Pes Planus
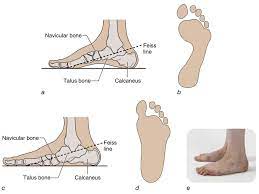
Introduction Pes planus/ pes planovalgus (or flat foot) is a foot deformity in which loss of the medial longitudinal arch of the foot, heel valgus deformity, and medial talar prominence are seen. This is frequently observed with the medial arch of the foot coming near (then typically expected) to the ground or making contact with…