Stress test of the Sacroiliac Joint
A stress test of the sacroiliac joint is a diagnostic procedure used to evaluate the stability and integrity of the joint. The sacroiliac joint is located in the lower back and connects the sacrum (the triangular bone at the base of the spine) to the ilium (the large, wing-shaped bones of the pelvis).
These tests are used to clinically evaluate the dysfunction of the SI joint.
This test applies stress to the SI joint.
These clinical tests are used by therapists when the patient is complaining about pelvic and lower back pain.
Table of Contents
Name of the Stress test of the Sacroiliac Joint:
- Prone gapping test
- Squish test
- Superior-inferior symphysis pubic stress test
- Thigh thrust test
- Torsion stress test
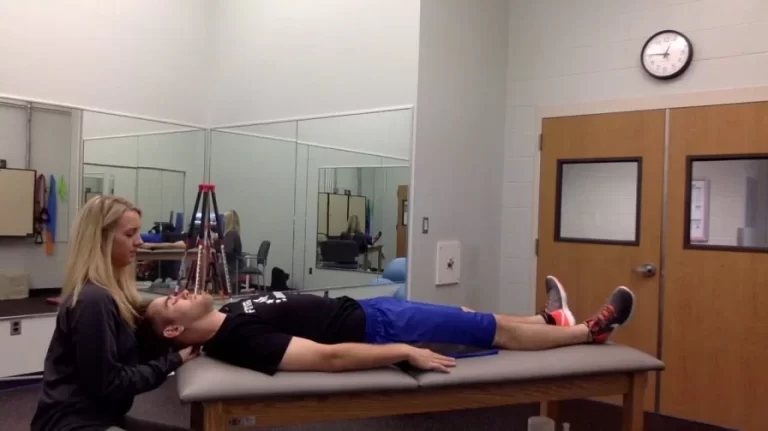
- Prone gapping test:
Prone gapping test
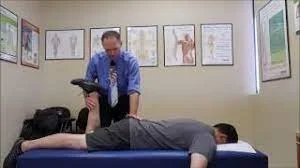
- This test is also called the Hibb’s test.
- When the patient is prone, the posterior sacroiliac ligaments may be stressed.
- The posterior sacroiliac ligament’s integrity is assessed using this prone gapping test.
- Technique: The patient’s hip must have a complete range of motion and be pathology-free in order to perform the test.
- For the test, the patient is in a prone alignment.
- The examiner (or therapist) uses his or her chest to support the pelvis.
- The patient’s hip is medially rotated, which means internally rotated as much as feasible, and the patient’s knee is flexed to 90 degrees or more.
- The examiner (therapist) palpates the sacroiliac joint on the same side while pressing the hip joint all the way into the medial rotation.
- The test is replicated on the other side, with the examiner comparing the degree of opening & the quality of the movement at each sacroiliac joint as well as stressing the posterior sacroiliac ligament.
Squish test:

- Purpose = This squish test is used to assess the integrity of the posterior sacroiliac ligament.
- Technique: For the test, the patient is in a supine position.
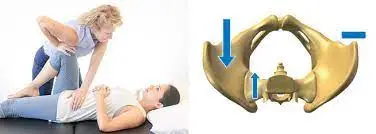
- The examiner [ therapist ] sets both hands on the patient’s ASIS = anterior superior iliac spine and iliac crest & pushes down & in at a 45′ angle.
- This movement tests the posterior sacroiliac ligaments.
- Result = A positive test is shown when the patient is feeling the pain.
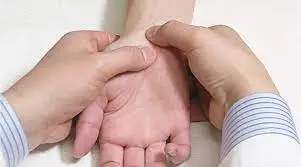
Superior-inferior symphysis pubic stress test:
- Purpose = This superior symphysis pubic stress test is used to evaluate the pain of the symphysis pubic.
- Technique: For the test, the patient is in a supine position.
- With the help of one hand, the examiner (therapist) places the heel on the superior pubic ramus of one pubic bone and the inferior pubic ramus of the other pubic bone.
- The examiner then stuffs the hands together, applying a shearing force to the symphysis pubic.
- Result =If the pain is present in the symphysis pubic, it is considered a positive test.
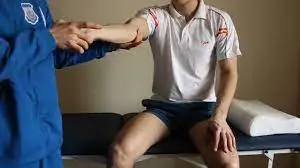
Thigh thrust test:
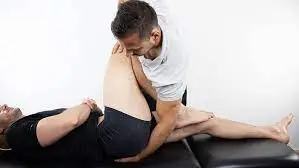
- This test is also understood as the sacrotuberous stress test / POSH posterior shear test.
- Purpose = This thigh thrust test is used to evaluate the pain in the sacroiliac joint.
- Technique = The patient lies in a supine while the examiner [ therapist ] passively flexes the hip on the test side to 90′.
- On the text side, the examiner (therapist) pushes through the knee and hip joints while using one hand to palpate the sacroiliac joint.
- Result = Pain is present in the sacroiliac joint on thrusting is a positive test.
Torsion stress test:
- The position of the patient lies in the prone position for the test.
- The examiner ( therapist ) palpates the spinous process of L5 with one thumb having it stable.
- The other hand of the examiner (therapist) fits around the anterior ilium on the opposite side and is used to raise the contralateral ilium.
- The rotational motion stresses the lumbosacral ligaments & the sacroiliac joint.
FAQ
The Sacroiliac Joint (SIJ) Compression Test or “Approximation Test” is a pain-inducing test that places stress on the SIJ components, particularly the posterior SIJ ligament, in order to approximate the patient’s symptoms.
Physical Therapy Management. Purposes Use cold packs and anti-inflammatory drugs to reduce discomfort. A sacroiliac belt can also be utilized if the sacroiliac joint is badly irritated. Enhance core strength and SI joint stability (with mobilizations, manipulations, and exercise therapy).
A squish test is performed to evaluate the sacroiliac joint’s mobility. The patient is in a supine position. Performing the test, the examiner maintains his or her body above the hands while placing their hands on each ASIS. To contact the tissue, push inward at a 45-degree angle with both hands.
Directly on the sacrum, one hand is positioned, while the other hand is supporting it. Since the ilia are fixed by the examination seat, the goal is to impart anterior shear stress to both sacroiliac joints. If discomfort is experienced in the sacroiliac area, the test is considered a positive test.