Elsons Test
Table of Contents
Introduction
The Elson test is a physical examination maneuver used to assess for a tear of the central slip of the extensor tendon of the finger. The central slip is a band of tissue that extends the proximal interphalangeal (PIP) joint of the finger. When it is torn, the PIP joint cannot fully extend and the distal interphalangeal (DIP) joint may hyperextend.
Other Names
- Elson Extensor Tendon Test
- Elson’s Test
Finger anatomy
The extensor tendon complex of each digit consists of a central band (or median band) and paired lateral bands.
Medial Ligament: The part of the extensor tendon that lies on the dorsal aspect of the middle phalanx
Lateral bands: extend from the interosseous muscles and insert at the root of the distal phalanx
A torn medial glans tendon injury causes volitional slippage of the collateral ligaments, causing abnormal flexion of the PIP joint and extension of the DIP joint.
What is Elson’s test?
The Elson test is a diagnostic procedure used to detect early injuries to the medial portion of the extensor tendon. If left untreated, these injuries can lead to Boutonniere deformity and associated functional limitations. The test aims to help detect such injuries early, allowing timely intervention and preventing further complications.
Purpose
The Elson test is a diagnostic test used for the early detection of medial gliding injuries of the extensor tendon that can lead to Boutonniere deformity if left untreated. The purpose of this test is to identify potential impairments and intervene before significant functional limitations occur.
How is the Elson test performed?
How to do the Elson test:
Positioning:
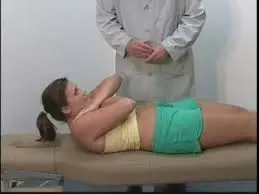
Place the patient’s hand on the table with the proximal interphalangeal joint (PIP) of the affected finger flexed 90 degrees over the edge of the table.
Palpation:
Palpate (touch and palpate) the middle phalanx of the involved finger, which is the finger segment between the PIP joint and the distal interphalangeal (DIP) joint.
Resistance:
Ask the patient to actively extend the PIP joint while providing resistance. This means that you gently try to prevent the patient from extending the finger all the way.
If the medial gliding of the extensor tendon is impaired, performing this test may reveal an inability to fully extend the PIP joint, indicating a positive result. Health professionals, especially hand surgeons or orthopedists, may perform the test to help diagnose certain hand injuries and conditions.
It is important to remember that medical procedures and tests must be performed by qualified health professionals. If you suspect an injury or are concerned about the function of your hand, contact your doctor for a proper evaluation and diagnosis.
What does a positive Elson test mean?
Lack of traction at the PIP joint and fixed extension at the distal joint suggests a complete metatarsal tear (positive Elson test).
If the PIP joint is in tight extension and the distal interphalangeal joint (DIP) is flexed, Elson’s test is negative.
“Modified” Elson test
Here is a trick that can help in this situation. This is an interesting variation of Elson’s test, published in 2006 in the British Journal of Hand Surgery:
The injured and uninjured contralateral fingers are placed between the knuckles in 90 degrees of PIP flexion, with the middle fingers pressed against each other. The patient is then asked to continue with both DIPs.
If the two fingers remain in a symmetrical half-curved position, there is no injury.
A finger with a slip injury may extend the DIP more than an uninjured hand.
Abnormal modified Elson test. The injured finger (blue tourniquet) should not extend that much, but the key to diagnosis is asymmetry. abnormal modified Elson test. The injured finger (blue tourniquet) should not extend that much, but the key to diagnosis is asymmetry.
For comparison:
Standard modified Elson test with limited distal phalanges. Again, the key is to appreciate the symmetry. For comparison: standard modified Elson test with limited distal phalanges. Again, the key is to appreciate the symmetry.
There you have it – a few ways to make sure you don’t miss out on serious injuries. Another interesting case involving a special tendon injury test.
FAQ
The Elson test is a diagnostic test used for early detection of extensor tendon injuries.
The Elson test, used to diagnose CS rupture, is performed by asking the patient to extend the PIP joint against resistance from a 90° flexed position over the edge of the table and assessing the resistance of the DIP joint to flexion.
In this modified Elson test, the injured finger is bent approximately 90° at the PIP joint and pressed against the dorsal side of the middle phalanx of the same finger of the uninjured hand. In this position, the patient is asked to extend the DIP joints.