Adductor pollicis muscle
Table of Contents
Description
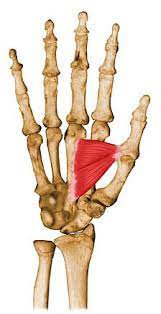
A hand muscle called the adductor pollicis is located in the palm of the hand, particularly near the base of the thumb. The oblique head and the transverse head are their two components. The transverse head develops from the distal third of the ulna and the interosseous membrane, whereas the oblique head comes from the capitate bone and the bases of the second and third metacarpal bones.
The base of the thumb’s proximal phalanx is where the adductor pollicis muscle’s two heads attach. The muscle helps in both thumb adduction (bringing the thumb toward the palm) and thumb opposition (bringing the thumb toward the other digits).
The base of the thumb’s proximal phalanx is where the adductor pollicis muscle’s two heads attach. The muscle helps in both thumb adduction (bringing the thumb toward the palm) and thumb opposition (bringing the thumb toward the other digits). It also plays a role in gripping and grasping objects, particularly those that need a strong grip.
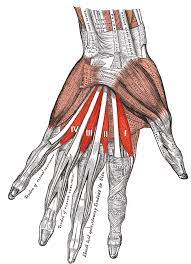
The deep branch of the ulnar nerve, which emerges from the medial chord of the brachial plexus, innervates the adductor pollicis muscle. The innate adductor pollicis of the hand is a triangle muscle. It is a member of the thenar muscles group, which also includes the abductor pollicis, flexor pollicis brevis, and opponens pollicis. The thenar muscles on the lateral side of the hand create an elevation known as the thenar eminence.
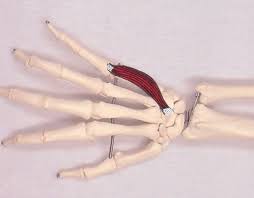
Tangential and transverse heads are seen on the adductor pollicis. This muscle extends from the base of the first proximal phalanx to the capitate and third metacarpal bones. The main action of this muscle is the adduction of the thumb at the carpometacarpal joint.
Origin of adductor pollicis muscle
The oblique head originates from the bases of the 2nd and 3rd metacarpals, whereas the transverse head originates from the shaft of the 3rd metacarpal.
Insertion of adductor pollicis muscle
The thumb’s inner side of the base of the proximal phalanx
Relations
- The biggest and deepest muscle in the thenar muscle group is the adductor pollicis.
- The adductor pollicis’ ventral component is crossed by the flexor tendons of the flexor pollicis brevis, first lumbrical, and index finger.
- On its dorsal side, the muscle is connected to, or occasionally attached to, the first dorsal interosseous muscle.
- Furthermore, the pathway formed by the 2 heads of the adductor pollicis is used by the deep branch of the ulnar nerve, the deep palmar arch, and the radial artery.
Innervation
The deep ulnar nerve branch innervates the adductor pollicis muscle (root value C8, T1).
Blood supply
The anastomosis of the radial artery and the deep palmar branch of the ulnar artery forms the deep palmar arterial arch, which supplies the adductor pollicis.
The function of adductor pollicis muscle
- The adductor pollicis is the intrinsic hand muscle with the greatest influence.
- The thumb’s primary function is adduction, or the move of the thumb from an abducted posture towards the first finger.
- This movement is crucial while completing activities that demand pinching and grabbing.
- Additionally, the adductor pollicis supports the thumb’s resistance in its final stages.
- This development involves a variety of actions, including the thumb’s adduction, average rotation, flexion, and adduction in order for it to touch the tips of each finger on the same hand.
- As a result, the therapist may attempt to pull them apart while pressing the thumb on the index finger to measure the strength of the adductor pollicis.
clinical relevance
- The adductor pollicis muscle’s strength may be noticed using the Froment sign.
- After the ulnar nerve is stimulated, the adductor pollicis contraction force is considered during neuromuscular monitoring., extending the adductor pollicis muscle
Stretching of adductor pollicis muscle
The adductor pollicis, a part of the central compartment group, is stretched by the thumb’s abduction and extension at the metacarpophalangeal joint.
Strengthening exercises for the adductor pollicis
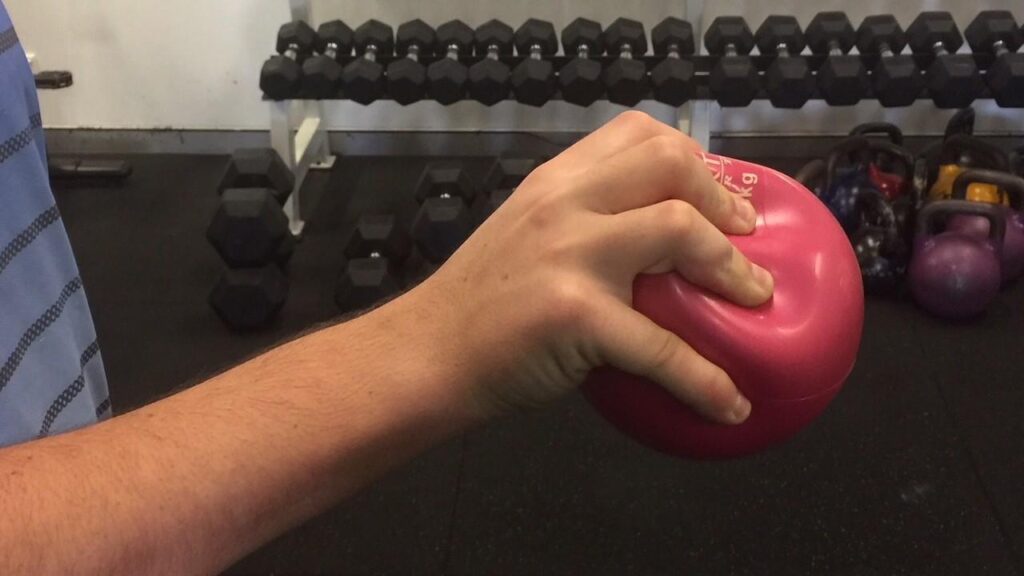

- One can perform a simple workout to develop this muscle with the use of a tennis ball or rubber stress ball.
- Ten seconds after securing the ball with all four fingers and the thumb, let go.
- 2 times a day, perform 10 reps of this exercise.
FAQ
The Abductor pollicis longus (APL) is one of the deep extensors of the forearm and is accountable for generating motion and stabilization of the thumb. Its tendon is present in the 1st extensor compartment of the wrist. It lies directly below the supinator and occasionally unites with it.
The adductor pollicis muscle lies profound to the thenar muscles. It has 2 heads, an oblique head, and a transverse head.
Functioning independently or with abductor pollicis brevis, abductor pollicis longus stretches the thumb out from the palm. More specifically, it generates (mid-) extension and abduction of the thumb at the 1st metacarpophalangeal joint. This action is seen in activities namely bowling and shoveling.
Weakness of thumb adduction is because of a problem with the adductor pollicis muscle, which is mainly innervated by the ulnar nerve. The distinct sign of such an ulnar palsy is the Froment’s sign, named after the French physician, Jules Froment.

3 Comments