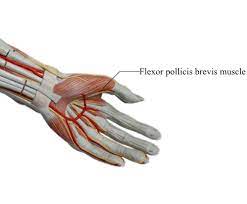
Flexor Pollicis Brevis Muscle
Table of Contents
Description
The flexor pollicis brevis is the name of the tiny and broad intrinsic muscle of the hand. It is a part of the thenar muscles grouping together with the opponens pollicis, adductor pollicis, and abductor pollicis brevis.
The heads of the flexor pollicis brevis are superficial and profound. The deep head, on the opposite hand, may be small or even absent at times. The flexor pollicis brevis flexes the thumb at the metacarpophalangeal joint, the same as the other thenar muscles.
Origin of Flexor pollicis brevis muscle
- The trapezium and flexor retinaculum’s range is the origin of the superficial Head.
- The trapezoid and capitate bones, in addition to the palmar ligaments of the distal row of carpals bones, are the origins of the deep head.
Insertion
Both heads become tendinous and insert combine into the medial side of the base of the proximal phalanx of the thumb; at the junction in the middle of the tendinous heads, there is a sesamoid bone.
Relations
- The thenar muscle with the most extensive is the flexor pollicis brevis.
- It is outside of the adductor pollicis muscle and is medial to the abductor pollicis brevis and opposed pollicis muscles.
- Along its course, the superficial top of the muscle varies along the outer side of the ligament of flexor pollicis longus, while the profound head goes profoundly to the same ligament.
- Likewise, the opponens pollicis muscle and the superficial head are usually connected.
- The motor branch of the median nerve runs across the muscle’s shallow surface.
Innervation
- The innervation of the flexor pollicis brevis’s 2 heads typically differs.
- The recurrent branch of the median nerve gives a supply to the flexor pollicis muscle’s superficial head, while the deep head takes the innervation from the deep branch of the ulnar nerve, which arises from the spinal roots C8 and T1.
Blood supply
Flexor pollicis brevis take blood supply from the various regions of the radial artery; branches of the princeps pollicis artery, the superficial palmar artery, and the radialis indicis artery.
The function of Flexor pollicis brevis muscle
- The flexor pollicis brevis, which is a component of the thenar muscles, flex the thumb at the metacarpophalangeal and carpometacarpal joints.
- This controls the thumb movement in the opposite direction, and if it persists, it will cause the thumb to rotate in the internal direction.
- When the thumb is flexed against force, the flexor pollicis brevis may be tested and palpated on the thenar eminence.
Clinical relevance
- The sensory impairments of FPB, which implicate numbness, paresthesias, and motor weaknesses in the superficial belly, are the development of the compression of the median nerve that takes in carpal tunnel syndrome.
- For circumduction and opposition, all 3 thumb joints—CMC, MCP, and IP—must be moved at the same time and coordinated.
- These patterns of motion are disrupted by carpal tunnel syndrome.
Assessment
Manual Muscle Testing of FPB
Position of Patient:
The wrist is in a neutral position, with the forearm in a supinated position, the Carpometacarpal (CMC) joint at neutral, and the thumb adducted in front of the second Metacarpal.
The position of a therapist:
A relaxing position that stabilizes the 1st metacarpal to prevent wrist and CMC movement by putting a finger on the proximal phalanx in the direction of extension with the other hand.
Test:
The patient is asked to extend the IP joint while flexing the MP joint of the thumb in a native or non-technical language.
Flexor pollicis brevis stretching exercise
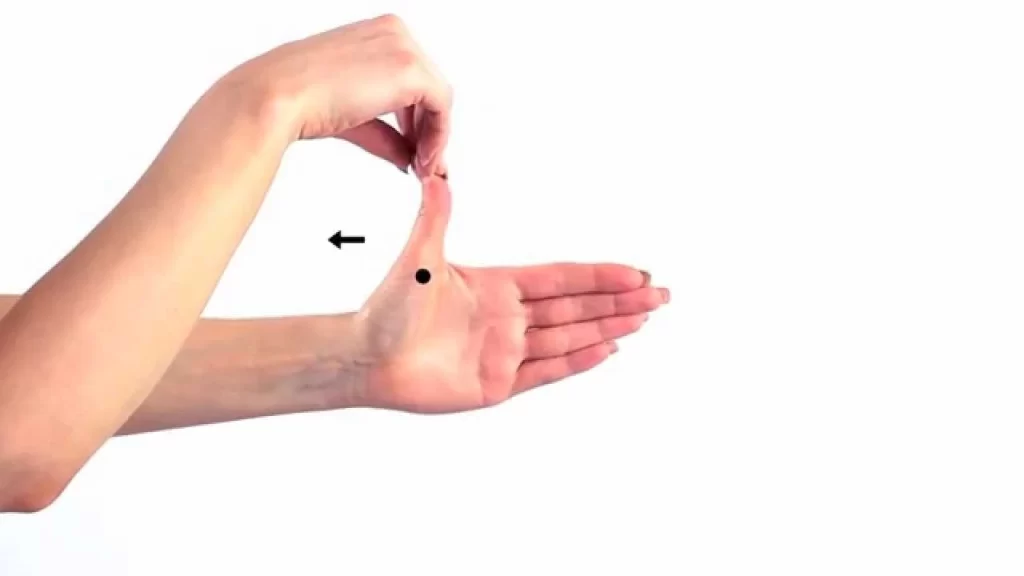
- Keeping up the wrist and hand extended, put a finger from the contrary hand in the middle of the knuckle and end joints of the thumb.
- Make an effort to flex the thumb’s knuckle without flexing the tip by resisting the motion with the other hand.
- Try to hold this position at all times.
Flexor pollicis brevis muscle strengthening exercise
- Start by leaning forward and spread the legs slightly as you sit.
- Then, with the hand and wrist in front of the knee, put the involved forearm on the thigh.
- Step on the opposite end of an exercise band by grabbing one end with the palm up.
- Roll the palm inward toward the thigh for 5 counts while keeping up the wrist straight.
- Gently move the wrist back to the starting position for 10 counts.
- Repeat up to 10 times.
FAQ
Damages to flexor pollicis brevis may concern strain, tears, atrophy, infectious myositis, and overuse. The injury should be detected when hand or thumb pain is present or if there is reduced flexion of the thumb.
The flexor pollicis longus pollicis, of the thumb; longus, long) is a muscle in the forearm and hand that bends the thumb.
Activate Flexor Pollicis Brevis Muscle – Put the palm facing up and the wrist in a neutral position. Bring the thumb to touch the base of the pinky finger and give pressure as much as possible. Hold the pressure for 10 seconds and release it.
Apply cold. Icing the joint for 10 to 15 minutes several times a day may help reduce swelling and pain. Apply heat. For some, heat may be more useful than cold in reducing pain.
Chopchini. Chopchini can treat symptoms of a disorder such as thumb arthritis due to its antioxidant and anti-inflammatory impact. Problems namely inflammation, muscle weakness, and stiffness may be effectively handled with Chopchini, which performs as an ayurvedic part.

2 Comments