Wrist Muscles
Table of Contents
Introduction
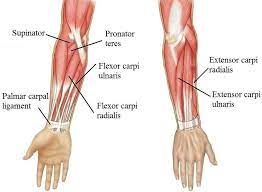
The wrist muscles are a group of muscles that are responsible for controlling the movement of the wrist joint. There are two main groups of wrist muscles: the wrist flexors and the wrist extensors.
Both the wrist flexors and extensors work together to control the movement of the wrist joint and allow us to perform a wide range of activities. Strengthening these muscles can help improve grip strength, prevent injury, and improve overall wrist mobility.
Flexor muscles of the wrist
Flexor Pollicis Longus
The word pollicis makes reference to the thumb and so the flexor pollicis longus is the long muscle that helps in the flexion of the thumb.
Origin: This muscle arises at the Middle anterior surface of the radius.
Insertion: This muscle is inserted into the Base of the distal phalanx of the thumb.
Actions: It helps in the Flexion of the thumb. And Flexion of the wrist.
Innervation: Anterior interosseous nerve.
Daily uses: This muscle is used in Gripping something.
Flexor Digitorum Superficialis
Flexor Digitorum Superficialis is also known as Flexor Digitorum Sublimis. It is placed on the palm side of the forearm and wrist.
Origin: It arises from the Medial epicondyle of the humerus,
Medial coronoid process and
Radial tuberosity.
Insertion: This muscle is divided into 4 tendons which are inserted into the sides of the middle Phalange of the four fingers.
Actions: It helps in the Flexion of the wrist and Flexion of the fingers.
Innervation: Median nerve.
Daily uses: This muscle does the Making of a fist.
Flexor Carpi Ulnaris
The flexor carpi ulnaris is the wrist flexor muscles of the palmar side of the forearm. It also uses full extensor carpi ulnaris for ulnar deviation of the wrist.
Origin: It arises from the Medial epicondyle of the humerus bone.
Insertion: It is inserted into the Base of the 5th metacarpal bone, Pisiform, and hook of the hamate.
Actions: It helps in the Flexion of the wrist.
Ulnar deviation of the wrist.
Innervation: Ulnar nerve.
Daily uses: This muscle is used in Pulling rope towards you.
Flexor Carpi Radialis
This is a wrist muscle that also crosses the elbow joint and so is also known as a weak elbow flexor.
Origin: This muscle arises from the Medial epicondyle of the humerus.
Insertion: This muscle is inserted into the Base of the 2nd and 3rd metacarpals.
Actions: This helps in the Flexion of the wrist. and Radial deviation of the wrist.
Innervation: Median nerve.
Daily uses: It is useful in Pulling rope towards you.
Extensor muscles of the wrist
Extensor Pollicis Longus
The tendon of this muscle can be seen on the radial side of the wrist, at the base of the thumb where it creates the bottom edge of the ‘anatomical snuffbox’ a triangle shape between two tendons.
Origin: This muscle arises from the Upper posterior surface of the ulna.
Insertion: This muscle is inserted into the Base of the distal phalanx of the thumb.
Actions: It helps in the Extension of the wrist and Extension of the thumb.
Innervation: Posterior interosseous nerve.
Daily uses: It is useful in letting out your grip on an object.
Extensor digitorum communis
Extensor Digitorum Communis is sometimes simply mentioned as Extensor Digitorum. It is one of the extensor muscles of the wrist bone, located in the forearm.
Origin: This muscle arises from the Lateral epicondyle of the humerus bone.
Insertion: This muscle is divided into 4 tendons which are inserted into the bottom of the 2nd and 3rd Phalanges of the four fingers.
Actions: It helps in the Extension of the wrist and Extension of the fingers.
Innervation: Posterior interosseous nerve.
Daily uses: It is useful in Pulling the hand back and straightening the fingers for waves.
Extensor Carpi Ulnaris
Extensor carpi ulnaris is placed on the back side of the forearm with the other wrist extensor muscles. This is the only muscle liable for ulnar deviation (moving the hand towards the little finger).
Origin: This muscle arises from the Lateral epicondyle of the humerus bone
Insertion: This muscle is inserted into the bottom of the 5th metacarpal.
Actions: It helps in the Extension of the wrist and also the Ulnar deviation (adduction) of the wrist.
Innervation: Radial nerve.
Daily uses: It use to Accelerate a motorbike.
Extensor Carpi Radialis Longus
As the name proposes, the longer of the two extensor carpi radialis muscles as its origin is the ridge over the lateral epicondyle of the humerus, different from the other wrist extensors which connected to the epicondyle itself.
Origin: This muscle arises from the Lateral supracondylar ridge of the humerus.
Insertion: This muscle is inserted into the bottom of the 2nd metacarpal (dorsal side).
Actions: It helps in the Extension of the wrist.also Radial deviation (abduction) of the wrist.
Innervation: Radial nerve.
Daily uses: It is helpful in an activity such as Typing.
Extensor carpi radialis brevis
It is necessary for racket sports and golf which need strong wrist extensions.
Origin: This muscle arises from the Lateral epicondyle of the humerus bone.
Insertion: This muscle is inserted into the bottom of the third metacarpal bone.
Actions: It is helpful in the Extension of the wrist.Also in the Abduction of the wrist. It is a Weak extension of the elbow.
Innervation: Radial nerve (c6 and c7 nerve roots).
Daily uses: This muscle is used in Gripping things.
Strengthening of wrist muscle
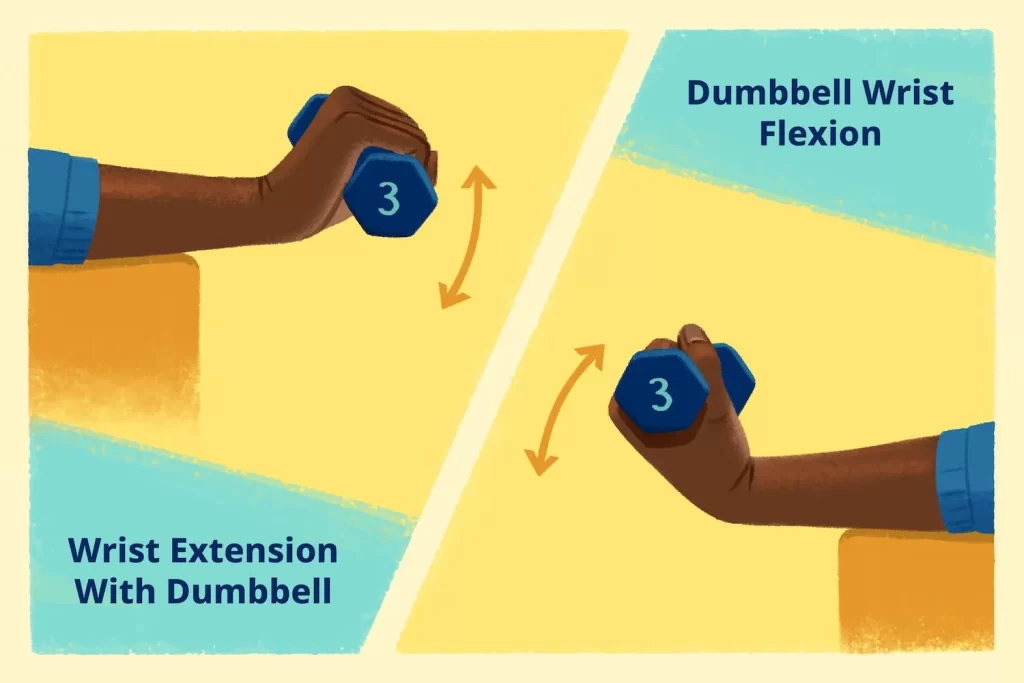
There are several exercises that can be done to strengthen wrist muscles. Here are some of them:
- Wrist curls: Hold a weight in your hand and sit on a bench or chair. place your forearm on a table with your palm facing upward. Slowly curl the weight up towards your forearm and then lower it back down. Do this for 10-15 repetitions and then switch to the other hand.
- Reverse wrist curls: It is Similar to wrist curls, but with your palm facing downwards. take a weight in your hand and place your forearm on a table. Slowly curl the weight up towards your forearm and then lower it back down. Do this for 10-15 repetitions and then switch to the other hand.
- Grip strengthener: Use a grip strengthener to improve your grip strength and wrist muscles. Squeeze the grip strengthener for 10-15 seconds and then release. Repeat this for 10-15 repetitions.
- Tennis ball squeeze: Squeeze a tennis ball as hard as you can for 10-15 seconds and then release. Repeat this for 10-15 repetitions.
- Wrist rotations: Hold a weight in your hand and extend your arm out to the side. Do the rotation of your wrist in a circular manner, first clockwise and then counterclockwise. Do this for 10-15 repetitions and then switch to the other hand.
It is important to start with lighter weights and gradually increase the weight as your wrist muscles become stronger. It is also important to stretch your wrists before and after exercising to prevent injury.
Wrist muscle stretching
The wrist muscles are important for wrist flexion and extension, as well as for gripping and holding objects. Stretching these muscles can help to reduce tension, improve range of motion, and reduce the risk of wrist injuries.
To stretch the wrist muscles, follow these steps:
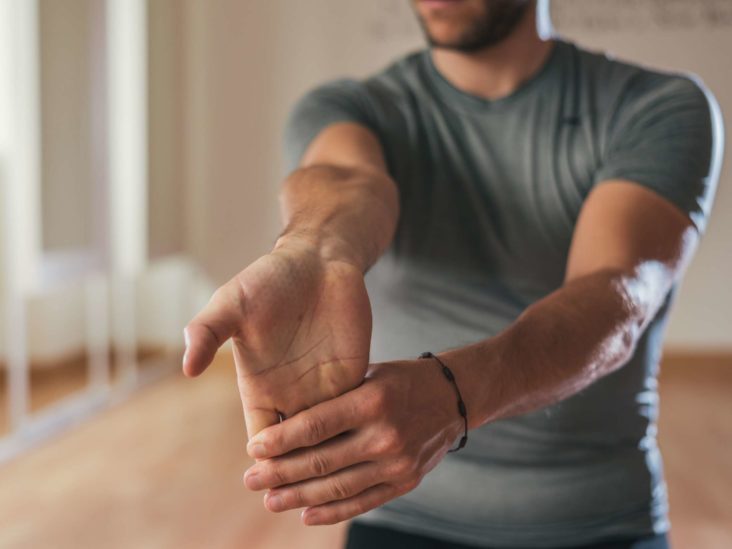

- Start by standing or sitting with your arm out in front of you, palm facing down.
- Use your other hand to softly pull your fingers back towards your wrist until you experience a stretch in your forearm.
- Hold the stretch for 15-20 seconds, then release and repeat on the other arm.
- To stretch the wrist extensor muscles, start by standing or sitting with your arm out in front of you, palm facing up.
- Use your other hand to softly push your fingers down towards your wrist until you experience a stretch in your forearm.
- Hold the stretch for 15-20 seconds, then release and repeat on the other arm.
- To stretch both the wrist flexor and extensor muscles, start by holding your arm out in front of you with your elbow bent at a 90-degree angle.
- Slowly rotate your forearm so that your palm faces up (supination), then slowly rotate it back so that your palm faces down (pronation).
- Repeat this movement for 10-15 repetitions on each arm.
When stretching the wrist muscles, it is important to move slowly and gently, avoiding any sudden or jerky movements. Hold each stretch for 15-20 seconds and repeat 2-3 times on each arm. If you feel any type of pain or discomfort while stretching, stop that movement and take advice from a healthcare professional.
FAQ
Strengthening wrist muscles can improve grip strength, prevent injuries, and increase overall wrist stability.
Yes, wrist exercises can help alleviate symptoms of carpal tunnel syndrome by strengthening the muscles and reducing pressure on the median nerve.
It is recommended to do wrist exercises 2-3 times per week, with at least one day of rest in between.
It depends on the how injury occurs. It is best to consult with a doctor or physical therapist before starting any exercises if you have a wrist injury.
Yes, strengthening wrist muscles can also improve performance in sports that require grip strength, such as tennis or rock climbing. It can also improve fine motor skills and dexterity in everyday activities.