Vitamin D Deficiency
Table of Contents
What is vitamin D deficiency?
Vitamin D deficiency is a common condition that occurs when the body doesn’t get enough vitamin D, which is essential for maintaining healthy bones, muscles, and overall health. This deficiency can be caused by a lack of sun exposure, certain medical conditions, and dietary restrictions. Symptoms can range from fatigue and bone pain to an increased risk of infections and chronic diseases. Treatment typically involves increasing vitamin D intake through supplements, diet, and exposure to sunlight.
Vitamin D deficiency suggests that don’t have sufficient vitamin D in the body. It mainly causes problems with the bones & muscles.
Vitamin D is an important vitamin in the body used for normal bone growth & maintenance. Vitamin D also plays an important role in the nervous, immune, and musculoskeletal systems.
Can get vitamin D in various ways, involving:
- Sun exposure on the skin. However, people with darker skin & elder people may not get sufficient vitamin D via sunlight. The geographical area may also prevent sufficient vitamin D exposure through sunlight.
- Via the food you eat.
- Via nutritional supplements.
Despite all these ways to get vitamin D, this deficiency is a common problem.
Why is vitamin D so important?
Vitamin D is one of the numerous vitamins the body requires to stay healthy. It plays an important role in keeping the balance of calcium in the blood, and bones & in building and maintaining bones.
More precisely, require vitamin D so the body can use calcium & phosphorus to build bones & support healthy tissues.
With chronic vitamin D deficiency, calcium is decreased & phosphorus absorption by the intestines causes hypocalcemia [ calcium levels are low in the blood ]. This cause to secondary hyperparathyroidism.
Both hypocalcemia & hyperparathyroidism, if extreme, can lead to symptoms, involving muscle weakness & cramps, fatigue & depression.
To try to balance calcium levels in the blood, the body takes calcium from the bones, which cause accelerated bone demineralization [ when a bone breaks down faster than it can improve ].
This can also result in soft bones [osteomalacia] in adults & rickets in children.
Osteomalacia & osteoporosis put you at improved risk for bone fractures. Rickets is the same as osteomalacia, it only impacts children. Since a child’s bones are still growing, demineralization leads to bowed or bent bones.
What does vitamin D deficiency affect?
Anyone can have vitamin D deficiency, involving infants, children & adults.
Vitamin D deficiency may be very common in people with darker skin [ higher skin melanin content ] & who wear clothing with comprehensive skin coverage, especially in the Middle Eastern world.
How common is vitamin D deficiency?
Vitamin D deficiency is a typical global problem. About 1 B people worldwide have vitamin D insufficiency, while 50% of the people have a vitamin D deficit.
Approximately 35% of grown-ups in the United States have vitamin D insufficiency
Functions of Vitamin D
Vitamin D has considerable crucial functions:
- Supporting bone health by promoting the absorption of calcium
- Boosting muscle health
- Modulating the immune system
- Helping cell growth
- Reducing inflammation, which helps control diseases such as rheumatoid arthritis & psoriasis
- Regulating blood pressure & helping cardiovascular health
Low vitamin D and diabetes
- Some professionals have recommended that vitamin D may help prevent type 2 diabetes.
- However, in a 2019 analysis, 2,423 people at threat of type 2 diabetes took either a vitamin D supplement of 4,000 international units (IU) a day or a placebo.
- Levels of vitamin D increased in those who took the supplement. However, taking the supplement did not seem to decrease the risk of diabetes developing.
Causes a vitamin D deficiency
This vitamin D deficiency is defined as containing blood levels below 20 ng/mL.
while levels from 21 to 29 ng/mL are considered inadequate. There’s no single reason for deficiency, the overall chance may be higher as an outcome of specific underlying diseases or lifestyle factors.
Some of the most common reasons for vitamin D deficiency are:
- Having dark skin
- Being older
- Having overweight or obesity
- Not eating much fish or dairy
- Living far from the equator or in places with little sunlight year-round
- Staying or working indoors
- Working overnight shifts
- Having chronic kidney disease, liver disease, or
- Hyperparathyroidism
- Having a health disorder that affects nutrient absorption, like Crohn’s disease or celiac disease
- Having gastric bypass surgery
- Using specific medications that influence vitamin D metabolism, such as statins & steroids
People who live near the equator & get regular sun exposure are less likely to have a deficiency because their skin produces sufficient vitamin D.
While people who usually wear sunscreen outdoors are also at an increased risk of weakness, using sunscreen is essential to reduce skin harm & cancer risk due to sun exposure.
Confer a healthcare professional about the vitamin D status if at increased risk of deficiency.
Signs and symptoms of vitamin D deficiency
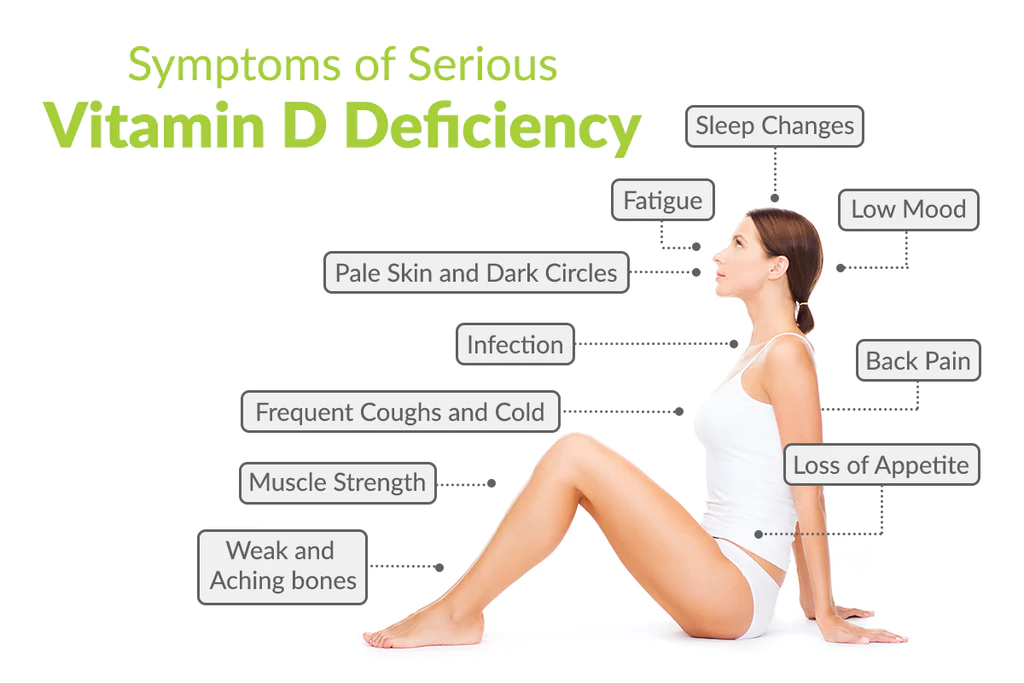
Vitamin D deficiency can be tough to notice because symptoms may not appear for many months or years. Sometimes, may have no symptoms at all.
Keeping that in mind, it’s still useful to know what signs & symptoms to look for.
Frequent illness or infections
One of the most crucial roles of vitamin D is supporting immune health, which helps ward off viruses & bacteria that lead to illness.
Vitamin D directly interacts with the cells that are accountable for addressing infections. Many large observational analyses have shown a link between a deficiency & respiratory tract infections like colds, bronchitis, and pneumonia.
Several investigations have discovered that taking up to 4,000 IU of vitamin D daily may decrease the risk of respiratory tract infections. Recently, vitamin D deficiency has been connected to an increased risk of COVID-19, as well as an expanded risk of experiencing painful effects from the disease. However, it is essential to note that taking vitamin D supplements at any dosage will not prevent COVID-19.
Fatigue and tiredness
Feeling tired can arise from several causes, one of which may be vitamin D deficiency.
For causes like:
- Stress, depression
- Insomnia.
Vitamin D deficiency is usually overlooked as a potential reason for tiredness.
One analysis in 480 older adults connected vitamin D deficiency with fatigue symptoms.
Observational analysis of female nurses discovered a powerful connection between low vitamin D levels & self-reported tiredness. What’s more, 89% of the participants were lacking in this vitamin.
Interestingly, many studies indicate that supplementing with this vitamin may decrease the stringency of tiredness in people with a deficiency.
Bone and back pain
Bone & lower back pain may be symptoms of insufficient vitamin D levels.
Vitamin D supports maintaining bone health by improving the body’s absorption of calcium.
One investigation in 98 adults with lower back pain connected lower levels of vitamin D to more intense pain. However, a large research study discovered that this association was inconsistent across other similar studies.
A study of 81 investigations also discovered that people with arthritis, muscle pain, & chronic widespread pain managed to have lower levels of vitamin D than people without these conditions.
Depression
Vitamin D deficiency has been connected to depression, mainly in older adults although some analysis results are conflicting.
The effects of vitamin D supplements have been mixed, but some investigations have discovered that they helped reduce symptoms of depression.
Impaired wound healing
Slow wound recovery after surgery or injury may be a signal that the vitamin D levels are too low.
Results from a test-tube study indicate that vitamin D increases the production of combinations that are essential for forming new skin as a region of the wound-healing process.
One study of 4 analyses discovered that vitamin D deficiency compromised specific parts of healing in people who had dental surgery.
Vitamin D’s important role in controlling inflammation & addressing infections may also be important for proper recovery.
One analysis of 221 people, 112 of whom had diabetes-related foot disorders, discovered that those with many vitamin D deficiencies were more probable to have higher levels of inflammatory features that can jeopardize recovery.
In a 12-week study affecting 60 people with diabetes-related foot ulcers, those who took a vitamin D supplement encountered considerable improvements in wound healing compared with the placebo group.
Bone loss
Vitamin D recreates an important role in calcium absorption & bone metabolism. This is necessary because taking vitamin D & calcium at the same time helps the body maximize absorption.
Low bone mineral density is an expression that the bones have lost calcium & other minerals. This places older adults, mainly women, at an increased risk of fractures.
In a considerable observational analysis of more than 1,100 middle-aged menopausal and postmenopausal women, researchers discovered a strong connection between low vitamin D levels & low bone mineral density.
However, a study on vitamin D supplementation therapy in separate older adults has produced mixed results. While some analyses show some benefits, like decreased muscle pain, others have not seen that it wards off fractures associated with bone loss.
One investigation discovered that women deficient in vitamin D participated in no gain in bone mineral density when they took high-dose supplements, even if blood levels were enhanced.
Nonetheless, sufficient vitamin D intake may be a good strategy to save bone mass & reduce the risk of fracture.
Hair loss
Many foods & nutrients may impact hair health. While stress is a typical reason for hair loss, severe hair loss may be the outcome of a disease or nutrient deficiency.
Hair loss in women is connected to low vitamin D levels, though analysis is lacking. In particular, investigations tie low vitamin D levels to alopecia areata, an autoimmune disorder characterized by extreme hair loss.
One analysis of people with this disease associated lower vitamin D levels with more extreme hair loss. In another analysis of 48 people in this situation, using an artificial form of vitamin D topically for 12 weeks greatly increased hair regrowth.
An examination study discovered that vitamin D levels may have an inverse relationship with non-scarring hair loss. This shows the higher the vitamin D levels, the less hair loss noticed in the study, & vice versa.
Muscle pain
The causes of muscle pain are usually difficult to pinpoint. However, proof indicates that vitamin D deficiency is a potential cause.
In an analysis, 71% of people with chronic pain were discovered to have a lack the vitamin, & the vitamin D receptor is present in nerve cells named nociceptors, which sense pain. This vitamin may be involved in the body’s pain-signaling ways, which may play an important role in chronic pain, and a few investigations note that high-dose vitamin D supplements may facilitate different types of pain in people with a vitamin D deficiency.
Weight gain
Weight gain is a risk factor for vitamin D insufficiency. An analysis in adults discovered a possible connection between low vitamin D status & both belly fat & increased weight, although these results were more prominent in males.
While vitamin D deficiency may be noticed in cases of obesity, further investigations are required to determine whether supplementing with this vitamin helps control weight gain.
Anxiety
Vitamin D deficiency is connected to anxiety conditions.
The analysis discovered that levels of calcidiol, a type of vitamin D, were lower in people with anxiety, as well as in those with depression.
A different study on pregnant females discovered that having sufficient vitamin D may help reduce stress symptoms, improve bedtime & help prevent postpartum depression.
Diagnosis of Vitamin D deficiency
The serum concentration of calcifediol, also named 25-hydroxyvitamin D [ abbreviated 25(OH)D ], is commonly used to define vitamin D status. Most vitamin D is restored to 25(OH)D in the serum, providing an accurate picture of vitamin D status. The level of serum 1,25(OH)D is not generally used to define vitamin D status because it usually is regulated by other hormones in the body like a parathyroid hormone. The levels of 1,25(OH)D can remain normal even when a person may be vitamin D insufficient.
A serum level of 25(OH)D is the laboratory examination ordered to suggest whether or not a person has vitamin D deficiency or deficiency. It is also considered useful to treat at-risk persons with vitamin D supplementation without checking the level of 25(OH)D in the serum, as vitamin D toxicity has only existed rarely reported to occur.
Vitamin D toxicity generally results from taking supplements in excess. Hypercalcemia is usually the cause of symptoms, & levels of 25(OH)D above 150 ng/mL (375 nmol/L) are generally discovered, although in some cases 25(OH)D levels may seem to be normal. Periodic measurement of serum calcium in people acquiring large doses of vitamin D is suggested.
Screening
The official request from the United States Preventive Services Task Force is that for individuals that do not tumble within an at-risk population and are asymptomatic, there is not sufficient evidence to confirm that there is any benefit in screening for vitamin D deficiency.
Treatment of vitamin D deficiency
UVB exposure
Overdose of Vitamin D is incomprehensible from UV exposure, the skin develops stability where the vitamin pollutes as fast as it is created.
Light therapy
Exposure to light [ photons ] at specific wavelengths of narrowband UVB helps the body to produce vitamin D to feast vitamin D insufficiency.
Supplement of Vitamin D
Vitamin D2 supplements
The amount of vitamin D suggested is 400 IU per day for children, 600 IU per day for adults, & 800 IU per day for people over age 70. The Canadian Paediatric Society suggests that pregnant or breastfeeding women think taking 2000 IU/day, that all infants who are only breastfed receive a supplement of 400 IU/day.
Treating vitamin D deficiency relies on the severity of the deficiency.
Treatment involves an initial high-dosage treatment phase until the needed serum levels are reached, followed by the maintenance of the acquired levels. The lower the 25(OH)D serum engagement before treatment, the higher the dosage that is needed to fast reach an acceptable serum level.
The initial high-dosage treatment can be provided on a daily or weekly basis or can be provided in form of one or many single doses. Therapy drugs differ, & there is no agreement yet on how best to come to an optimum serum level. While there is proof that vitamin D3 raises 25(OH)D blood levels more actually than vitamin D2, other evidence shows that D2 & D3 are equal for maintaining 25(OH)D status.
Foods sources of vitamin D

Good dietary sources of vitamin D contain:
- Oily fish, like mackerel or salmon
- Beef liver
- Cheese
- Mushrooms
- Egg yolks
- Fortified foods, involving some breakfast cereals, orange juice, milk, soy drinks, & margarine.
Complications
In most circumstances, vitamin D deficiency is asymptomatic. It may just be noticed on blood tests but is the reason for some bone diseases & is associated with other conditions:
Rickets: It is a childhood disorder characterized by restricted growth & deformity of the long bones. The premature symptom of vitamin D deficiency is thinning of the skull, craniotabes, and abnormal softening.
Osteomalacia: It is a bone-thinning disorder that appears only in adults & is indicated by proximal muscle weakness & bone fragility. Women with vitamin D deficiency who have been via multiple pregnancies are at elevated risk of osteomalacia.
Osteoporosis: It is a disease characterized by decreased bone mineral density & increased bone fragility
Improved risk of fracture
Muscle aches, weakness, & twitching, due to decreased blood calcium.
Periodontitis: It is the local inflammatory bone loss that can result in tooth loss.
Pre-eclampsia: There has been an association between vitamin D deficiency & women who develop pre-eclampsia in pregnancy. The accurate relationship between these disorders is not well comprehended.
Respiratory infections & COVID-19: Vitamin D insufficiency may raise the risk of severe acute respiratory infections & COPD. Emerging analyses have indicated a link between vitamin D deficiency & COVID-19 symptoms. An examination has shown that vitamin D deficiency is not associated with a higher probability of having COVID-19 but is associated with greater severity of the disease, including 80% increases in the swiftness of hospitalization & mortality.
Schizophrenia: Vitamin D deficiency is associated with the outcome of schizophrenia. People with schizophrenia commonly have lower levels of vitamin D. The environmental risk factors of the seasonality of birth, latitude, & migration connected to schizophrenia all involve vitamin D deficiency, as do other health disorders like maternal obesity. Vitamin D is important for the normal development of the nervous system.
Can too much vitamin D be toxic?
Accumulating too considerably vitamin D [ known as vitamin D toxicity ] can be harmful. Symptoms of toxicity contain nausea & vomiting, poor appetite, constipation, weakness, & weight loss.
Very high levels of vitamin D can harm the kidneys. High blood calcium levels [ hypercalcemia ] can lead to confusion, kidney failure, & arrhythmia [ irregular heartbeat ].
Issues of vitamin D toxicity happen when a person overuses vitamin D supplements. Cannot get too much vitamin D from sun exposure because the skin determines the amount of vitamin D it produces.
Risk factors
Those most likely to be impacted by vitamin D deficiency are people with little exposure to sunlight. Specific environments, dress patterns, the getaway of sun exposure & the usage of too much sunscreen security can all limit the production of vitamin D.
Age
Old people have a higher risk of having vitamin D insufficiency due to a combination of many risk factors, including reduced sunlight exposure, reduced intake of vitamin D in the diet, & reduced skin thickness, which cause further reduced absorption of vitamin D from sunlight.
Fat percentage
Since vitamin D3 & vitamin D2 are fat-soluble, humans & other animals with a skeleton require to store some fat. Without fat, the animal will have a difficult time absorbing vitamin D2 & vitamin D3, & the lower the fat percentage, the greater the risk of vitamin insufficiency.
Malnutrition
Rickets & Osteomalacia are irregular in Britain, osteomalacia outbreaks in some immigrant residents included women with seemingly sufficient sunlight outdoor exposure wearing typical Western clothing. Having darker skin & reduced disclosure to sunshine did not have rickets unless the diet differed from a Western omnivore pattern characterized by high infusions of meat, fish, & eggs & low intakes of high-extraction cereals.
This is characteristic of cereal-based diets with restricted access to dairy products. Rickets was previously a major public health issue among the US population.
An increase in the proportion of animal protein in the 20th-century American diet associated with improved consumption of milk hardened with relatively small amounts of vitamin D overlapped with a surprising drop in the number of rickets cases.
One study of children in a hospital in Uganda, however, revealed no substantial difference in vitamin D levels of malnourished children reached to non-malnourished children. Both groups were in danger due to darker skin pigmentation. Both groups had vitamin D insufficiency.
Diet
People who do not consume adequate vitamin D-rich foods, involving fortified dairy products & grains, may have insufficient levels of vitamin D.
Lifestyle factors
Some individuals consume little time outdoors due to jobs, ill health, a lack of outdoor space in the neighborhood, or other factors. These people have less chance to expose their skin to sunlight. Those who wear clothes that cover all of their body, whether to save it from the sun or for cultural or spiritual reasons, may also have a higher risk of a defect.
People who use a lot of sunscreens or wear clothing that protects the body should contain sources of vitamin D in their diet.
Geographical factors
People living in specific parts of the world may have less access to the sun’s UVB rays, mainly in winter. People who live in a hot environment may also be at risk, as they usually try to avoid the heat & strong sunlight by staying indoors.
Pollution
Particles in the air can block UVB rays & stop them from reaching the skin. People who live in highly contaminated locations may also be more likely to avoid expending time outside.
Medications
Some drugs decrease the body’s ability to absorb or synthesize vitamin D. These contain steroids & some drugs for lowering cholesterol, among others.
Smoking
Levels of deficiency seem to be higher among smokers. Many professionals have indicated that smoking may affect the gene that starts the production of vitamin D-3 in the body.

Research has discovered lower vitamin D levels in humans with obesity or a BMI (body mass index) of 30 or more. This link may stem from how body fat involves vitamin D absorption. Some people with obesity may spend a shorter time outdoors due to mobility issues. Those who have experienced bariatric surgery may have absorption issues. Contrarily, people whose BMI of 25–29.9 categorized them as overweight seemed to have a lower risk of a deficiency than those who were not heavy.
Kidney and liver health
People with liver illness and kidney disorders tend to have lower vitamin D levels. These conditions can impact the body’s ability to synthesize vitamin D or turn it into its functional form.
Pregnancy
The need for vitamin D increases during pregnancy, but uncertain whether supplements are a suitable idea. Pregnancy may decrease the risk of preeclampsia, gestational diabetes, low birth weight, & extreme bleeding after delivery. However, it may enhance the risk of preterm birth, which is labor before 37 weeks.
Breastfeeding infants
Mortal milk is low in vitamin D, which suggests that breastfeeding infants are at risk of insufficiency. The Centers for Disease Control & Prevention(CDC) suggest providing a vitamin D supplement to all breastfeeding infants from the first few days of life until they consume 1 l or more of instructions milk daily.
Prevention
The best type to contain a vitamin D deficiency is to consume foods that are rich in nutrients & to spend some time further every day.
Some tips for avoiding a deficiency include:
Maintaining a healthy body weight: Cycling or walking can supply both exercise & exposure to sunlight.
Treating medical conditions: People with health disorders that influence the absorption of nutrients may find that treating the underlying condition helps boost their levels of specific nutrients, involving vitamin D.
Being aggressive about preventive health: People with a family record of osteoporosis or vitamin D deficiency desire to consider talking to the physician about screening.
FAQ
The best sources are the meat of fatty fish & fish liver oils. Fewer amounts are seen in egg yolks, cheese, & beef liver. Specific mushrooms include some vitamin D2 in addition, some commercially marketed mushrooms include higher amounts of D2 due to consciously being revealed to high doses of ultraviolet light.
Developing proof has shown that vitamin D has a role in sleep limitation. Especially, vitamin D deficiency can increase the risk of sleep disorders & is associated with sleep problems, shorter sleep duration, & nocturnal awakenings in kids & adults.
Almond & soy milk have vitamin D. This is one of the best vegan seeds of healthy Vitamin D. Almond, oat, and soy milk are all rich in vitamins & minerals.
Glucosamine & chondroitin are two of the most generally used supplements for arthritis. They’re pieces of cartilage the substance that softens the joints. Analysis of these supplements has been integrated, in part because investigations have used variable designs & supplement types.
Some side consequences of taking too much vitamin D include weakness, dehydrated mouth, sickness, nausea, vomiting, & many others.
Have issues with your kidneys, like kidney failure, or ever had kidney stones? Have hypervitaminosis D and high levels of vitamin D in your blood. Have a rare condition named sarcoidosis. Have calcification of high levels of calcium in the body tissues and organs.
Yes, numerous analyses show that a deficiency of this vitamin can cause joint pain & swelling. As Vitamin D is needed for bone building & bone health, therefore a lack of it will negatively impact the bones.
When vitamin D levels are low & the body isn’t capable of properly absorbing calcium & phosphorus, there is an increased chance of bone pain, bone fractures, muscle pain & muscle deficiency.
Having insufficient levels of vitamin D may connect with unintentional weight gain. An analysis of females over the age of 65 discovered that parties with a lower vitamin D level encountered more additional weight gain. A systematic study of 23 different investigations uncovered similar associations between vitamin D insufficiency & obesity.




One Comment