Exercise for Hip osteoarthritis
Table of Contents
Introduction
- Exercise is a very effective factor if you have hip osteoarthritis or hip pain.
- It’s good to start slowly and build up gradually if you’re new to exercise.
- Remember to drink water while you’re exercising this will keep you energetic.
- An exercise program that targets specific muscle groups and the area (s) affected by osteoarthritis can help reduce pain and disability
- A program for osteoarthritis of the hip and knee should include aerobic (cardio) activity, muscle strength, neuromuscular exercises, and flexibility exercises.
- Exercise therapy during Hip OA is very helpful in decreasing pain and improving joint range of motion.
- If you have Hip OA then the key goal of a hip exercise program is to strengthen the muscles that mainly support your joints.
- The deep stabilizer muscles of the hip can absorb shock and protect the joint from painful and harmful movements.
What is hip osteoarthritis?
- Hip osteoarthritis is a condition in which the Hip joints become inflamed and the cartilage that lines the bones become worse because As the disease extends patients often experience pain, stiffness, and instability due to bone-on-bone wear.
- There are many possibilities that cause hip pain, ranging from muscle strains and injuries to arthritis and inflammatory conditions.
- yet gently exercising the hips can a lot of help with pain relief and restore mobility.
- In Hip osteoarthritis, bone-on-bone wear occurs because of this the joints become inflamed, and the cartilage that lines the bones become worse.
- As arthritis extends patients often experience pain, stiffness, and instability in the Hip. and during this phase, you need particular exercise for relief.
- Pain in the upper part of the leg and stiffness are common symptoms of OA of the Hip
- increasing age and genetic factors are the most common causes of OA hip.
Consideration before starting The Exercise
- Exercise plays an important role in effective exercise programs for patients who suffer from OA hip.
- Exercise of Hip OA changes according to the severity of arthritis.
- The goal is to maintain or improve strength, and mobility, and improve possible range of motion by giving particular exercises.
- Exercise also helps with pain relief at the hip and achieves normal movement which one restricted.
- specific exercise programs have been shown to decrease pain and improve the range of motion and function in hip osteoarthritis.
The patient must be aware of the benefits and use of exercises
- Benefits of Exercise and its interventions
- benefits of weight reduction
- Self-management of pain by Use of modalities such as heat and cold (cryotherapy) Relaxation techniques
- Assistive devices
- Personal experience
- Symptoms
- Perceived benefit of exercising
- improve the Quality time of sleep
- Mental status
- the experience of Exercise
- There are many possibilities that cause hip pain, ranging from muscle strains and injuries to arthritis and inflammatory conditions. yet gently exercising the hips can a lot of help with pain relief and restore mobility.
- Flexibility and strength exercises are key to relieving pain at the hip. Although these exercises may result in discomfort for some time, they shouldn’t cause or aggravate pain.
- If causes pain during exercise, stop doing it or try going at a slower or gentler pace.
- Individuals who have recently had hip replacement surgery should consult a doctor or physical therapist before performing any of the exercises shown below.
- All exercises should be performed gently, and slowly and exercises should be done 2 to 3 times a day.
Warm up and Cool down
- It is important to do a warm-up before you start the session.
- If possible with a gentle walk around your place for 3-4 minutes before you start your exercises.
- This will increase your circulation and help your muscles prepare for the activity and give speedy muscle recovery.
- When you have finished your exercises it is important to allow your heart rate to slow down gradually by ending with a gentle walk for a few minutes.
Exercise
strengthening Exercise for Hip OA
Knee to Chest

- lie on your back on the ground or bed.
- Then bend your knee and straighten it.
- Do not bend past 90°.
- Tighten the muscles on the upper thigh and buttocks. Hold for 5 seconds.
- Repeat the same exercise on the other side, then pull both legs together. Repeat the entire exercise four times turn by turn.
- Tip: Keep your lower back pressed into the bed or ground.
Hip Extension
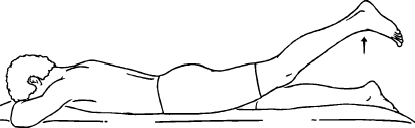
- this exercise Strengthens your buttocks.
- Please take a prone position on a flat surface with a pillow under your hips just above the knee.
- your head, neck, and upper body should be relaxed throughout the exercise.
- Bend one knee at 90°.
- Lift your leg straight up without bending at the knee.
- Slowly down your leg back to the starting position on the floor, by counting from 1 to 5.
- after 10 repetitions complete the same exercise on the other side.
- Tip: starting with 10 reps, by using only your body weight; and progress to 15, When that becomes easier, add ankle weights in one kg increments.
- After increasing the weight, start again at 10reps, working back up to 15.
Clamshell
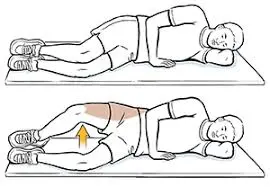
- please take a side-lying position, with your affected hip on top.
- bending your kneed by keeping your feet and knees together.
- Raise your top knee, but keep your feet together throughout the exercise.
- Hold for 5 to 6 seconds.
- Slowly lower your knee back to the starting position.
- Repeat 10 to 12 times and 2 to 3 times a day.
Sit-and-Stand

- this exercise Increases your mobility and strengthens your leg, core, and back muscles
- Stand in front of a chair that won’t move, feet planted on the floor about hip-distance apart. (the chair should be strong and tough enough)
- Press your hips back and bend your knees partially to lower yourself into a seated position.
- Then move ahead from the hips, push through your feet, and get up with your legs in a standing position.
- Repeat the sequence 5 times.
- Tip: Gradually build up to 7 or 10 reps, says “Sitting and standing is essential movement pattern you want to stay strong in.”
External hip rotation (sitting)
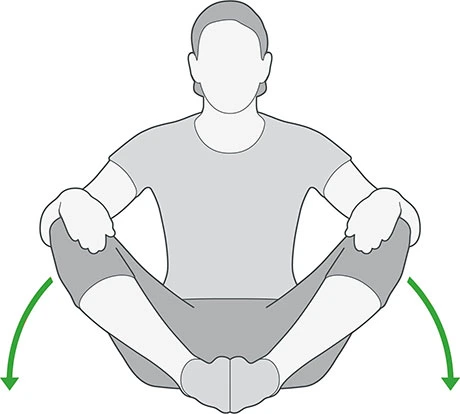
- First, sit on a chair or bed, bend your knees, and your feet should be fixed together.
- Press your knees down towards the floor using your hands if your hip is too weak or painful.
- Take the movement to the point where you feel a stretch, hold it for around 10 to 12 seconds, and then relax.
- Repeat 5-10 times and 2 to 3 times a day.
- If you had a recent hip surgery please avoid this exercise. Speak to a healthcare professional like physiotherapist if you’re unsure.
Heel slide
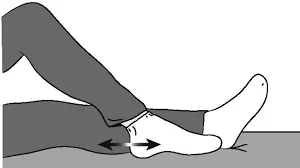
- First, take a supine position on the bed or ground.
- then gently bend your knee by sliding your heel towards your hip.
- movement should be in a pain-free range.
- do the same movement on the other side.
- do this for 2 to 3 times a day with 10 to 12 reps.
Hip abduction (standing)

- first, take a standing position with the support of a wall or chair.
- then gently lift your affected leg sideways by standing on another leg.
- after that slowly backward your leg to the starting position.
- do this exercise in alternative legs and movement should be in a pain-free range.
- do this for 2 to 3 times a day with 10 to 12 reps.
Short arc quadriceps exercise

- First, take a supine position then roll up a towel or smiley ball and place it under the back of your thigh by straightening the knee.
- Keep the back of your thigh on the towel or smiley then straighten your knee by raising your foot off the floor.
- Hold it for five seconds and then lower it slowly.
- do this for 10 to 12 reps and 2 to 3 times a day.
Bridging

- first, take a supine position on the ground or bed, and don’t take a pillow throughout the movement.
- then bend your both knees and the distance between your knees and feet remain the same.
- then gently lift your back and hold it for 5 secs then slowly take it back to the ground or bed.
- di this 10 to 12 times and 2 to 3 times a day and movement should be pain-free.
Stretching exercise for Hip OA
Standing Iliotibial Band Stretch
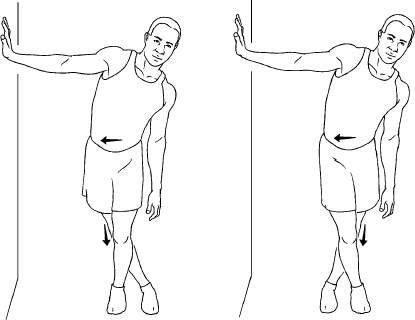
- stretching the outside of the hip.
- standing with the support of the wall.
- Cross the leg which is near the wall behind your other leg.
- take your hip toward the wall until you feel a maximum stretch at the outside of your hip. Hold the stretch for 30 seconds.
- Cross the leg behind your other leg which is further from the wall and movement should be done in a pain-free range.
- do this for 2 to 3 times daily with 10 to 12 reps.
Hamstring Stretch

- This will stretches the back of your thigh and just behind your knee.
- Lie on the floor with both knees completely straightened without a small degree of bend.
- Lift one leg off of the floor and bring the knee toward your chest by keeping another leg stable.
- grasp your hands behind your thigh below your knee and press them towards you.
- Straighten your leg and then pull it slowly toward your head until you feel a maximum stretch at the back of your thigh.
- Hold for 30 seconds and then relax.
- Repeat on the opposite side then repeat the entire sequence three times On both legs.
- Tip: Don’t pull at your knee joint.
Quadriceps Stretching
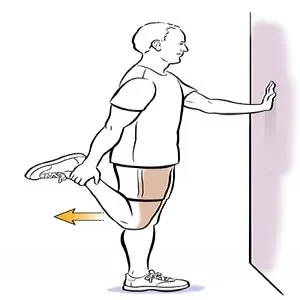
- first, takes a standing position by holding support on the wall.
- then slightly bend your knee of the affected leg then stretch it backward by holding on to the ankle with the hand.
- hold it for 5 to 7 secs.
- then bring it back to normal position and the patient should maintain the balance throughout the exercise.
- do this same movement in another leg.
- movement should be pain-free.
- do this for 2 to 3 times a day with 3 to 5 reps.
Hip Flexor Stretch
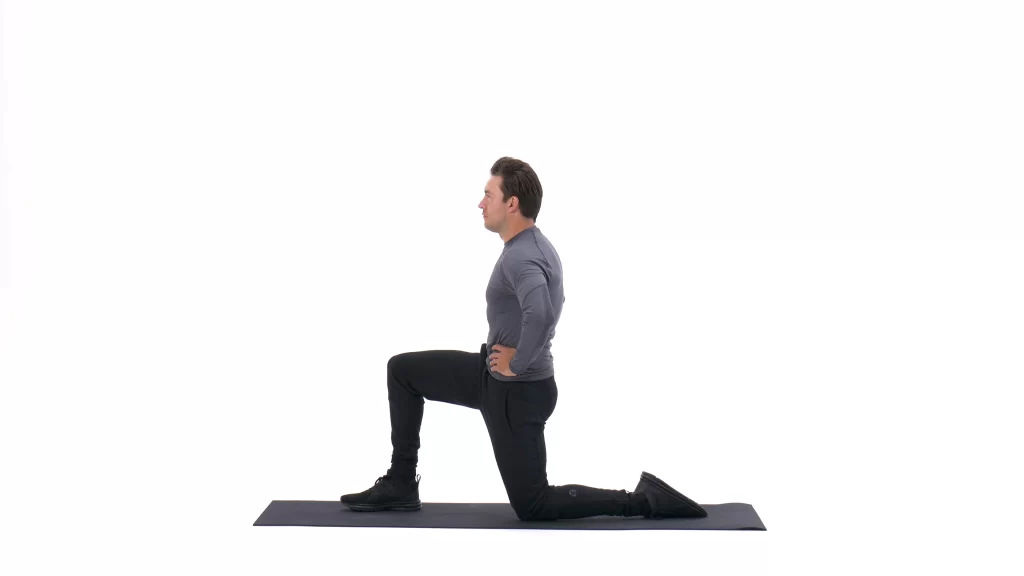

- Stand in a wide walking position. Put both of your hands on firm support in front of you if you feel unstable.
- Lean forwards and bend your front knee, push your hips forwards and keep your back straight throughout the movement.
- You can feel a stretch in the front of the hip and thigh of the back leg.
- Hold for 20—30 seconds with 3 to 5 reps.
- do this 2 to 3 times a day.
Exercise after hip replacement surgery
- If exercise, weight loss, and lifestyle measures aren’t helpful as well, or if OA is affecting your mobility or quality of life, replacement of the hip is necessary.
Ankle Pumps

- first, take a supine position and keep your knees straight throughout the movement.
- then do a normal ankle movement like moving your ankle up and then down.
- This will help you to increase blood flow and relief joint stiffness.
- Do this several times a day if possible or whenever you lay on the bed or floor.
Ankle Rotations

- Move your ankle inward and outward from the other foot whenever you lay on the bed or floor.
- Repeat 10 to 12 times in each direction.
- This exercise should take more minutes than ankle pumps and is much tough than ankle pumps if you have stiffness or ankle pain.
- Do 3 to 4 times a day.
Buttock Contractions (static gluteal exercise)

- first, take a supine position then tighten your buttock muscles and hold to a count of 5 by pressing the back of your head and heel at the same time against the ground or bed.
- your back should remain straight throughout the movement.
- Repeat 10 times.
- Do 3 to 4 sessions a day.
Abduction Exercise (supine)

- first, take a supine position and Slide your leg out to the opposite of the other leg another leg should be straight and stable.
- slide your leg as long as you can then bring it back to normal or starting position.
- if the patient can not do him or herself then the therapist should give assistance through the movement.
- Repeat it 10 times.
- Do 3 to 4 sessions a day.
- movement should be done in a pain-free range.
Quadriceps Set (static quadriceps exercise)

- first, take a supine or long sitting position on a bed or ground.
- Try to straighten your knee by contacting your thigh muscles.
- Hold it for 5 to 10 seconds. by putting some soft object like rolling a towel or smiley ball just below the knee or patella.
- Repeat this exercise 10 times during a 10-minute period, take some rest, and repeat.
- Continue until your thigh feels fatigued or feels any pain.
Straight Leg Raises (SLR)

- first, take a supine position then contract your thigh muscles and keep your leg straight without bending at the knee.
- and another leg should be bent throughout the movement.
- then bring your leg in an upward direction and put it back to normal.
- and the patient must have to keep their knee straight through the movement.
- Hold for 5 to 10 seconds.
- Slowly lower your leg to the ground or bed.
- Repeat 10 to 12 times.
- do this 2 times\day.
Early Activity
- Soon after hip replacement surgery, you will begin to walk some distance in your hospital room or in the hospital lobby and perform light routine activities.
- This early activity aids your recovery and helps your hip regain its muscle strength and joint movement.
Walking
- walking is the best therapy for all lower joints. if you walk properly it will help you to regain all your hip joints and muscle strength.
- first, you need any assisted ambulatory device for walking like a cane or crutches.
- in starting phase don’t give too much pressure on your foot it can lead to further increasing pain in the hip joint.
- so at first, you take total pressure on your unaffected leg.
- As you move ahead day by day, your knee and ankle of the affected leg will bend and your entire foot will rest evenly on the floor.
- don’t put too much pressure on the hip of the affected leg.
- As you complete the one step, your toe will lift off the floor and your knee and hip will bend so that you can go for your next step easily.
- Remember that you have to touch your heel first, then flatten your foot, then lift your toes off the floor.
- Walk as rhythmically and smoothly as you can and you got a good result in days.
Stair Climbing and Descending
- Stair Climbing and Descending is the best strength and endurance exercise for each.
- It starts after you walk completely and perfectly on the floor.
- At first, the patient has to Climb and Descend with the stick and keep in mind that Always lead up the stairs with your good leg (unaffected) and down the stairs with your operated(affected) leg. Remember, “up with the good” and “down with the bad.”
- This will improve your joint mobility and flexibility.
Advanced Exercises and Activities
- after hip replacement surgery, the pain in your thigh and hip muscles is increased so for pain relief the strengthening of these muscles must need. and this will help to regain your joint mobility and function.
- for further muscle strengthening the resisted exercise must be needed.
Resisted exercise for Hip OA
Resisted Hip Flexion with elastic tube

- Stand with your feet slightly apart.
- Bring your operated or affected leg forward by keeping the knee straight.
- and then bring back your leg to its previous starting position.
- do this exercise slowly and gently to maintain balance throughout the movement.
Resistive Hip Abduction with elastic tube

- Stand sideways from the door where the tubing is attached.
- Extend your operated leg sideways.
- and then bring back your leg to its previous position.
Resistive Hip Extensions with elastic tube

- face to the door where the tubing is attached.
- Pull your leg straight back.
- and then bring back your leg to its previous position.
- Do all stretches 3 to 5 times by holding for 5 secs.
Exercycling
- First, adjust the seat height according to the condition or pt’s height so that the bottom of your foot just touches the pedal.
- Pedal backward at first.
- only after a comfortable cycling motion is possible in backward comfortably then allow the patient to Ride forward
- As you become stronger (after some days) slowly increase the tension in the cycle. Exercycle for 8 to 10 minutes 2 times a day at first, gradually building up to 12 to 15 minutes.
Walking
- walking is the best exercise for a normal human being in routine life to maintain health and all joints in normal conditions
- In the beginning, walk for 5 to 10 minutes, 3 to 4 times a day in a room or lobby. with wearing orthosis or external aids.
- As your strength and endurance improve, and you seem to gain your muscle power back you can walk for 20 to 30 minutes, 2 to 3 times a day.
- Walking boosts your blood flow to joint damaged cartilage, giving it the nutrients necessary to provide cushion to the ends of your joints.
- Once you have fully recovered, regular walks of 20 to 30 minutes, 3 to 4 times a week, will help you gain muscle power and endurance also.
which types of exercises you should avoid in Hip OA?
- There are particular types of exercises that people should avoid with hip arthritis.
- Some exercises increase joint contact stress, putting the joints under more pressure than trusted Sources and potentially resulting in hip pain in a person with OA.
- exercises that involve repetitive hip flexion, the motion can bring your hip or leg up toward your chest.
- Running, on uneven surfaces. like,
Exercises that create sudden changes in movement and direction
- Sports and exercises that involve quick stops and movements .like tennis and basketball give sudden stress to joints.
Bending too much at the hip
- Most exercises for hip pain will involve bending at the hips more than any joints, those exercises put too much strain on your hips. You should avoid this type of exercise that causes further strain and pain when bending at the hips.
- do exercises that require more bending at the knees than the hips. These may help take some strain off the hips while strengthening the muscles connected to them.
High-impact exercises
- Step aerobics and other workouts that involve jumping significantly impact the hip joint.
Weightlifting exercises
- Bending too much at the hip, Strengthening exercises, which include heavy weightlifting, can be helpful for people who have hip arthritis.
- However, if a person does not perform the exercises in the perfect manner may worsen pain or cause further joint injury because Lifting heavy weights with the legs puts a severe strain on the hips.
- Heavy Bodyweight Squat.
Over-stretching
- Remaining in one position for too long causes severe hip pain.
- routine Stair climbing.
some self-care tips that help in pain relief
- Use hot or cold packs.
- Eat a balanced diet.
- Lose weight.
- Get enough rest.
- Manage stress.
- Try splints, braces, and other aids.
- Seek support.
FAQ
Walking
It is the best exercise for a normal human being in routine life to maintain health and all joints in normal functional condition.
In the beginning, walk for 5 to 10 minutes, 3 to 4 times a day in a room or lobby with wearing orthosis or external aids for support if you have severe Hip OA.
As your strength and endurance increase, and you seem to gain your muscle power back you can walk for 20 to 30 minutes, 2 to 3 times a day.
Bone and joint specialists suggest walking because it is one of the best forms of exercise for hip arthritis.
Walking boosts blood flow to your cartilage by giving it the nutrients necessary to provide cushion to the ends of your joints.
Any condition like Hip osteoarthritis that causes swelling, inflammation, pain, discomfort, mechanical issues, or spasticity of the muscles around the hip can cause you to lose some ROM.
Stretching exercises can help to improve the strength of many of the muscles that support your hip joint.
Hip muscle-strengthening exercises can also help to improve hip ROM.
These exercises should first be performed under the guidance of a healthcare professional like physiotherapist to make sure you are doing them properly and without pain.
The first sign is Hip Pain or Groin Pain. The pain is usually felt between the hip and the knee.
Stiffness Swelling and Tenderness are common symptoms in the hip which cause difficulty putting on your shoes or socks.
Then affected the range of motion because of swelling, inflammation, and spasticity of the muscles around the hip.
It is important to do a warm-up before you start the session.
If possible with a gentle walk around your place for 3-4 minutes before you start your exercises.
This will increase your circulation and help your muscles prepare for the activity and give speedy muscle recovery.
When you have finished your exercises it is important to allow your heart rate to slow down gradually by ending with a gentle walk for a few minutes.
There are many possibilities that cause hip pain, ranging from muscle strains and injuries to arthritis and inflammatory conditions.
yet gently exercising the Hips can a lot of help with pain relief and restore mobility.
Exercise therapy during Hip OA is very helpful in decreasing pain and improving joint range of motion.
If you have Hip OA then the key goal of a hip exercise program is to strengthen the muscles that mainly support your joints.
The deep stabilizer muscles of the hip can absorb shock and protect the joint from painful and harmful movements.