt pressed close up to the wall. Your feet may need to be 10 – 12 inches from the wall.
- Keeping your knees slightly bent will reduce muscle pressure.
- With the reverses of your hands against the wall, stretch your arms straight above your head. you’re in the starting position.
- Squeeze your mid-back muscles as you slide your arms down close to your shoulders. Keep your body firmly pressed close to the wall.
- When elbows are just below shoulders, pause for just a sec, also slide your arms back to the starting position.
- Do 10 – 20 repetitions
Shoulder Diagonals exercise

- The patient stands with theraband lower their opposite foot
- While grasping theraband, move shoulders up and down
- With your hand at your opposite hip, slowly raise it beyond
- your body, as if you’re pulling a blade
- Hold 3 seconds and repeat 10-15 times
Lateral Raises exercise
- Stand with the arm at your side with the elbow straight and the hands twisted so that the thumb’s face is ahead.
- put up the arm straight out to the side, palm downward, until the hands reach shoulder position.
- Do not put up the hands forward than the shoulder. Pause and slowly down the arm.
- Perform 3 sets of 10-15 repetitions. for progression do this exercise with a dumbbell
Upright row exercise
- This is a common exercise for strengthening the trapezius. You can also try this exercise with dumbbells or a therabend in your hands.
- Stand up straight.
- With your fists held, pull up your fists as high as you can while bending your elbows, keeping your hands close to the front of your body. Hold for a count of ten.
- Release your arms back into a relaxed position, fists still hold
- Reprise 20 times.

Physioball Scapular Exercises
- Stand with hand placed on physio ball beside a wall
- Bring shoulders up and down
- Slowly rotate your hand up and down over the ball
- Maintain shoulders up and down. repeat 15 to20 times
Horizontal Rows exercise

- Attach theraband around a stable object, like a pole
- The patient can either kneel or stand,
- Grasp both ends of the theraband, Bring shoulders up and down
- Slowly pull your elbows up, squeezing your shoulder blades together
- Hold 3 seconds and repeat 10-15 time
Wall Push-ups exercise
- Stand facing a wall.
- Place your hands on a wall, slightly wider than shoulder-width apart.
- Gently bend your body to the wall while squeezing your shoulder blades together, repeat the 10-15 time
Push up exercise
- lying face down on the floor, positioning your hands slightly wider than your shoulders.
- Don’t lock out the elbows; keep them slightly bent.
- your legs should be straight back and balanced by your hands and toes. raise your body off the floor and back to starting position,
- 10-12 times.
Shoulder blade squeeze exercise
- You are Standing up straight.
- Bring the elbow joint back & inward.
- Pulling the shoulder joint blades down & back.
- Then Return to the starting position.
- Repeat this exercise 10 times in 1 session & repeat this session 3 times per day.

Arm circles exercise
- You are standing upright with your arms are feet shoulder-width apart & your arms straight down your sides.
- Then Move your arms around in big circles going forward.
- Must Be sure to keep your arms straight.
- After several reps, switch – to the opposite direction so that you move your arms in a circle going backward.
- Repeat this exercise 10 times in 1 session & repeat this session 3 times per day.
Plank exercise
- You are lying on the floor facing down, with your elbow joint bent.
- Then Tighten your abdominal muscles as you lift the hip & knee joints off the floor.
- Then Hold this position for 30 seconds & return to starting position.
- Repeat this exercise 10 times in 1 session & repeat this session 3 times per day.
Shoulder raises exercise
- You are standing or sitting position.
- This exercise starts with your arms by your side & a straight back.
- Then slowly lift your shoulder joint toward your ears.
- Hold this exercise for 10 seconds & return to the slowly starting position.
- Repeat this exercise 10 times in 1 session & 3 sessions per day.
Shoulder rolls exercise
- First Maintain good posture in the standing or sitting position.
- Then Roll your shoulders joint up, back & down.
- Do this exercise movement 10 times.
- Then roll your shoulder joint up, forward & down 10 times.
- Repeat this exercise 10 times in 1 session & 3 sessions per day.
Standing arm swings exercise
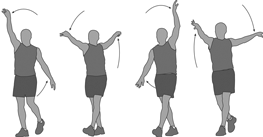
- You are standing with your arms by your side & your palms facing your body.
- Then Swing your arms forward to bring your arms as high up as they go without raising your shoulders joint.
- Lower the arms back down & bring them as far back as you can.
- Keep the rest of your body still.
- Continue this movement for 1 minute.
- Repeat this exercise 10 times in 1 session & 3 sessions per day.
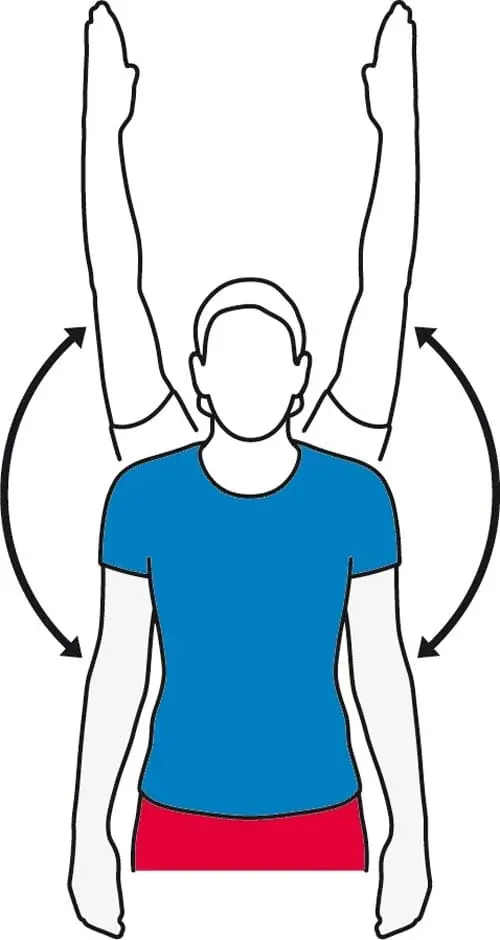
Standing arm lifts exercise
- First Make fists with your hands & bring them in front of your hip joint.
- Then do the Inhale as you lift your arms overhead so that your hands come together above your head.
- After that Lower back down to the original position.
- Repeat this exercise 10 times in 1 session & 3 sessions per day.
Wide-legged standing forward bend exercise
- You are standing with your feet wider than hip distance with your toes facing forward.
- Then Interlace your hands behind your back & open your chest.
- Engage your leg muscles & must keep a slight bend in your knee joint.
- Hinge at the hip joint to fold forward & bringing your arms over your head toward the floor.
- Then Allow your head to hang down & tuck your chin in slightly to your chest.
- Remain in this pose for up to 1 minute.
- Repeat this exercise 10 times in 1 session & 3 sessions per day.
Cat cow pose exercise
- First Place your hands underneath your shoulder joint & your knee joint underneath your hip joint.
- During inhale fill your belly with air & let it sink as you look up.
- During Exhale as you engage your abdominal muscle.
- Then try to tuck your chin into your chest & around your spine.
- Continue to do this movement for a few minutes & must focus special attention on your shoulder joint.
- Repeat this exercise 10 times in 1 session & 3 sessions per day.
Reverse prayer pose exercise

- You are performing this pose in the sitting, standing position & tree pose.
- Then start this exercise with your hands behind your back with the backs of your hands facing each other & your fingers facing down.
- From this position flip your hands in the other direction so that your fingers are facing up.
- Then turn your palms to face each other.
- Press your palms together & draw your elbow joint slightly back & open your chest.
- Must be Keep your spine straight.
- Then Hold this pose for 10 seconds.
- Repeat this exercise 10 times in 1 session & 3 sessions per day.
Cow face pose exercise

- Start this exercise in the sitting position & take to your left elbow joint up to the side of your head with your hand facing down your spine.
- With the help of your right hand draw your left elbow joint over to the right as your hand moves further down your spine.
- When you feel comfortable you can also bend your right arm & bring your right hand up to clasp your left hand.
- Hold the pose for 1 minute.
- Repeat this exercise 10 times in 1 session & 3 sessions per day.
Eagle arms spinal rolls exercise
- In the sitting position, extend your arms out to the sides.
- Cross your elbows joint in front of your body with place your right arm on top.
- Then Bend your elbow joint & placing the backs of your forearms & hands together.
- Try to reach your right hand around to bring your palms together.
- Hold this position for 30 seconds.
- During the exhale, roll your spine as your draw your elbow joint in toward your chest.
- During the inhale, open your chest & lift your arms.
- Then Continue this movement for 1 minute.
- Repeat this exercise 10 times in 1 session & 3 sessions per day.
Cross-body arm swings exercise
- You are standing with the feet hip-width apart.
- During Inhale lift the arms out to the sides & squeezing the shoulder blades together.
- During Exhale gently bring the arms in toward each other.
- Try to Cross the right arm under the left must keep both arms straight.
- During the Inhale & swing the arms back out to the sides & squeezing the shoulder blades together.
- During the Exhale & gently swing the arms in toward each other again.
- Cross the left arm under the right & must keep both arms straight.
- Repeat this exercise 10 times in 1 session & 3 sessions per day.
Ragdoll Pose exercise
- It is a forward-bend yoga pose which is help to release tension in the shoulder joint.
- You are in a Standing position with the feet hip-width apart.
- Bend the knee joint slightly.
- Bend forward & try to touch the toes.
- Must be Keep the stomach against the bent knee joint to support the lower back.
- Then Place each hand on the elbow joint of the opposite arm.
- Try to crown the head should point toward the floor.
- Let the head hang heavily & releasing tension in the neck & shoulders joints.
- Hold this pose for 1 minute.
- Repeat this exercise 10 times in 1 session & 3 sessions per day.
Shoulder rotation exercise
- With your back to a wall allows your shoulder blades to rest in a neutral position & bring both elbow joints out to 90 degrees.
- Then Without moving your elbow joint & turn your right arm upward, so that the back of your right-hand touches the wall & your left arm downward, so that your left palm is touch the wall.
- Then Slowly switch for about 30 seconds & trying to must keep your arms at 90 degrees.
- Repeat this exercise 10 times in 1 session & 3 sessions per day.
T, Y & I movements
- Start this exercise With your back to a wall & stand with your palms facing out.
- Then slowly bring your arms up to make a T shape & must be keeping your arms & back in contact with the wall.
- After that Continue to bring your arms up to make a Y shape, then do the I shape & try to touch your thumbs overhead.
- But must be kept Focus on your shoulder blades flat against the wall.
- Repeat this all movement 10 times in every shape & 3 sessions per day.


12 Comments