TAPPING TECHNIQUE FOR KNEE PAIN
Table of Contents
Introduction
Tapping for knee pain is the most popular technique nowadays. Elastic therapeutic tape, also called kinesiology tape or kinesiology therapeutic tape, is an elastic cotton strip with an acrylic adhesive that is purported to ease pain and disability from athletic injuries and a variety of other physical disorders. Taping your knee can help stabilize it when you’re active and can give relief from pain.
Kinesiological taping is a rehabilitative cum protective use of stretchable kinesiological tapes to provide
- reduction of Knee pain
- enhancing performance
- preventing injuries
- support to the knee joint
- reposition of structure
- facial and ligamentous correction.
- It facilitates the healing method while providing full memory with support to the joints’ supportive structure in addition to mobilization effects.
- Knee pain may be a common symptom in folks of all ages. it should begin suddenly, typically once an Associate in Nursing injury or exercise. Knee pain conjointly might begin as a gentle discomfort, then slowly decline. mostly seen in aged folks.
- Knee pain is that the most common system grievance that brings folks to their doctor. With today’s progressively active society, the amount of knee issues area unit increasing.
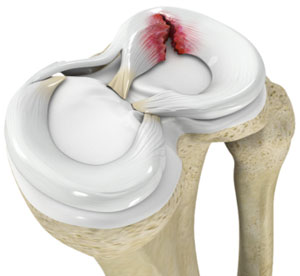
Anatomy of the Knee Joint
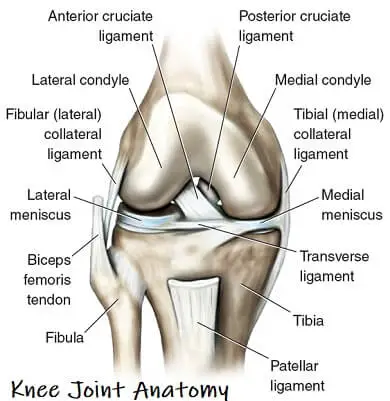
- The knee is the largest joint within the body, and one of the foremost simply abraded. it’s created from four main things: bones, cartilage, ligaments, and tendons.
- 1. Bones: 3 bones meet to create your knee joint: your leg bone (femur), shin (tibia), and kneecap (patella).
- 2. articulary cartilage: The ends of the leg bone and shin, and therefore the back of the patella are lined with articulary animal tissue. This slippery substance helps your knee bones glide swimmingly across one another as you bend or straighten your leg.
- 3. Meniscus: 2 wedge-shaped items of meniscal animal tissue act as “shock absorbers” between your leg bone and shin. completely different from articulary animal tissue, the gristle is hard and rubbery to assist cushion and stabilize the joint. once folks name torn animal tissue within the knee, they’re typically relating torn gristle.
- 4. Ligaments: Bones are connected to alternative bones by ligaments. The four main ligaments in your knee act like robust ropes to carry the bones along and keep your knee stable.
- 5. Collateral ligaments: These are found on the perimeters of your knee. The medial collateral ligament is on the within of your knee, and therefore the lateral collateral ligament is on the skin. They manage the sideways motion of your knee and brace it against uncommon movement.
- 6. symmetric ligaments: These are found within your ginglymus. They cross one {another} to create an “X” with the anterior symmetric ligament before and therefore the posterior symmetric ligament in the back. The symmetric ligaments manage the rear and forth motion of your knee.
- 7. Tendons: Muscles are connected to bones by tendons. The extensor sinew connects the muscles within the front of your thigh to your patella. Stretching from your patella to your shin is the sesamoid bone sinew.
Symptoms of Knee pain:
- The location and severity of knee pain might vary, depending on the reason behind the matter. Signs and symptoms that typically accompany knee pain include:
- Swelling and stiffness
- Redness and heat to the bit
- Weakness or instability
- Popping or crunching noises
- Inability to totally straighten the knee
- When to examine a doctor
- Call your doctor if you:
- Can’t bear weight on your knee or feel as if your knee is unstable or provides out
- Have marked knee swelling
- Are unable to totally extend or flex your knee
- See a visible deformity in your leg or knee
- Have a fever, additionally to redness, pain and swelling in your knee
- Have severe knee pain that’s related to associated injury.
Causes of Knee pain:
- Knee pain is often caused by injuries to the knee, mechanical problems of the knee, varieties of arthritis, and alternative issues to the knee.
- Injuries:
A knee injury can affect any of the ligaments, tendons, or fluid-filled sacs (bursae) that surround your knee joint because the bones, and animal tissue ligaments that create up the joint itself. several knee injuries area unit a lot of more common embrace :
Anterior symmetric ligament injury: Associate in Nursing ACL injury may be a tear of the anterior symmetric ligament (ACL) — one in every of four ligaments that connect your tibia to your leg bone. Associate in Nursing ACL injury is especially common in people who play basketball, football games, or alternative sports that need unforeseen changes in the direction of the knee.
Fractures: The bones of the knee, together with the kneecap (patella), is broken throughout falls or any accidents. Also, individuals whose bones are weakened by pathology will generally sustain a knee fracture just by stepping wrong or unforeseen jerk to the knee.
Meniscus tear: The cartilage is the powerful, rubbery animal tissue that acts as a shock absorbed between your tibia and leg bone. It is torn if you suddenly twist your knee while bearing weight on the knee.
Knee bursitis: Some knee injuries cause inflammation within the bursae, the little sacs of fluid that cushion the skin of your knee in order for tendons and ligaments to glide swimmingly over the joint.
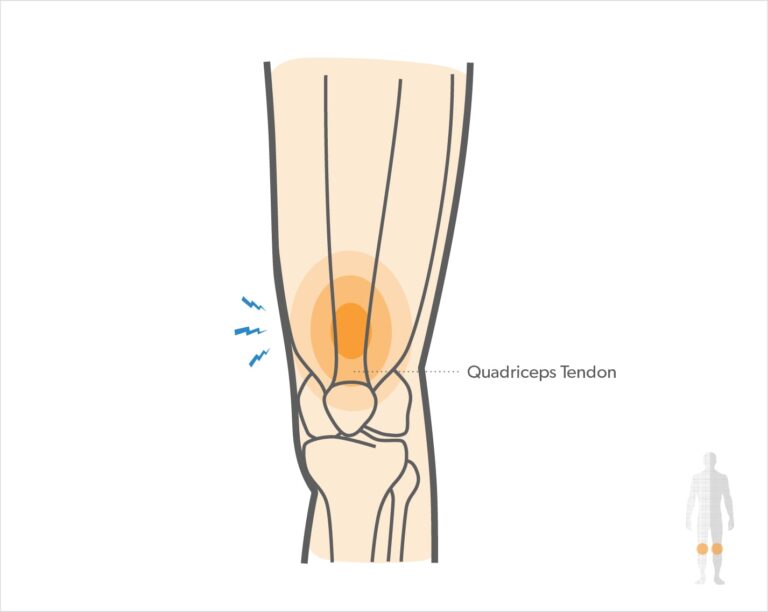
Patellar rubor: rubor causes irritation and inflammation of 1 or a lot of tendons — the thick, fibrous tissues that attach muscles to bones. This inflammation will happen once there is an Associate in Nursing injury to the sesamoid bone sinew, that runs from the patella to the tibia and permits you to kick, run, and jump. Runners, skiers, cyclists, and people concerned with jumping sports and activities could develop sesamoid bone rubor or sesamoid bone inflammation. - Mechanical issues:
Some samples of mechanical issues that will cause knee pain include:
Loose body: generally injury or degeneration of bone or animal tissue will cause a bit of bone or animal tissue to interrupt off and float within the joint area. this could not produce any issues unless the loose body interferes with knee movement, during which case the impact is a few things sort of a pencil caught in a very door hinge.
Iliotibial band syndrome: this happens once the powerful band of tissue that extends from the skin of your hip the skin of your knee (iliotibial band) becomes so tight that it rubs against the outer portion of your leg bone. Distance runners and cyclists are unit particularly liable to iliotibial band syndrome.
Dislocated kneecap: this happens once the triangular bone that covers the front of your knee (patella) slips out of place, sometimes to the skin of your knee. In some cases, the kneecap could remain displaced and you may be ready to see the dislocation.
Hip or foot pain: If you have hip or foot pain, you will amend the means you walk to spare your painful joint. however, this altered gait will place a lot of stress on your knee and cause knee pain. - styles of inflammatory disease :
Many types of inflammatory disease area units exist. The styles of inflammatory disease that possibly have an effect on the knee include:
Osteoarthritis: generally referred to as osteoarthritis, {osteoarthritis|degenerative inflammatory disease|degenerative joint disease|arthritis} is the most typical style of arthritis. it is a wear-and-tear condition that happens once the animal tissue in your knee deteriorates with use and age.
Rheumatoid inflammatory disease: the foremost draining sort of arthritis, arthritis is associated with a Nursing response condition that will have an effect on virtually any joint in your body, together with your knees. though rheumatism|autoimmune disorder} may be a chronic disease, it tends to vary in severity and should even return and go.
Gout: this sort of inflammatory disease happens once acid crystals build up within the joint. whereas arthritics most ordinarily affect the massive toe, it also can occur within the knee.
Pseudogout: typically mistaken for arthritis, pseudogout is caused by calcium-containing crystals that develop within the joint fluid. Knees area unit the foremost common joint suffering from pseudogout.
Septic arthritis: generally your knee will become infected, resulting in swelling, pain, and redness. Septic inflammatory disease typically happens with a fever, and there is sometimes no trauma before the onset of pain. Septic inflammatory disease will quickly cause in-depth harm to the knee animal tissue. If you have knee pain with any of the symptoms of septic inflammatory disease, see your doctor promptly. - alternative problems:
Patellofemoral pain syndrome may be a general term that refers to pain arising between the kneecap and therefore the underlying leg bone. it’s normal in athletes; in young adults, particularly those whose kneecap does not track properly in its groove; and in older adults, UN agency sometimes develops the condition as a result of inflammatory disease of the kneecap.
Risk factors of Knee pain:
- excess weight on the knee joint
- lack of muscle strength and suppleness
- certain sports or occupations
- previous injuries
Types of Knee Tape:
The two main forms of tape are effective in numerous studies.
- Rigid tape: this sort does not stretch. It’s designed to assist in keeping a neighborhood from moving.
- Elastic tape: this sort, conjointly referred to as kinesio tape, is intended to be a similar weight and thickness as your skin. It’s manufactured from stretchable cotton with adhesive on one aspect. this is often the bright-colored tape you have most likely seen on athletes throughout races and games. Kinesio tape offers stability however with a wider variety of motions than rigid tape. Keeping a joint from moving will generally make it stiffer.
Methods for Taping Your Knee
The McConnell taping technique for Knee pain:

- This methodology uses rigid tape to align the kneecap (or patella) to ease pain. you’ll be able to use it for knee degenerative arthritis, patellofemoral pain syndrome (otherwise called runner’s knee), and chondromalacia patella (when the animal tissue behind your kneecap is damaged).
- You’ll need a roll of 2-inch-wide adhesive gauze to shield your skin and a roll of one 1/2-inch-wide rigid athletic tape.
- Sit along with your leg slightly bent and extended before of you.
- Cut a pair of items of adhesive gauze and place them across your kneecap to shield your skin.
- Start the strip of rigid tape within the middle of the kneecap and pull it over the kneecap toward the inner part of your knee.
- Push the soft tissue on your inner knee toward the kneecap.
- Secure the tape to the inner aspect of the kneecap.
Kinesio taping technique for Knee pain:
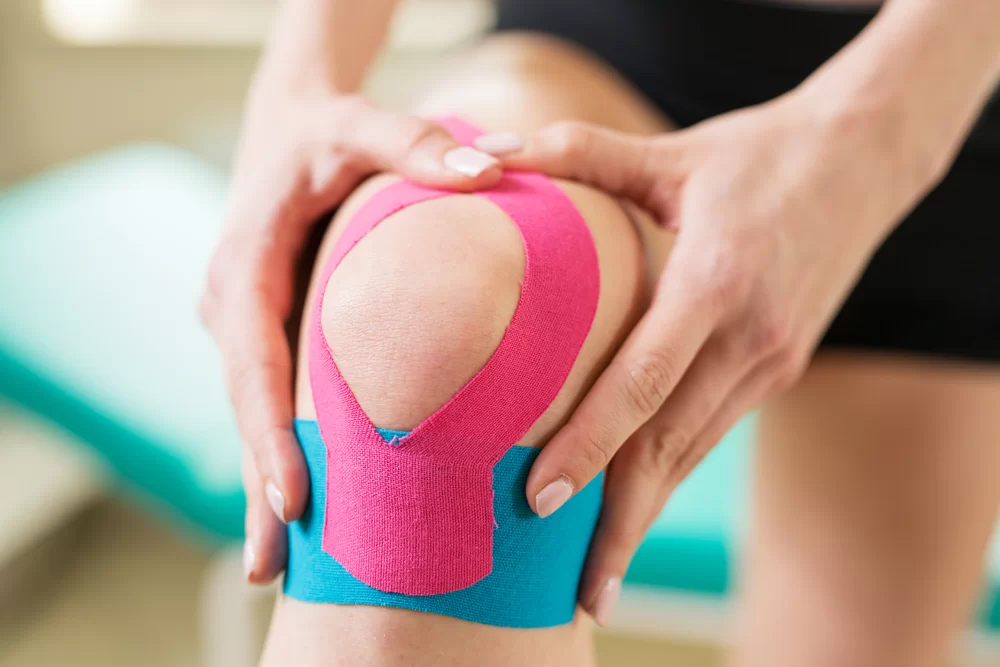
- This methodology uses a lot of versatile elastic tape to support your knee permitting a decent variety of motion. you’ll have 2 pre-cut Y strips and 2 pre-cut I strips. Rub the tape to activate the adhesive once you set it on every strip.
- Sit in a chair along with your knee bent. placed on very cheap a part of the formed piece of tape beginning at mid-thigh.
- Slightly stretch one tail of the formed tape and around one aspect of the kneecap, coming to the middle below the kneecap.
- Repeat with the opposite tail on the opposite aspect of your kneecap. The kneecap ought to be enclosed.
- Take the opposite piece of formed tape and place it on a very cheap half, beginning many inches below the kneecap.
- Slightly stretch one tail of the formed tape and apply it around the kneecap, ending on the skin of the opposite strip.
- Repeat with the opposite tail on the opposite aspect of your kneecap. Place the center of the primary I strip below the kneecap.
- Straighten your knee slightly and continue applying the strip upward on either aspect of the thigh, outside of the Y strips.
- Repeat with the second I strip placed slightly less than the primary.
- These are solely 2 ways of the many. Your doctor or therapist will assist you in realizing the simplest methodology to assist with your problems.
How to remove KT?
- So currently you’ve got your tape on and you’ve gotten that further support throughout your chosen sporting activity, it’s time to take it off,
- so allow us to ease the method of removing physiology tape for you. the most effective tip we will supply once it involves removing your physiology tape is to peel the skin from the tape, not the tape from the skin.
- But in terms of the particular method, first confirm you’re removing the tape within the same direction because of the growth of the hair beneath it, and no matter what you are doing don’t rip the tape off sort of a plaster!
- Start slowly, folding the corners of the sting back bit by bit, guaranteeing that you’re egg laying the removed tape on the rear of the applied tape, as opposition propulsion the tape higher than and removed from your arm.
- As you’re scraping the tape, hold your skin down along with your different hand and either faucet it or pull it gently within the other way of the tape.
- This helps the skin and therefore the tape to separate a lot of with efficiency however with no discomfort.
- If the tape has been applied over a very furry a part of the body, it helps to move on the tape as you’re peeling it off, because the pressure helps avoid more pain.
- It’s knowing to have smooth-shaven the realm before applying the tape however, as this isn’t continually sensible, taking this precaution are going to be necessary to some.
- want a touch further assistance? Apply oil directly onto the tape, rub it in, and wait around ten to twenty minutes before removing it slowly. This will facilitate scaling back the viscosity of the tape and make it easier to get rid of.