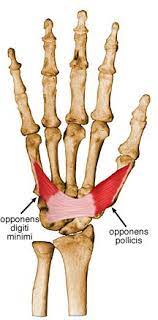
Opponens Pollicis Muscle
Table of Contents
Description
The hand’s tiny intrinsic muscle is known as the Opponens Pollicis. Along with the adductor pollicis, abductor pollicis, and flexor pollicis brevis, it is a part of the thenar muscles group.
The thenar eminence is an eminence originating from the thenar muscles on the lateral side of the hand. The opponent’s pollicis runs through the 1st metacarpal bone from the flexor retinaculum and trapezium bone. The opposition of the thumb in the 1st carpometacarpal joint is this muscle’s initial function.
Origin of Opponens pollicis muscle
The tubercle of the trapezium, the most outsider bone in the distal row of carpal bones, and the distal edge of the flexor retinaculum create the muscle’s superficial head. It travels with the flexor pollicis longus tendon’s radial side.
Insertion
It inserts on the lateral side of the thumb’s proximal phalanx base, where a sesamoid bone connects the two tendinous heads.
Relations
On the hand’s lateral side, the opponent pollicis is a relatively tiny and thin muscle. It is positioned radially to the flexor pollicis brevis and deep to the abductor pollicis brevis. Opponent pollicis and the superficial head of the flexor pollicis brevis are often combined.
Innervation
The thenar branch of the median nerve (root values C8 and T1) and traditionally the deep terminal branch of the ulnar nerve supply the opponens pollicis.
Blood supply
The superficial palmar branch from the radial artery initially gives its blood supply to the opponent’s pollicis muscle. Too many extra arteries give the additional blood supply too;
- Princeps pollicis artery
- Radialis indicis artery
- Deep palmar arch
The function of Opponens pollicis muscle
- The initial purpose of opponent pollicis, as its name suggests, is to create a thumb opposition.
- The thumb’s an instead tough motion of flexion, adduction, and medial rotation at the 1st carpometacarpal joint is referred to as opposition.
- The capacity to bring the thumb’s tip into contact with any other fingertip on the same hand is the goal of this motion.
- This allows productive and exact development of the hand, for instance getting a handle on round items or fine holding of a pencil.
Assessment
- It is done with the forearm in supination, the wrist in neutral, the thumb adducted, and the MP and IP joints flexed.
- The patient is then told to bring his or her thumb to the pinky finger and touch the 2 pads, making the word “O” with the thumb and tiny finger.
Opponents pollicis muscle stretching
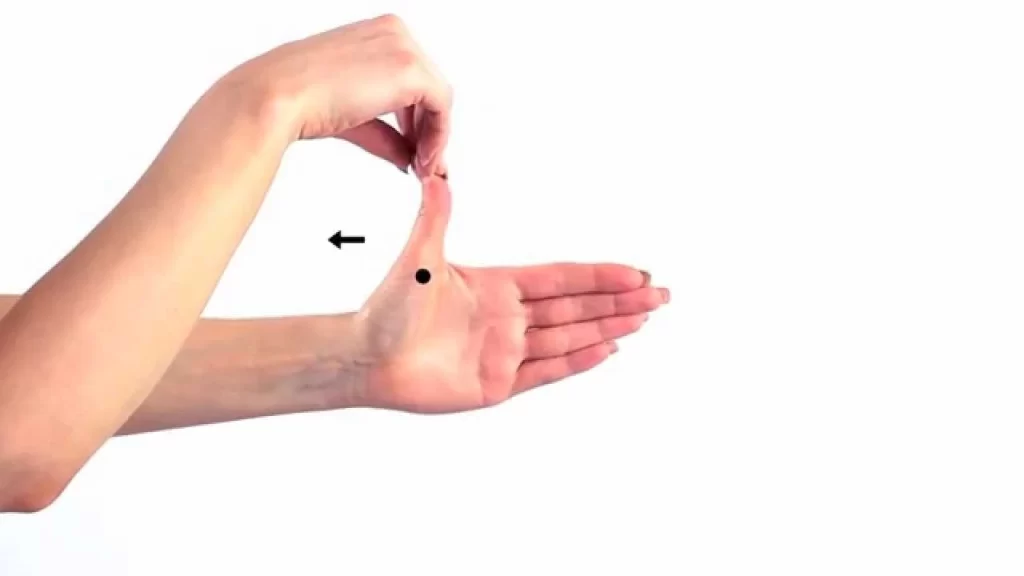
- Start with flipping the palm over.
- Lift the thumb in the opposite direction (90 degrees from the posterior of the palm) with the other hand’s fingers.
- Release after about 20 seconds.
Opponents pollicis muscle strengthening exercise
Finger opposition
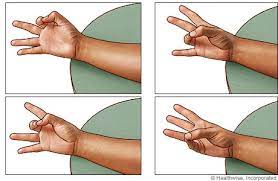
- This is the perfect practice for the fingers.
- To generate a pinch grip, alternately touch the thumb with every finger and maintain it for up to 5 to 10 seconds.
Thumb isometrics

- The thumb muscles may be strengthened in various directions with this exercise.
- Start with doing a fist with the thumb and applying pressure in both directions with further hand.
- Keeping up an upright thumb to oppose the pressure, and maintain for 10 to 15 seconds.
FAQ
A sharp pain in the hand beneath the thumb and down into the inside of the wrist can best describe the symptoms of injury, which can happen because of repetitive use of the muscle or tendons. Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatories such as ibuprofen will help with pain and inflammation.
The thenar musculature consists of 4 short muscles situated on the radial aspect of the hand. The adductor pollicis, abductor pollicis brevis, flexor pollicis brevis, and opponens pollicis are group of muscles called thenar muscles.
Treatment involves rest, anti-inflammatory medications, splinting, and steroid injections. Most patients rehabilitate without surgery. If symptoms preserve with treatment, triggering the thumb release surgery is very useful and has low risks.
As its name indicate, the important function of opponens pollicis is to generate an opposition of the thumb. Opposition tends to the rather difficult movement of the thumb which is a mixed version of flexion, adduction, and medial rotation at the first carpometacarpal joint.
The inability to oppose the thumb to the other fingers owing to paralysis of the intrinsic thenar muscles tends to “flat hand” deformity. This is initially because of the loss of function in the musculus opponens pollicis.


One Comment