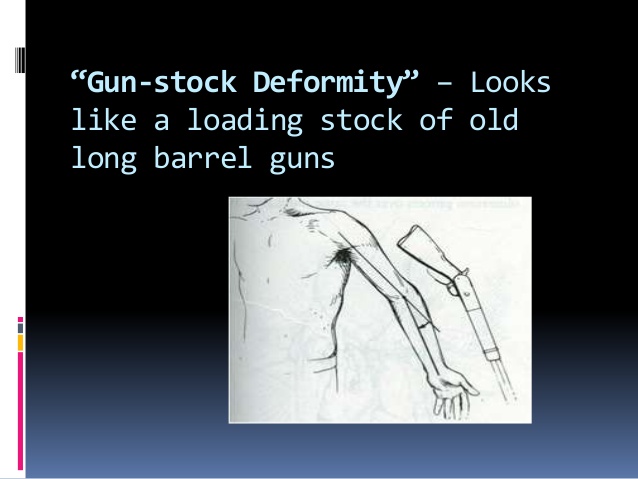
Gunstock Deformity
Table of Contents
What is a Gunstock Deformity?
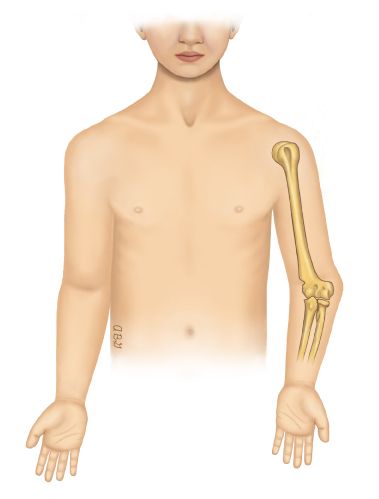
- Gunstock deformity also called Cubitus varus (varus means a deformity of a limb in which part of it is deviated towards the midline of the body) is a common deformity in which the extended forearm is deviated towards midline of the body.
- Cubitus varus is often referred to as “Gunstock deformity”, due to the crooked nature of the healing.
- Forearm deviated inwards with respect to arm at elbow with resulting lateral angulation in full extension.
- Reduction of physiological valgus:
- 8-15 ; males:-10
- females:-15-20
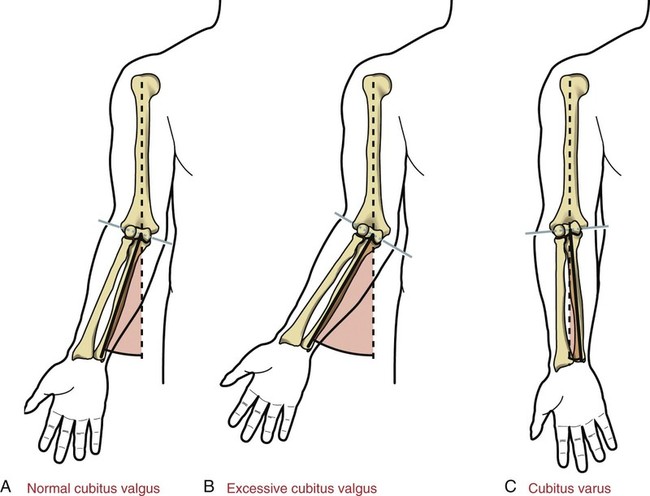
- Normally forearm is aligned in valgus with respect to arm in full extension with medial angulation.
- Deacres in valgus with neutral alignment (loss of angulation) is called “Cubitus Rectus”.
DEFINITION:
- Cubitus varus (gunstock deformity) is a malalignment of the distal humerus that results in a change of carrying angle from the physiologic valgus alignment (5-15 degrees) of the arm and forearm to varus malalignment. Historically, it is a complication of supracondylar fractures with a frequency as high as 30%.
EPIDEMIOLOGY:
- Historically, the incidence of this deformity following supracondylar humerus fractures occurred in up to 30% cases. However, the incidence has decreased substantially with the operative treatment of these injuries. Less commonly, this can occur after lateral condyle humeral fractures. Other causes include physeal injuries, osteonecrosis, infection, or rarely, tumorous conditions.
PATHOPHYSIOLOGY:
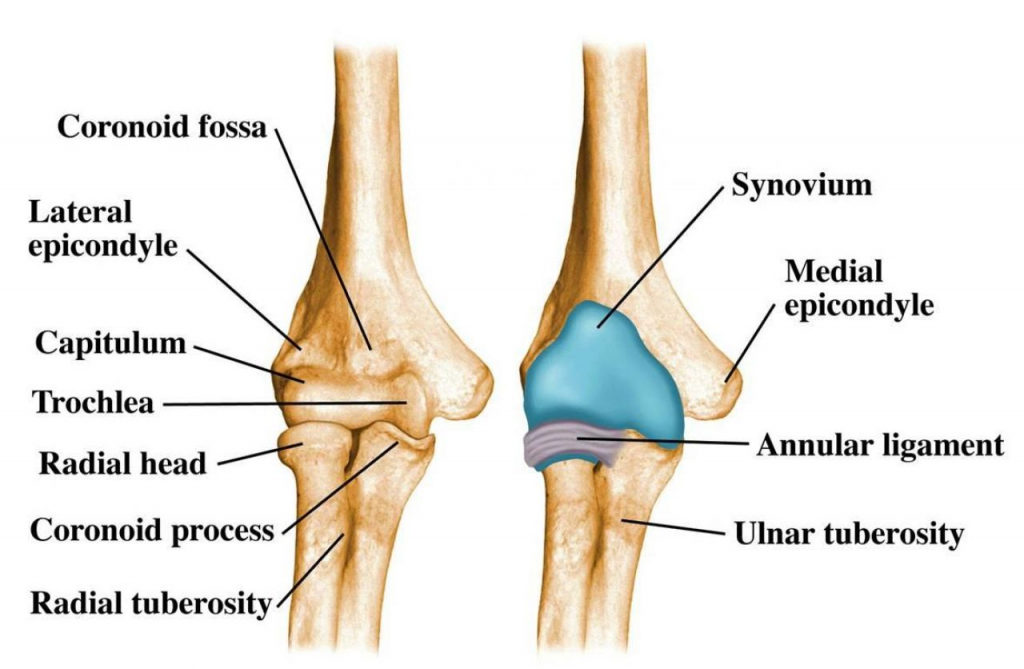
Anatomy:
- The distal humerus and the proximal radius and ulna forms the elbow joint. It is one of the most complex joints in the body, allowing flexion, extension, pronation, and supination. The ligamentous and bony anatomy provides static stability to the elbow joint. In full supination and extension, the elbow joint deviates between 5 and 15 degrees in the coronal plane known as the carrying angle or physiologic valgus of the elbow. In cubitus varus, the carrying angle decreases, and the hands are closer to the midline than expected The resulting structure and function of the elbow joint with cubitus varus deformity may be compromised.
Pathoanatomy:
- The medial deviation of the upper extremity mechanical axis, and the medially directed triceps force vector with this deformity, can ultimately lead to attenuation of the lateral ulnar collateral ligament and ulnar supination, causing symptomatic elbow PLRI. Bone remodeling in the axis of the elbow joint in immature children often restores elbow flexion, although the arc of elbow motion is altered with increased hyper extension and decreased flexion. However, there is little remodeling, and therefore correction, in the rotational component of the deformity. Additionally, these patients can have reduced range-of-motion in pronation.
- Internal rotation malunion of the distal humerus leads to several pathoanatomic features such as posterior trochlear, capitellar, and radial head overgrowth. These primary abnormalities lead to secondary adaptive changes, including increased anteroposterior trochlear articular arc and lateral shift of trochlear notch convexity. Furthermore, the ulna adjusts to a distal and medial location with increased varus, flexion, and external rotation. Ulnar nerve instability and delayed ulnar nerve palsy can also occur due to internal rotation malunion of the distal humerus or concomitant fibrosis and entrapment in the cubital tunnel. The nerve can sublux or even dislocate anterior to the medial humeral epicondyle and becomes entrapped in the fibrous bands of the flexor carpi ulnaris muscle causing symptoms of ulnar nerve neuropathy.
DIFFERENTIAL DIAGNOSIS:
- The cubitus varus usually occurs as a consequence of malunited supracondylar fractures. The differential includes varus deformity occurring as a result of previous fractures involving lateral condyle, trochlear osteonecrosis, distal humerus physis injury.
What are the causes of Gunstock Deformity?
- The main cause is mal-united supracondylar humerus fractures.
- Infective:-Medial growth plate damage.
- Vascular:-Osteonecrosis of trochea.
- Traumatic:-Lateral condyle fracture.
- Neoplastic:-Secondary to exostosis in distal,lateral humerus.
- Congenital:-Epiphyseal dysplasia.
Factors for malunion are:
1) Impacted/Comminuted type1 supracondylar fractures.
2)Rotationally unstable type2 fractures treated in a cast with subsequent loss od reduction.
3)Poorly stabilized or reduced tyoe3 fracture or delayed neglected fracture.
Displacement that occures at elbow joint:
- Medial displacement
- medial tilt
- Internal rotation
- posterior displacement
- posterior tilt
- proximl migration
Graded by severity:
Grade 1: loss of the physiological valgus angle.
Grade 2: 0 to 10 degrees of varus
Grade 3: 11 to 20 degrees.
Grade 4: More than 20 degrees.
COMPLICATIONS:
- stiffness (myositis ossificans)
- nerve injury (radial and ulnar)
- persistant deformity (under correction)
- recurrent deformity
- non-union
- osteomyelitis
- unsatisfactory scar
- lateral prominence
TREATMENT PLANNING:
- The planning of corrective osteotomy includes full-length radiography of bilateral upper limbs, recording of clinical and radiological parameters, and calculation of the correction angle. The paper tracing is required to prepare a template for the osteotomy.
Physiotherapy Treatment:
- Background: Physiotherapeutic intervention in a phasic manner has been in practice after orthopedic surgeries .graded physiotherapy has a great value in reducing post surgical inflammation pain and improving mobility .this work is done towards presenting the data regarding post surgical condition of corrective osteotomy for cubital varus on left side the treatment techniques were chosen on the basis of phasic evaluation and post treatment evaluation was done in order to check the prognosis in terms of inflammation, pain and ROM .several exercise therapeutic techniques and electro therapeutic techniques have been selected periodically on a basis of pre- treatment assessment. In this data presentation electro therapeutic techniques like,faradism under tension for correction of deformity, TENS,ULTRA SOUND , PARAFFIN WAX BATH (pain relief and extensibility)where the treatment modalities selected.
- Method : Treatment techniques were selected based on the evaluation in every particular session. . faradism under tension ,Paraffin wax bath, TENS ,muscle energy techniques, cyriax deep friction massage and ultrasound therapy modalities were used selectively.
- Results : Faradism under tension ,Paraffin wax bath, TENS ,muscle energy techniques, cyriax deep friction massage and ultrasound therapy modalities were used selectively with range of movement exercise in four phases and evaluation was done in every session. each phase was of 3 days at the end of 12 days re evaluation was done and found that there was a marked decrease in pain, inflammation and increased range of motion.
- Conclusion : after the selective physiotherapy approaches there was reduction of pain,oedema and range of motion was improved. graded physio therapeutic intervention is important to most of the orthopedic post operative conditions in reducing pain, decreasing inflammation, increasing mobility.
- Keywords : CYRIAX deep friction massage, faradism under tension, muscle energy techniques.
- TOOLS : Inch tape, goniometer
PROGNOSIS:
- The cubitus varus, if left untreated, doesn’t cause functional loss. The prime indication for corrective osteotomy is cosmesis. However, surgery is necessary in the cases having longstanding deformity with additional clinical symptoms of instability and ulnar neuropathy.
FAQ
Is Gunstock deformity varus or valgus?
When supracondylar fractures are malunited mostly leads to gunstock deformity also called cubitus varus.
Gunstock Deformity is a triplanar malalignment at the elbow, in which varus angulation in the coronal plane, extension in the sagittal plane, and internal rotation in the transverse plane. So it is a Varus deformity of the elbow.Why is it called gunstock deformity?
Gunstock Deformity is a varus deformity of the Elbow in which the extended forearm has deviated towards the midline of the body. Cubitus varus is also called as “Gunstock deformity”, due to the twisted nature of the healing.
What is the most serious complication of supracondylar fracture?
The difficulty in sustaining the reduction and ultimately leads to the Gunstock Deformity deformity is the most common long-term complication with an incidence shown from 3 to 57%. Enough reduction and pinning have reduced the risk of this deformity.