Test for the Intermittent Claudication
- Intermittent claudication indicates arterial insufficiency in the tissue.
- The increased circulatory demand of the tissues during activity makes it most frequently obvious.
- Both neurogenic and vascular conditions can cause intermittent claudication.
- The vascular form frequently presents with symptoms in the legs and is most frequently caused by arteriosclerosis, embolism, or thrombi-angiitis obliterans.
- The neurogenic form, also known as pseudo claudication/claudaquina syndrome, is frequently brought on by spinal stenosis and the impact it has on the blood flow to the spinal cord and cauda equina.
- In this instance, the back/sciatic nerve distribution may show symptoms.
Table of Contents
Name of the special test of the intermittent claudication
Bicycle test of van gelderen
Stoop test
Treadmill test
Bicycle test of van gelderen:
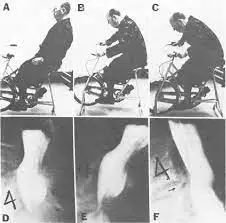
- Purpose = In order to establish whether a patient has neurogenic intermittent claudication, the van Gelderen bicycle test is performed.
- Technique: The patient is sitting on a stationary bike.
- The patient begins the test by cycling while stooping backward to emphasize the lumbar lordosis.
- The first phase of the test is successful if the patient experiences discomfort in the buttock and posterior thigh, which is a sign that something is happening, followed by tingling in the afflicted lower extremity.
- The patient is then instructed to lean forward while still pedaling by the tester.
- The second phase of the test is positive if the pain passes quickly.
- if the test’s second ingredient is positive.
- When the patient sits up straight again, the discomfort in the seated posture returns.
- Whether the patient has neurogenic intermittent claudication is determined by the test.
Stoop test:
- The goal of this stoop test is to evaluate neurogenic intermittent claudication and see if there is a correlation between neurogenic symptoms, posture, and walking.
- Technique: Neurogenic intermittent claudication patients experience discomfort within 50 m (165 ft) of where they are standing when they move quickly.
- As a result, the patient flexes forward to ease their discomfort.
- When the patient is seated and stretching their body forward, these sensations may also be alleviated.
- The test is unsuccessful if the flexion movement does not alleviate the symptoms.
- The symptoms might possibly return by using an extension.
Treadmill test:

- Purpose: This test is also used for the diagnosis of intermittent claudication in patients.
- Technique=The patient’s preferred walking up is tested in two trials, one at 1.2 mph and the other at that speed.
- The patient walks upright, which means that for the first 15 minutes or until the emergence of severe symptoms (symptoms that would cause the patient to stop walking in everyday life), no leaning forward or holding onto the handrails is permitted on the treadmill.
- Recorded are the times of the initial symptoms, overall ambulatory time, and triggering symptoms.
FAQ
With no central canal or foraminal stenosis that may be mistaken for intermittent neurogenic claudication, the van Gelderen cycling test is developed to stress the LE vascular system.
The “bicycle test” typically verifies the link between posture and radicular discomfort and helps rule out intermittent claudication caused by vascular insufficiency. Walking often might exacerbate the discomfort associated with intermittent claudication and so-called “pseudoclaudication” conditions.
Stress tests demonstrate how effectively your heart functions under stressful conditions. When your heart is exerting maximum effort to pump blood throughout your body, some cardiac illnesses are simpler to detect. Stress tests thus measure your heart rate when you work out on a treadmill or stationary bike.
An exercise stress test is intended to identify the presence of fatty deposits (plaques) that obstruct a blood vessel by at least 70% in one or more of the coronary arteries supplying the heart. To validate the test findings, further testing is frequently necessary.
Your age has a maximum heart rate of 220 for adults. Therefore, your maximal heart rate estimate at 40 years old is 220 – 40 = 180. Some medical professionals aim for 85 percent of the anticipated maximum heart rate while doing diagnostic treadmill tests.