Proximal Interphalangeal Joint Flexion And Extension
Table of Contents
What is Proximal Interphalangeal Joint Flexion And Extension?
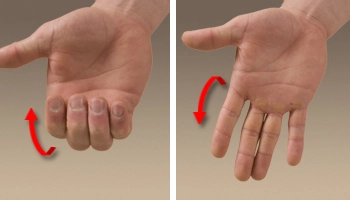
Proximal Interphalangeal (PIP) joint flexion and extension discuss the bending and straightening actions of the center joint of the fingers, that’s the PIP joint. The PIP joint is positioned among the proximal and center phalanges of the finger.
Flexion of the PIP joint entails bending the finger toward the palm. This motion brings the fingertips towards the palm, developing a concave form withinside the finger. The flexion of the PIP joint is vital for gripping gadgets, creating a fist, and appearing diverse excellent motor obligations.
Extension of the PIP joint, on the opposite hand, entails straightening the finger with the aid of using shifting it far from the palm. This motion brings the finger returned to an impartial or prolonged position, with the joint aligned with the opposite joints withinside the finger. Extension of the PIP joint is vital for finger and hand actions that require reaching, pointing, or greedy gadgets with a prolonged finger.
Both flexion and extension of the PIP joint are essential for normal finger characteristics and dexterity. Adequate flexibility and variety of movement withinside the PIP joint permit diverse sports, which include writing, typing, gambling musical instruments, and appearing everyday obligations that contain excellent motor skills.
Exercises focused on PIP joint flexion and extension are frequently encouraged in hand remedy and rehabilitation to enhance finger strength, flexibility, and coordination. These physical activities can assist people regain or decorate their capacity to carry out useful sports and hold top-of-the-line hand characteristics.
Proximal Interphalangeal Joint Flexion
What is Proximal Interphalangeal Joint Flexion?
Proximal interphalangeal joint flexion refers back to the bending or flexing of the proximal interphalangeal (PIP) joint, that is one of the joints withinside the arms or toes. The PIP joint is placed among the proximal phalanx bone (the bone closest to the hand or foot) and the center phalanx bone.
Flexion on the PIP joint permits for the bending of the finger or toe, bringing the fingertip or toe in the direction of the palm or sole. This motion is critical for numerous sports that contain gripping, grasping, and manipulating objects. It is managed via way of means of the muscles, tendons, and ligaments surrounding the joint.
Injuries or situations affecting the PIP joint, including arthritis, trauma, or inflammation, can limit or impair flexion, main to a reduced variety of movement and useful limitations. Rehabilitation exercises, bodily therapy, and every so often surgical intervention can be endorsed to enhance or repair PIP joint flexion if it turns problematic.
Proximal Interphalangeal Joint Flexors Muscles
The proximal interphalangeal (PIP) joint is the second joint of the fingers, placed among the proximal and center phalanges. The PIP joint flexors are the muscular tissues answerable for bending or flexing this joint. There are numerous muscular tissues concerned with PIP joint flexion. Here are the primary muscular tissues:
- Flexor Digitorum Superficialis (FDS): This muscle is placed withinside the forearm and has tendons that expand to the center phalanges of the fingers. It flexes the PIP joint in addition to the metacarpophalangeal (MCP) joint.
- Flexor Digitorum Profundus (FDP): Also placed withinside the forearm, this muscle’s tendons by skip via the FDS tendons and connect to the distal phalanges of the fingers. It flexes the PIP joint and the distal interphalangeal (DIP) joint.
- Lumbricals: These are small muscular tissues that originate from the tendons of the FDP and connect to the extensor growth at the dorsal floor of the fingers. They flex the MCP joints and expand the interphalangeal joints (PIP and DIP).
- Interossei Muscles: There are each palmar and dorsal interossei muscular tissues, and they’re placed among the metacarpal bones of the hand. They assist with PIP joint flexion, in addition to abduction and adduction of the fingers.
- Flexor Digiti Minimi: This muscle is placed withinside the palm of the hand and is answerable for flexing the PIP joint of the 5th finger.
These muscular tissues paint collectively to flex the PIP joint and are managed with the aid of using the ulnar and median nerves. It’s crucial to word that the precise anatomy and association of muscular tissues can range barely among individuals.
Range Of Motion Of Proximal Interphalangeal Joint Flexion
The regular variety of motion (ROM) for proximal interphalangeal (PIP) joint flexion withinside the hands is usually taken into consideration to be around one hundred to a hundred and twenty degrees. This method that the finger may be bent or flexed to about a proper attitude or barely beyond.
However, it is vital to observe that the real ROM can range amongst people and can be stimulated via way of means of elements inclusive of age, joint health, and former injuries. Some people might also additionally have barely much less or more flexion of their PIP joints because of anatomical variations or situations affecting the joint.
When assessing the ROM of the PIP joint flexion, healthcare experts frequently use goniometry, which is a dimensioning method concerning a specialized device known as a goniometer. This device facilitates quantifying the diploma of joint motion and affords a greater correct dimension of flexion.
If there are boundaries in PIP joint flexion, it is really helpful to talk over with a healthcare professional, inclusive of a hand therapist or orthopedic specialist, who can determine the unique situation and offer suitable steerage or remedy options.
To take a look at the variety of motion (ROM) of the proximal interphalangeal (PIP) joint flexion, you could carry out the subsequent steps:
- Prepare for the evaluation: Find a well-lit vicinity and make certain the man or woman being assessed is seated without difficulty with their arm supported on a desk or their hand resting on a flat surface.
- Locate the PIP joint: Identify the PIP joint, that’s the joint positioned withinside the center of the finger among the proximal and center phalanx bones.
- Determine the beginning function: Ask the man or woman to increase their finger fully, preserving it straight. This is the beginning function of the evaluation.
- Stabilize the finger: Use your different hand to stabilize the finger being assessed with the aid of using lightly keeping the adjoining joints (metacarpophalangeal joint and distal interphalangeal joint) to save you any unintentional motion.
- Assess flexion: Instruct the man or woman to slowly flex their finger, bending it on the PIP joint. Encourage them to flex as a good deal as they are able to without difficulty and without inflicting aches or soreness.
- Observe and measure: While they’re flexing their finger, take a look at the motion of the joint and decide the most perspective achieved. You can estimate the perspective or use a goniometer for an extra specific measurement.
- Repeat for every finger: Perform the equal evaluation for every finger, one at a time, because the ROM may also range among fingers.
- Document the measurements: Record the measurements for every finger in degrees, noting any obstacles or asymmetries.
It’s critical to technique the evaluation lightly and be aware of the man or woman’s comfort. If they revel in aches or soreness all through the evaluation, it is fine to forestall and visit a healthcare expert for additional assessment and guidance.
Proximal Interphalangeal Joint Flexion Test
The Proximal Interphalangeal (PIP) Joint Flexion Test is a medical exam used to evaluate the variety of movements and versatility of the PIP joint withinside the hands. Here’s how the take a look at is accomplished:
Positioning: Ask the individual being assessed to take a seat down effectively with their arm supported on a desk or their hand resting on a flat surface.
Starting position: The individual’s hand ought to be comfortable and hands prolonged naturally.
Stabilize adjoining joints: Use one hand to stabilize the adjoining joints, together with the metacarpophalangeal joint (MCP) and the distal interphalangeal joint (DIP), to save you any unintentional movement.
Test one finger at a time: Begin with the finger you need to evaluate.
Application of stress: With your different hand, lightly follow stress to the fingertip, perpendicular to the finger, pushing it closer to the palm. The stress ought to be implemented on the distal quit of the finger, simply past the DIP joint.
Assessing flexion: Instruct the individual to flex their finger on the PIP joint whilst you preserve stress at the fingertip. Encourage them to flex as a good deal as they are able to without inflicting aches or discomfort.
Observe and measure: Observe the perspective at which the PIP joint begins off evolved to flex. Note the diploma of flexion carried out and any ache or barriers skilled with the aid of using the individual all through the movement.
Repeat for Other Fingers: Perform the take a look at every finger, one at a time, documenting the measurements and any observations.
It’s critical to bear in mind that this take a look at ought to be accomplished lightly to keep away from inflicting any undue ache or discomfort. If the individual reviews great ache, it’s far really useful to stop the take a look at and are searching for an additional assessment from a healthcare professional.
Exercise For Proximal Interphalangeal Joint Flexion
Here is an exercise you may carry out to enhance the flexion of the proximal interphalangeal (PIP) joint:

- Finger Flexion Exercise:
- Start by setting your hand flat on a desk or some other flat surface.
- Begin with the hands prolonged directly out.
- Slowly and steadily flex the PIP joint of 1 finger, bringing the fingertip in the direction of the palm.
- Hold the flexed role for some seconds, feeling a mild stretch withinside the PIP joint.
- Then, slowly increase the finger lower back to the beginning role.
- Repeat this exercise for 10 to fifteen repetitions on every finger, steadily growing the range of repetitions through the years as your flexibility improves.
- Perform this exercising more than one instance at some stage in the day, aiming for a minimum of 3 units in line with the day.
Make positive to carry out the exercising inside your ache-unfastened variety of motion. If you revel in any ache or discomfort, lessen the depth or variety of the motion and talk over with a healthcare expert or a hand therapist for similar guidance.
Additionally, it is crucial to observe that sports on my own might not be enough for all cases. If you’ve got precise issues or situations affecting your PIP joint flexibility, it is endorsed to are seeking expert recommendation from a healthcare company that can offer a correct analysis and creates a customized exercise plan primarily based totally on your character needs.
Special Test For Proximal Interphalangeal Joint Flexion
To check the flexion of the proximal interphalangeal (PIP) joint, you may carry out the subsequent unique check referred to as the “Modified Allen Test.” This check is typically used to evaluate the integrity and variety of movement of the PIP joint.
Here’s how you may carry out the Modified Allen Test:
- Positioning: Ask the affected person to take a seat down or stand effectively with their hand comfortable and palm going through upward.
- Stabilization: Use one hand to stabilize the affected person’s forearm, mainly the metacarpophalangeal (MCP) joint, to save you any motion all through the check.
- Test initiation: Using your different hand, region your thumb at the distal give up of the affected person’s center phalanx (P2 segment) and your index finger at the affected person’s proximal interphalangeal (PIP) joint (among the center and proximal phalanx, P2-P3 joint).
- Range of movement assessment: Ask the affected person to actively flex their PIP joint at the same time as you observe resistance together along with your index finger. Observe the variety of movements and any limitations, aches, or soreness skilled with the aid of using the affected person.
- Repetition: Repeat the check for the opposite hands if necessary.
During the check, take into account the affected person’s consolation and any symptoms and symptoms of ache or soreness. Compare the variety of movement among each finger and notice any sizable differences.
It’s vital to notice that that is a popular description of the check, and it is constantly advocated to seek advice from a healthcare expert or therapist for correct commands and guidance. They can offer you extra unique info and concerns primarily based totally on the affected person’s situation and the man or woman’s needs.
Proximal Interphalangeal Joint Extension
What Is Proximal Interphalangeal Joint Extension?
Proximal Interphalangeal (PIP) joint extension refers back to the motion of extending or straightening the PIP joint, that’s positioned among the proximal and center phalanges of the finger. When the PIP joint is extended, the finger is stretched out and the joint attitude increases.
The PIP joint lets in for flexion (bending) and extension (straightening) of the finger. Flexion happens while the joint attitude decreases, together with while creating a fist or bending the finger. Extension, on the opposite hand, takes place while the joint attitude increases, as in straightening the finger.
The PIP joint extension is a crucial motion for numerous sports regarding finger dexterity and grip strength. It is critical for responsibilities together with greedy objects, typing, gambling musical instruments, and acting great motor skills.
Evaluation of PIP joint extension is frequently a part of a complete exam of hand and finger function. Healthcare professionals, together with hand therapists or orthopedic specialists, can also additionally check PIP joint extension at some point of bodily examinations to assess a joint variety of motion, become aware of any boundaries or abnormalities, and have manual remedy or rehabilitation plans for situations affecting the hand and fingers.
It’s essential to observe that in case you are experiencing any discomfort, pain, or boundaries in PIP joint extension or other finger movements, it is really helpful to seek advice from a healthcare expert for correct evaluation, diagnosis, and remedy.
Proximal Interphalangeal Joint Extensores Muscles
The number one extensor muscle mass is accountable for extending the proximal interphalangeal (PIP) joint is positioned at the again (dorsal) facet of the hand and forearm. These muscle mass paintings collectively to provide the important pressure for PIP joint extension. The important extensor muscle mass of the PIP joint includes:
- Extensor Digitorum Communis (EDC): The EDC muscle is the number one extensor muscle for the fingers. It originates from the lateral epicondyle of the humerus and runs alongside the again of the forearm. The tendon of the EDC divides into 4 separate tendons, one for every finger (index, center, ring, and little). These tendons go to the wrist and insert into the bottom of the center phalanges, contributing to the extension of the PIP joints.
- Extensor Indices Proprius (EIP): The EIP muscle is positioned adjoining to the EDC muscle and runs alongside the again of the forearm. It originates from the posterior floor of the ulna and inserts into the extensor growth of the index finger. The EIP muscle on the whole extends the index finger and assists in PIP joint extension.
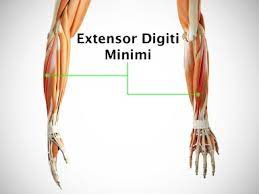
- Extensor Digiti Minimi (EDM): The EDM muscle is positioned at the ulnar facet of the forearm and extends from the lateral epicondyle of the humerus. It runs alongside the again of the forearm and inserts into the extensor growth of the little finger. The EDM muscle is accountable for extending the little finger and contributes to PIP joint extension.
These muscle mass paintings are in coordination with different muscle mass and tendons of the hand and forearm to carry out unique finger movements, which includes PIP joint extension. It’s crucial to be aware that the extensor muscle mass can also additionally have extra actions, inclusive of wrist extension and metacarpophalangeal (MCP) joint extension.
Maintaining the electricity and versatility of those extensor muscle masses is essential for finger function. In instances of harm or situations affecting the hand and fingers, rehabilitation physical games and treatment plans can also additionally attention on strengthening and enhancing the variety of movement of those muscle masses to repair PIP joint extension capabilities.
Range Of Motion Of Proximal Interphalangeal Joint Extension
The variety of movement (ROM) for proximal interphalangeal (PIP) joint extension can range among people and may be motivated through elements consisting of age, anatomical versions, and any underlying situations or injuries. The ordinary variety of movement for PIP joint extension is generally around zero to one hundred ranges.
Here’s a breakdown of the overall ranges of PIP joint extension:
Zero ranges: Full extension or straightening of the PIP joint, in which the finger is in a totally direct position.
70 to ninety ranges: The finger is in part prolonged, forming a moderate perspective on the PIP joint.
one hundred ranges: Maximum PIP joint extension, in which the finger is completely prolonged and parallel to the lower back of the hand.
It’s critical to word that a few people can also additionally obviously have barely one-of-a-kind levels of movement of their PIP joints, and small versions may be taken into consideration in the ordinary variety. Additionally, personal finger joints can also additionally showcase barely one-of-a-kind levels of movement.
Assessing the variety of movements of the PIP joint extension may be carried out through a healthcare expert, consisting of a hand therapist or orthopedic specialist. They can also additionally use goniometry, a dimension tool, to quantify the ranges of joint motion accurately.
If you’re experiencing limitations, pain, or issue in reaching the entire variety of PIP joint extensions, it is really helpful to seek advice from a healthcare expert for correct assessment and guidance. They can diagnose any underlying issues, offer suitable remedy options, and advise physical activities or treatment plans to enhance your PIP joint extension variety of movement.
To take a look at the variety of motion (ROM) of proximal interphalangeal (PIP) joint extension, you may comply with the steps:
- Positioning: Ask the affected person to take a seat down or stand quite simply with their hand comfortable and palm going through upward.
- Stabilization: Use one hand to stabilize the affected person’s forearm, in particular the metacarpophalangeal (MCP) joint, to save you any motion all through the test.
- Finger placement: With your different hand, preserve the affected person’s finger simply underneath the PIP joint, close to the center phalanx, with the use of your thumb and index finger.
- Passive extension: Gently and slowly pass the affected person’s finger backward, closer to the lower back of the hand, even as preserving the MCP joint and the relaxation of the finger still. Take care now no longer to pressure or purpose any ache all through the motion.
- Observe and measure: As you enlarge the finger, take a look at the factor wherein the PIP joint stops shifting further. Note the attitude at which the joint stops or any soreness or ache skilled with the aid of using the affected person.
- Repeat: Repeat the technique for every finger, assessing the PIP joint extension individually.
During the evaluation, be conscious of the affected person’s comfort, any symptoms and symptoms of ache or soreness, or any obstacles withinside the variety of motion. Comparing the PIP joint extension throughout unique hands and evaluating it to the affected person’s unaffected hand can offer precious records of approximately any abnormalities or regulations in motion.
It’s crucial to be aware that that is a famous description of the way to test the ROM of PIP joint extension. For a greater correct evaluation and interpretation of the results, it’s miles advocated to seek advice from a healthcare expert or therapist who can offer precise commands and concerns primarily based totally on the affected person’s situation and man or woman’s needs.
During the take-a-look, be careful now no longer to pressure or reason any immoderate pain to the affected person. Pay interest to any ache, stiffness, or peculiar resistance for the duration of PIP joint extension, as those can also additionally suggest joint pathology or different conditions.
Proximal Interphalangeal Joint Extension Test
The proximal interphalangeal (PIP) joint extension test is a clinical examination method used to assess the range and integrity of motion of the PIP joint of the fingers. This is usually done by health professionals such as doctors, physiotherapists, and occupational therapists.
Perform the PIP joint extension test as follows.
- Ask the patient to sit or stand comfortably with the hand resting on a flat surface.
- Explain the procedure to the patient and tell him that you will gently stretch his fingers.
- Begin with the patient’s arm relaxed and the fingers slightly flexed.
- Starting with the index finger, hold the finger proximal to the PIP joint with one hand and gently squeeze the distal finger with the other hand, moving it into extension.
- Observe the range of motion of the PIP joint when extending the finger.
- Repeat the process with each finger, including the middle finger, ring finger, and little finger.
- Watch for pain, stiffness, or limitation of range of motion during the test.
- Compare findings between fingers and hands for asymmetry or abnormalities.
- During the PIP joint extension test, a normal range of motion is usually considered a full extension of the PIP joint, allowing the finger to rest flat or nearly flat. If a patient experiences pain, stiffness, or limited extension of some fingers, further evaluation may be necessary to determine the cause. It is important to note that this description provides an overview of the procedure. Always ask a doctor for precise instructions and interpretation of test results in clinical settings.
Exercise For Proximal Interphalangeal Joint Extension
You could include precise physical activities into your routine to enhance proximal interphalangeal (PIP) joint extension. These physical activities goal the muscular tissues and systems chargeable for PIP joint extension. Assist the growth of a variety of movements and strengths. Here are some physical activities you could try:
- Active PIP Joint Extension:
- Sit or stand together with your hand comfortable and your palm going through upward.
- Start together along with your finger(s) in a flexed function (bent).
- Slowly and actively straighten the PIP joint, extending your finger(s) as a great deal as possible.
- Hold the prolonged function for some seconds, then release.
- Repeat the exercise for a fixed of repetitions, aiming for a sluggish growth withinside the variety of movements.
2. Passive PIP Joint Extension with Assistance
- Sit or stand together with your hand comfortable and your palm going through upward.
- Use your different hand or an assistive device (which includes a finger splint or a towel) to softly practice. stress at the finger(s) to help in extending the PIP joint.
- Hold the prolonged function for some seconds, then release.
- Repeat the exercise for a fixed of repetitions, step by step growing the help or stress applied.
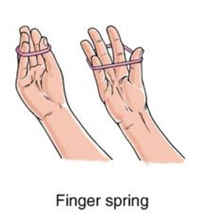
3. Finger Spring Exercises:
- Place a small, bendy rubber band or a finger spring exerciser across the guidelines of your palms.
- Start together along with your palms in a flexed function.
- Actively increase your palms towards the resistance of the rubber band or finger spring, specializing in PIP joint extension.
- Hold the prolonged function for some seconds, then release.
- Repeat the exercise for a fixed of repetitions, step by step growing the resistance or tension.
4. Range of Motion Finger Exercises:
- Sit or stand together with your hand comfortable and your palm going through upward.
- One at a time, actively flexes and increases every finger, inclusive of the PIP joint, thru their complete variety of movements.
- Repeat the exercise for a fixed of repetitions, specializing in clean and managed movements.
Remember to begin those physical activities lightly and step by step grow the depth as tolerated. If you revel in pain, discomfort, or every other concern, it is crucial to seek advice from a healthcare professional, which includes a hand therapist or bodily therapist, who can offer customized steerage and endorse physical activities tailor-made to your precise desires and condition.
Special Test For Proximal Interphalangeal Joint Extension
To examine the proximal interphalangeal (PIP) joint extension, you may carry out a unique check known as the “Bunnel-Littler Test.” This check enables us to compare the passive PIP joint extension and examine the tightness of the intrinsic muscle tissues and systems that restrict the joint’s mobility. Here’s how you may carry out the Bunnel-Littler Test:
- Positioning: Ask the affected person to take a seat down or stand quite simply with their hand comfortable and palm going through upward.
- Stabilization: Use one hand to stabilize the affected person’s forearm, especially the metacarpophalangeal (MCP) joint, to save you any motion at some stage in the check.
- Test initiation: With your different hand, keep the affected person’s finger simply beneath the PIP joint, close to the center phalanx, the use of your thumb and index finger.
- PIP joint extension: Gently and slowly enlarge the affected person’s PIP joint whilst preserving the MCP joint and the relaxation of the finger still. Apply a mild quantity of stress to stretch the PIP joint passively.
- Observation: Observe the diploma of passive extension executed withinside the PIP joint. Note any resistance, ache, or lack of ability to absolutely enlarge the joint. Compare the extension to the alternative palms and the unaffected hand if applicable.
- Additional variation: To similarly examine the tightness of the intrinsic systems, you may carry out the Bunnel-Littler Test with the metacarpophalangeal (MCP) joint flexed and stabilized. This isolates the motion to the PIP joint.
During the check, be cautious now no longer use immoderate pressure or reason any pain or ache to the affected person. The Bunnel-Littler Test enables perceive any obstacles or tightness withinside the PIP joint extension, which may be indicative of situations together with joint contracture, muscle tightness, or different structural problems.
It’s vital to word that the Bunuel-Littler Test is a scientific evaluation executed via way of means of healthcare professionals, together with hand therapists or orthopedic specialists, to assess hand and finger features accurately. If you observed any problems with PIP joint extension or if the affected person reviews ache or obstacles, it is advocated to seek advice from a healthcare expert for the right evaluation, diagnosis, and suitable remedy options.
Summary
The proximal interphalangeal joint (PIP) is a joint in the fingers that allows flexion (bending) and extension (straightening). Here is a summary of PIP joint flexion and extension:
- Anatomy: The PIP joint is located between the proximal and middle fingers of the fingers except for the thumb. It is formed by the junction of the convex end of the proximal fingertip and the concave base of the middle finger. Ligaments and tendons surround the joint to control stability and movement.
- Flexion: Flexing the PIP joint involves bending the finger and bringing the tip of the finger into the palm. This movement is primarily controlled by the forearm flexors. Flexor tendons such as flexor digitorum profundus (FDP) and flexor digitorum superficialis (FDS) cross the PIP joint and attach to the middle finger. Contraction of these flexor muscles causes the PIP joint to flex, allowing activities such as grasping and grasping.
- Extension: Extending the PIP joint means extending the finger and moving the fingertip away from the palm. This movement is mainly controlled by the extensor muscles of the forearm. Extensor tendons such as the extensor tendon (EDC) extend from the forearm, run through the back of the hand, and attach to the base of the middle phalanx. Contraction of these extensor muscles causes the PIP joint to expand, allowing finger extension and movements such as pointing.
- Range of motion and function: The range of motion of the PIP joint varies from person to person and can be affected by factors such as age, injury, or disease. Flexion and extension of the PIP joint allow for finger dexterity and fine motor skills needed for things like writing, typing, and manipulating objects. Injuries or diseases affecting the PIP joint, such as fractures, sprains, or arthritis, can limit its motion and cause pain, stiffness, or deformity.
FAQs
Proximal interphalangeal (PIP) joint damage
The joint is a joint that allows flexion and extension, and the bony architecture and ligaments of the proper and accessory ligaments provide significant lateral stability. The volar plate provides volar stability to prevent hyperextension.
The interphalangeal joints of the foot are classified as uniaxial joints, which are a type of joint that allows movement along a single axis, in this case, flexion (plantarflexion) and extension (dorsiflexion) of the middle and distal toes.
superficial finger flexor
Interossei and glutes are the muscles that flex the MP and extend the PIP and DIP joints, whereas flexor digitorum profundus flexes all three and is the only muscle that can flex the DIP joint. Flexor digitorum superficialis only flexes the MP and PIP joints.
The largest external muscle that extends the fingers is the digitorum (ED), which has several divisions and separate tendons in each finger. Other external extensors include the extensor indices (EI) and the extensor minimus (EDM), which extend the index finger and little fingers, respectively.