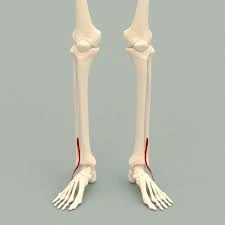
Fibularis tertius muscle Anatomy, Origin, Insertion, Function, Exercise
Table of Contents
Introduction
- The Fibularis tertius muscle, also known as peroneus tertius, is situated on the lower lateral aspect of the leg. It is a portion of the leg’s anterior, or extensor, compartment, together with 3 additional muscles; extensor digitorum longus, extensor hallucis longus & tibialis anterior. They are responsible for ankle dorsiflexion.
- Fibularis tertius extends from the distal end of the fibula to the base of the 5th metatarsal bone. Therefore, it spans & acts on 2 main joints of the foot; the talocrural (ankle) &bsubtalar joints. Due to its relatively small size & poor mechanical leverage, fibularis tertius is considered a weak dorsiflexor & evertor of the foot. In addition, the muscle is quite varied; it can be absent in some individuals, while in others it forms a portion of the extensor digitorum longus, being described as the muscle’s 5th tendon’.
Origin and insertion
Fibularis tertius originates from 3 locations:
- Is a direct attachment of the extensor digitorum longus muscle from the distal 3rd of the medial surface of the fibula.
- The anterior part of the interosseous membrane connects the tibia to the fibula. It divided the anterior from the deep posterior muscles of the leg.
- Anterior intermuscular septum, which divides the anterior & lateral compartments of the leg.
- The muscle fibers root in an inferolateral direction, forming a tendon that proceeds underneath the superior extensor retinaculum. Then, it is constant towards the inferior extensor retinaculum & courses through its loop, accompanied by the extensor digitorum longus muscle. Fibularis tertius finally inserts onto the medial part of the base of the 5th metatarsal bone
Structure
- The fibularis tertius attach from the lower 3rd of the front surface of the fibula, the lower portion of the interosseous membrane, & septum, or connective tissue, between it & the fibularis brevis. The septum is sometimes known as the intermuscular septum of Otto.
- The muscle passes downward & ends in a tendon that passes under the superior extensor retinaculum & the inferior extensor retinaculum of the foot in the same canal as the extensor digitorum longus muscle. It may be mistaken as a 5th tendon of the extensor digitorum longus.The tendon inserts into the medial portion of the posterior surface of the shaft of the 5th metatarsal bone.
- The fibularis tertius muscle is supplied by the deep fibular nerve. In rare cases, it may also be innervated by the common fibular nerve. This is unlike the other fibularis muscles, which are situated in the lateral compartment of the leg & are innervated by the superficial fibular nerve, & since the fibularis tertius muscle is found in the anterior compartment of the leg.
- The fibularis tertius may be absent in humans. It may be absent in as few as 5% of people, and as many as 72%, depending on the population surveyed. It is rarely found in other primates, which is 1 reason its action has been linked to efficient bipedalism.
Function
Due to its poor mechanical leverage, fibularis tertius can produce only 2 weak motions:
- Foot dorsiflexion around the talocrural joint, and with the help of extensor digitorum longus & tibialis anterior muscles.
- Foot eversion at the subtalar joint with the help of fibularis longus & fibularis brevis muscles.
- Through these functions fibularis tertius has a role in the gait cycle, acting with other foot dorsiflexors during the swing phase to clear the foot & toes off the floor. In addition, it has kept up functions for the ankle joint, preventing excessive inversion of the foot during physical activities. However, it is difficult to assess the true main of fibularis tertius because its function can be completed efficiently by other, more powerful muscles. In fact, fibularis tertius is absent in many individuals who do not accuse of any particular motion impairment.
Relations
- The Fibularis tertius is anterior to the fibularis brevis muscle and the anterior lateral malleolar artery. It also travels laterally to the extensor digitorum longus, with their tendons sharing a common sheath.
- Throughout its course, fibularis tertius passes laterally to the distal 3rd of the tibia, posterolaterally to the talocalcaneonavicular joint, & laterally to the tarsometatarsal joint of the foot.
Nerve supply
- Fibularis tertius is supplied by the deep fibular nerve, a branch of the sciatic nerve. It originates from the L5 & S1 spinal nerves.
Blood supply
Fibularis tertius collect arterial blood from several sources:
- Anterior tibial artery, across the anterior lateral malleolar artery
- Dorsalis pedis artery & its branches, such as the lateral tarsal artery, arcuate artery, metatarsal arteries, 4th dorsal metatarsal artery & digital arteries
- Posterior tibial artery, & the lateral plantar artery
Assessment
- Active motion & resisted movement for manual muscle testing involves combined ankle dorsiflexion & eversion.
Clinical important
The strength of eversion & dorsiflexion is not compromised in a person who lacks the Peroneus Tertius muscle. Peroneus Tertius seems to not provide higher protection against ankle ligamentous injury.
Peroneus Tertius Syndrome
- Peroneus Tertius Syndrome is a condition characterized by catching, clicking, locking, and popping the peroneus tertius tendon over the ankle during walking. It is a rare condition of anterolateral ankle pain and rear foot pain. This could be secondary to impingement & constriction of peroneus tertius in the extensor retinaculum.
- The Peroneus tertius muscle may be affected when a person has anterior compartment syndrome.
- The tendon may be used by surgeons as a donor for tendon transfer & tendoplasty procedures.
While the motion of fibularis tertius cannot be tested in isolation, its tendon can sometimes be palpated. Firstly, the foot & toes should be dorsiflexed against resistance. The tendon can be felt laterally within the shallow depression situated anterior to the lateral malleolus. A tear of the tendon, which can result during a violent inversion, will result in pain & swelling over this specific location.
The strength of eversion & dorsiflexion is not compromised in a person who lacks the Peroneus Tertius muscle. Peroneus Tertius seems to not provide higher protection against ankle ligamentous injury.
Fibularis tertius muscle stretching exercise
- Standing Shin Stretch
- Kneeling Shin Stretch
- Seated Shin Stretch
- Lying Shin Stretch
- Toe walking
- Ankle ABC’s
- Standing Stretch
- Standing Shin Stretch

Standing Shin Stretch
How to do:
- Stand tall. You need to use a hand on a wall & other support for balance.
- Slightly bend both knees.
- The right foot remains squarely on the floor. The foot is to be stretched or the left foot is placed just behind this stable & right foot, with the toe of the left foot touching the ground.
- Keeping your toe firmly on the ground, pull the left leg forward so you feel a stretch from the top of your left foot through the shins.
- Once you feel a stretch, hold it for 10-30 seconds.
- Repeat the stretch with the right foot.

Kneeling Shin Stretch
- How to do: Kneeling can be used for gradually stretching the shins.
- You must have good knee flexion to perform this stretch as you will be sitting on the heels. If it causes pain in the knees, don’t perform it.
- Kneel on a mat with the tops of the feet flat on the ground & the buttocks over the heels.
- You feel stretching on the shin.
- Hold for 10-20 seconds.

Seated Shin Stretch
- How to do: Sit on a chair.
- Drop the knee towards the floor so the toe of your foot is extended into the ground as in the standing stretch.
- gradually pull forward while the toe is planted on the floor, similar to the standing stretch but seated.
- Hold for 10-20 seconds.
- Repeat for both feet.
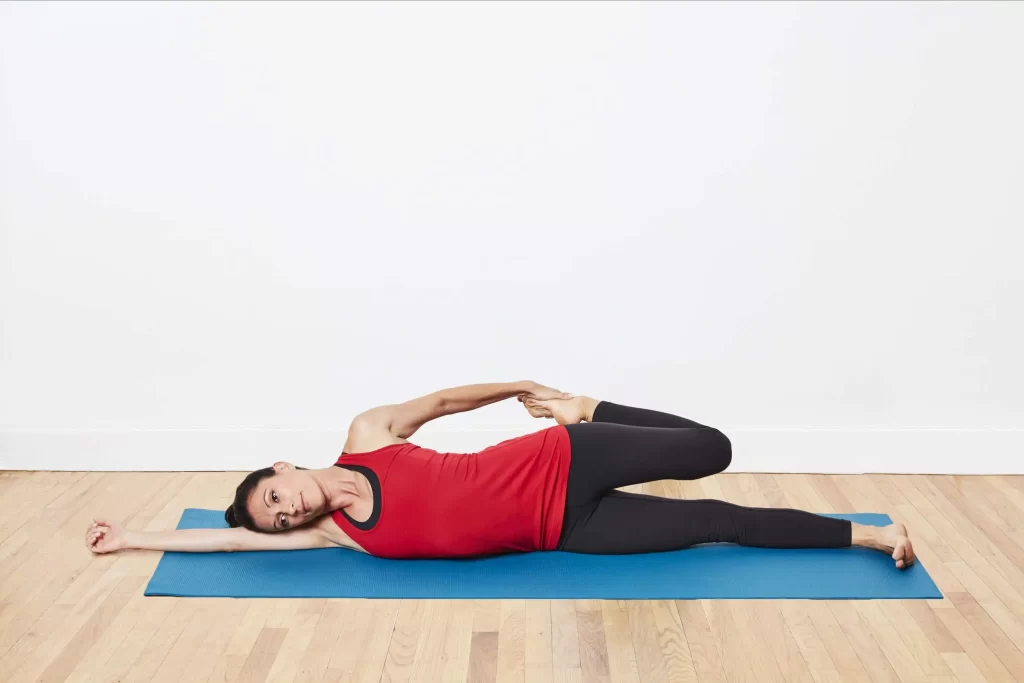

Lying Shin Stretch
How to do:
- The lying Shin Stretch stretch is similar to the lying quadriceps stretch.
- Lie on the one side. Now, bend the upper knee so your foot is behind the back.
- Reach back & grasp the forefoot, pulling it towards the back.
- Hold for 10-20 seconds.
- Repeat for both feet.
Toe walking
- How to do: Stand tall. Now transfer the body weight onto the toes & heels off the floor.
- Then walk on the toes which gives to you dynamic shin stretch.
- You can use the wall for support throughout the walk.
- Walk for 1-2 minutes.
Ankle ABC’s
- How to do: Moving the ankle in multiple directions is one way to slowly stretch the extensor hallucis Angus.
- Take a comfortable sitting position with the feet unsupported. Remove your shoes & socks.
- Slowly draw the alphabet in the air, leading with the big toe. Take as far as possible in each direction. Never allow your knee to move — all movement might come from your ankle.
- Every time the foot is pointed downward, you should feel a pulling sensation along the front of your shin.
- Repeat the alphabet 2-3 times on both legs.
Manual Toe Stretching:

- You can also use a towel to stretch the toes. Sit on the floor with the legs perfectly outstretched and a towel wrapped properly around your toes. Make sure that you hold the towel ends with your hands & pull the toes towards you. maintain yourself in this position for 20 to 30 seconds. You can also forgo the towel if you like & try pulling the toes by using your hands.
Toe Taps:
- This toe exercise helps to stretch the joint. As you sit in a comfortable chair, gently extend the big toe towards the ground as you try to point the other toes up. hold onto that position for about a second & then tap them lightly back down to the floor. Repeat this about 10-12 times & then reverse this process by gently pulling the big toe up as you keep the other toes on the floor.
Hammer Toe Finger Splint:
- The claw Toe Finger Splint is also referred to as “squeeze” & involves using the fingers for creating little splits between the toes for stretching them. Sit in a comfortable position & then bring one foot up & then place it right on your opposite thigh. Then slide the fingers gently in between the toes, gently pinching the fingers for squeezing the toes together. Repeat the exercise 12 times. If you like you can perform each toe simultaneously by putting one finger between them & pinching.
Rolls:
- This particular claw toe exercise involves tapping the toes gently on the floor from one side to the other. First, stand barefoot on some flat surface && try lifting all the toes off the ground, while making sure that you keep the heel planted. Now bring the toes gently down on the surface one by one, starting with the small & then ending with the big. Repeat the exercise 10 times & then move in the opposite direction.
Health Benefits of fibularis tertius stretching exercises:
There are many type benefits you might know:
- Reduce the risk of injury to calves, ankles & feet
- Reduced chance of getting tibialis anterior tendonitis
- Better ground clearance when walking to avoid tripping
- Reduce the risk of growing shin splints & stress fractures
- Fast-up recovery of shin splints.
- Increased athletic performance in sports where the ankle is “locked” like in soccer to kick a ball
- Increases the ankle range of motion. such as dorsiflexion,inversion, & adduction.
- It also maintains the medial arch of the foot.
- It also helps in the anticipatory postural adjustment part during gait beginning tibialis anterior perform knee flexion at the stance limb by causing forward displacement of the tibia.
- It also helps in eccentric deceleration of foot plantar flexion, pronation & eversion.
Strengthening exercise of fibularis tertius muscle
- Foot eversion
- Calf raises
- Seated Elastic Band Exercise
- Cuff Weight Exercise
- Isometric Exercise
- Seated Calf Stretch
- Seated Toe Raises
- Wall Toe Raises
- Heel Walk
Foot eversion
- Bind a resistance band to something sturdy, such as the leg of a table. Sit on the ground with the legs straight out in front of the body, & position the foot into the loop at the ball of the foot & with the loop put on the outside of the foot. Starting with the toes facing up to the ceiling, then turning the foot outward. Return the foot back to the starting position, making sure to keep the rest of the leg as still as possible. Complete 10-20 repetitions on both sides.
Calf raises
- Start standing with each foot flat on the ground at shoulder-width apart. Maintain the rest of the body straight, but without locking the knees. gradually, press on the toes, causing the heels to raise up off the floor. Hold this raised position for a couple of seconds, then gradually return the heels back to the ground. Perform ten repetitions for 3 sets. Additional resistance may be added by holding 5-pound weights in each hand with the arms down beside the body while performing the exercise.

Seated Elastic Band Exercise
How to do it?
- For the Seated Elastic Band Exercise exercise, you need an elastic resistance band.
- To perform the Seated Elastic Band Exercise exercise you have to Sit on the floor with the leg extended in front of you. now Alternatively you can sit on a chair with the foot propped up on another chair.
- Wrap a resistance band over the ankle. Attach one end to a stable object like the leg of a table, & secure the other around the foot near the toes. It may be helpful to have the lower leg resting on a small pillow so the heel of the foot does not rub on the floor.
- To perform this exercise Pull the toes & foot up while keeping the knee extended. The ankle might be moved as you flex the foot up
- Pull the foot up as much as you can, & hold the end position for 2 seconds.
- Slowly relax back to the starting position.
- Do this exercise for 10-20 repetitions or until the anterior tibialis muscle tires & you can no longer flex the ankle up.

Cuff Weight Exercise
How to do it?
- For Cuff Weight Exercise you need a cuff weight.
- A cuff weight is a padded weight that you can wrap around the ankle. for Cuff Weight Exercise you have to sit in the chair & wrap a cuff weight around the toes. Make sure it is secure. Let the footrest on the floor, start this exercise by sitting with the cuff weight on the foot & then flexing the ankle so the foot & toes move up towards the knee.
- When the foot is flexed up, hold the position for 2 seconds,
- Gradually lower your toes back down to the initial position.
- Repeat the exercise for 10-20 repetitions.
Isometric Exercise
How to do it?
- Isometric exercise is a type of movement in which you push against an object you can not move. It is simple to do, & it can help strengthen the muscle in specific ranges of motion (ROM) in the ankle.
- To do isometric anterior tibialis strengthening you have to Sit in a chair & lie down.
- Cross 1 leg over the other with the affected leg on the bottom.
- Put the foot on top of the ankle you wish to exercise.
- Press the top of your weak foot into the sole of the other foot. Press down with the powerful foot to resist it. Remember, that movement occurs from the foot not from the ankle.
- Hold this position for 5 seconds, & then slowly release. Perform about 10 -15 repetitions of the exercise, 2 – 3 times a day. Isometric exercise can help to strengthen the muscles, but strength only occurs in the specific ROM in which you are exercising. That means that you might vary the position of the ankle when performing the exercise.

Seated Calf Stretch
How to do it?
- If your anterior tibialis muscle is weak, then you have difficulty flexing the foot. This means you have a shortened calf. A shortened calf will be a tight muscle, so stretching the calf may be necessary to correct the foot drop fully.
- To perform this exercise you have to Wrap a towel around the ball of the foot, & the knee should be extended.
- Pull the ends of the towel so your foot flexes up & stretches your calf.
- Hold the stretch for 15-30 seconds.
- Relax. Perform this 3 times.
Seated Toe Raises
How to do it?
- For the Seated Toe Raises exercise, you have to Sit on a chair with the feet placed in front of you
- Now gradually raise your toes off of the ground.
- Hold for 2-5 seconds at the top
- Repeat for 2 -3 sets of 20-25 repetitions
Wall Toe Raises
How to do it?
- For the Wall Toe Raises exercise, you have to Stand 12-15 inches away with the back towards the wall with the feet hip-width apart.
- the knees might be slightly flexed then lean back into the wall.
- Elevate the toes off the floor & hold at the top for 2-4 seconds then lower the toes back to the floor.
- Repeat for 2-3 sets of 15-20 repetitions

Heel Walk
How to do it?
- For the Heel Walk exercise, you have to stand on both feet hip-width apart with no shoes on.
- Elevate the toes off the floor so that your heels are in contact with the floor.
- Walk forward while leaning back and placing weight on the heels.
- Do this for 30-40 seconds.
- Repeat this 2 to 3 times.
Health benefits of Besides Fibularis tertius strengthening exercise:
- Assist to Reduce the risk of injury to the calf, foot, & ankle joints.
- Assist to reduce the chance of getting Besides Fibularis tertius tendonitis.
- Assist to increase ground clearance when walking to avoid tripping
- Reduce the risk of growing shin splints & stress fractures
- Speed up recovery of shin splints.
- Boost player performance in sports where the ankle is locked like in soccer to kick a ball
When did you not do the fibularis tertius strengthening exercise?
- If you feel any pain during this exercise then do not do this exercise.
- If you are already suffering from foot & ankle pain.
- If your doctor advised you to take rest.
- If the lower limb bones are recently fractured.
- Health benefits of Besides fibularis tertius strengthening exercise:
- Assist to Reduce the risk of injury to the calf, foot, & ankle joints.
- Assist to reduce the chance of getting Besides fibularis tertius tendonitis.
- Assist to increase ground clearance when walking to avoid tripping
- Reduce the risk of growing shin splints & stress fractures
- Speed up recovery of shin splints.
- Boost player performance in sports where the ankle is locked like in soccer to kick a ball
What are the safety & precautions of doing the Besides fibularis tertius exercise?
There are some safety measures you require to look for:
- Don does not bounce during the stretch. it causes injuries to the muscles. Such as strain.
- Never overstretch a Besides fibularis tertius muscle.
- Do not perform it so many times, it causes fatigue to the muscle. You might use a suggested time of repetition
- The holding time of the stretch should be recommended by your therapist which is normally 30-60 seconds.
- Never perform a stretch on the prior injured part of the body. Such as fractures, sprains, etc.
- Never stretch cold muscles, it causes pain. stretch it once you warm up the muscle.
FAQ
Some examples include inversion sprains of the ankle, wearing too-tight running shoes, work boots & ski boots, direct trauma, a new activity needing overuse of the muscle, & weakness from prolonged periods of immobility due to injury.
The Action of the fibularis longus muscle is to plantar flex & evert the foot. It also provides support to both the longitudinal & transverse arches of the foot.
Place the hands on the wall & lean in. Stand so the leg with the Peroneus you want to stretch is behind the right foot. Bend the left foot, such that the toes are pointing to the right leg. Stay in this position for about 30 seconds & release, remembering to stretch the other side.
Due to its poor mechanical leverage, fibularis tertius can produce only 2 weak motions: Foot dorsiflexion around the talocrural (ankle) joint, with the help of extensor digitorum longus & tibialis anterior muscles.
Artery anterior tibial artery
Nerve deep fibular nerve
Actions dorsiflexion & eversion of the foot