Lower Back Pain:
Lower Back pain is a most commonly seen painful condition affecting the lower lumbo-sacral portion of the spine.
The low back also called the lumbar region which is the area of the back that starts below the ribcage. Almost everyone feels low back pain at some point in life.
It becomes too uncomfortable & debilitating for any person.
This lower back muscle pain is due to injury, some activity & some medical conditions.
This lower back muscle pain is affect any age of people but due to different reasons.
lower back muscle pain is released by to RICE principle, pain mediation & physiotherapy treatment.
Table of Contents
What is the lower back?
- The lumbar spine & low back is a remarkably well-engineered structure of interconnecting the bones, nerves, joints, ligaments & muscles all working together to provide support, strength & flexibility.
- This complex structure also leaves the low back susceptible to injury & pain.
What are the types of lower back pain?
lower back pain is classified as chronic or acute pain:
- Acute muscle pain the low back pain:
- This muscle pain starts suddenly & lasts for up to 6 weeks.
- Chronic & long-term muscle pain in the lower back pain:
- This muscle pain develops over a longer period & lasts for over 3 months which is lead to ongoing problems.
What are the causes of lower back muscle pain?
- Muscle Strain and Ligament Sprain:
- A low back muscle sprain or strain that happens suddenly & develops too slowly over time from repetitive movements.
- These muscle strains occur when a muscle is stretched too far & tears by the damage to the muscle.
- Sprains happen when occurring to over-stretching & tearing which is lead to effects on the ligaments & these ligaments connect the bones.
- Common causes of muscle sprain & strain include:
- When you lift a heavy object & twisting the spine while lifting.
- If occur to sudden movements that place too much stress on the low back like a fall.
- It occurs to sports injuries mostly in sports that involve twisting & large forces of impact.
- Poor posture over time
- Lumbar herniated disc:
- The jelly-like center of a lumbar disc is breaking through the tough outer layer & irritates a nearby nerve root.
- This herniated portion of the disc is full of proteins that produce inflammation when you try to reach a nerve root as well as nerve compression produces nerve root pain.
- The herniated disc wall is also richly supplied by nerve fibers & a tear through the wall which is lead to severe pain.
- Degenerative disc disease:
- At birth time intervertebral discs are full of water & at their healthiest.
- With over age discs lose hydration & wear down.
- When occur to disc loses hydration, it resists forces & transfers force to the disc wall which is develop tears & produces pain & becomes to weak disc which is lead to herniation.
- Due to this condition discs also become to collapse & contribute to stenosis.
- Facet joint dysfunction:
- In our body, two facet joints are located behind each disc for each motion segment in the lumbar spine.
- In these facet joints cartilage between the bones which are surrounded by a capsular ligament, which is innervated by nerves. when these joints become too painful which leads to disc pain.
- Sacroiliac joint dysfunction:
- The sacroiliac joint connects the sacrum at the bottom of the spine to each side of the pelvis bone.
- This joint is a strong & low-motion joint that primarily absorbs shock & tension between the upper body & the lower body. This sacroiliac joint becomes too painful it becomes inflamed (sacroiliitis) & there is too much & too little motion in the joint.
- Spinal stenosis:
- This condition produces pain through the narrowing of the spinal canal when the nerve roots are located. this
- Narrowing of the spinal camel which is lead to central, formal & sometimes both which is lead to a single level or multiple levels in the lower back.
- Spondylolisthesis:
- This condition occurs when one vertebra slips over the adjacent one.
- In the body occur 5 types of spondylolisthesis but the most common spondylolisthesis is secondary to a defect & fracture of the pars between all the facet joints & mechanical instability of the facet joints means degenerative.
- This pain is caused by instability (back) & compression of the nerves (leg).
- Osteoarthritis:
- This osteoarthritis condition occurs results from the wear & tear of the disc & facet joints.
- This condition is produced by pain, inflammation, instability & stenosis to a variable degree.
- This condition occurs at a single level & multiple levels of the lower spine.
- This spinal osteoarthritis is associated with aging & progressive slowly.
- Sometimes this condition is referred to as spondylosis & degenerative joint disease.
- Deformity:
- The curvature of the spine includes scoliosis & kyphosis.
- This deformity is also produced in lower back pain when occurring to the breakdown of the discs, sacroiliac joints, facet joints, or stenosis.
- Trauma:
- Acute fractures & dislocations of the spine which is also lead to pain.
- This lower back pain also develops after a trauma like a motor vehicle accident & a fall which is need to be medically evaluated.
- Compression fracture:
- This fracture occurs in the cylindrical vertebra in which the bone essentially caves on itself & produces sudden pain.
- This type of compression fracture most commonly occurs due to weak bones like osteoporosis.
- This condition is more common in older age people.
What are the Symptoms of Lower Back pain?
- You feel dull, aching pain in the lower back area.
- Sometimes you feel to burning, stinging & sharp type of pain.
- This muscle pain is lead to mild or severe muscle spasms.
- You feel too limited or have difficulty in mobility & also pain in the hip joint & pelvis.
- This pain also radiates to the buttocks, legs & feet.
- This pain becomes worse after a prolonged sitting position.
- You are feeling pain worse in the morning due to stiffness, decreased blood flow with sleep, long periods of rest, and possibly the quality of mattress & used pillows.
- You are observed to have swelling & inflammation around the back pain area.
- You also feel trigger points & tenderness in the area of pain.
- You feel stiffness & spasm in the area of muscle pain.
Low Back Pain Symptoms by Location:
The body’s largest vertebrae are found in the lumbar spine which is supporting most of the weight of the upper body.
These all lumbar vertebrae are highly susceptible to degeneration & injury.
- L3-L4 level :
- This level of nerve root pain is produced by shooting pain in the front of the thigh including numbness with tingling.
- This Pain & neurological symptoms radiate to the front of the knee joint, shin & foot as well as are less common.
- L4-L5 level :
- This level of pain is typically manifesting as sciatic pain in the back of the thigh & possibly pain that reaches the calves or combined with the axial low back pain.
- L5-S1 level :
- This level is where the base of the spine is connected to the sacrum which is a couple of joints that provide support & flexibility.
- One of these is the lumbosacral joint, which is allow the hip joint to swing side to side.
- The other joint is the sacroiliac joint, which is limited mobility & mainly absorbs shock from the upper body to the low body.
- This level of pain is produced generally due to problems with these joints & from a compressed nerve root.
- This level of pain commonly occurs due to sciatica.
In which condition do you need to contact a doctor as an emergency?
Sometimes this low back pain is a signal of a serious underlying medical condition.
When you feel & experience any of the following symptoms which need medical care include :
- When your body loses bladder & bowel control.
- If recent you notice weight loss due to lifestyle changes like diet & exercise.
- You feel fever & chills
- When you feel severe & unrelenting pain in the abdomen area.
- If you feel numbness & tingling sensation in the area of pain which is radiated to the leg.
What is the Diagnosis of lower back muscle pain?
- History :
- Before starting a physical exam of the lower back doctor is asked to you give information about symptoms & medical history.
- Asked questions about your activity level like your lifestyle [ active or sedentary ].
- Asked a question about your position as work requires sitting at a desk & standing at an assembly line for long periods.
- Asked questions about your sleep habits means hours of sleeping, your sleep position, quality of the mattress & pillow.
- Then the doctor observes your posture [ sit upright & slouch ]
- Palpation:
- A doctor is palpate by hand the low back area which is located any muscle areas of tenderness, spasms, or tightness & joint abnormalities.
- Neurologic exam:
- In the diagnosis, the doctor also does the motor examine involves manual movement of the hip joint, knee joint & big toe extension – flexion movement as well as ankle joint movement.
- The sensory examination includes testing your reaction to light touch, other senses in the lower trunk, a pinprick, buttock & legs.
- The range of motion test:
- The doctor asked to you bend & twist in certain positions.
- These all activities are done to look for positions that worsen & recreate pain or certain movements which is limited by discomfort.
- Reflex test:
- Then the doctor performs to reflexes test on the legs for checking to evaluate weakened reflexes & decreased muscle strength.
- When the reflexes are diminished it is indicated to be a nerve root problem.
- Leg raise test:
- When you are asked to lay on the back & raise one leg as high and as straight as possible.
- During the performance of the test when you feel low back pain it is indicated to be suspected of a herniated disc.
Diagnostic Imaging Tests
Sometimes the doctor advises to you do diagnostic Imaging Tests when you feel severe pain & that is not relieved within two or three months, & does not get better with the nonsurgical treatments.
- X-rays:
- It is used to help the doctor check the bones of the spine.
- It also helps to show the abnormalities like arthritis, bone spurs, fractures & tumors.
- CT scan/Myelogram:
- It provides a cross-sectioned image of the spine.
- This detailed image allows doctors to look closely at the spine from different angles.
- Sometimes the doctor is advised to take a myelogram with a CT scan, in this process injected dye is around the nerve roots to highlight the spinal structures which is giving the image more clarity.
- MRI [ Magnetic Resonance Imaging scan]:
- it provides a detailed image of spinal structures without using any radiation required with x-rays.
- An MRI of the spine helps to doctor detect the abnormalities with soft tissues like muscles, ligaments & intervertebral discs.
- this MRI is also used to locate the misalignments & joint overgrowth in the spine.
- Injection studies:
- Fluoroscopic-directed injections of local anesthetic & steroid medication injections are helpful for the doctor for confirming the source of the pain.
What are the risk factors for lower back muscle pain?
- Age:
- People over the age of 30 feel more back pain.
- Disks are soft, rubbery tissue which is provided cushions for the bones in the spine to wear away with age.
- When the disks become too weak & wear down of gives to pain & stiffness.
- Weight:
- People who are obese & carry extra weight which is likely to have lower back pain.
- This Excess weight puts pressure on joints & disks.
- Overall health:
- When occur to weak abdominal muscles which are given to support the spine, which leads to lower back muscle strains & sprains. when you do smoke & drink alcohol excessively with live a sedentary lifestyle it is also a higher risk of lower back muscle pain.
- Occupation and lifestyle:
- Jobs and activities are required for heavy lifting & bending which is increase the risk of a lower back injury.
- Structural problems:
- Severe lower back pain is the result of conditions like scoliosis which is a change in the spine alignment.
- Disease:
- When you have suffered from a family history of osteoarthritis, certain types of cancer & another disease which is lead to a higher risk of low back pain.
- Mental health:
- Lower back pain sometimes also results from depression & anxiety.
What is the treatment for lower back muscle pain?
RICE principle:
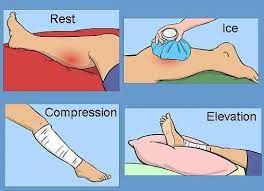
When you feel pain in the back muscle doctor is advised to RICE principle as home treatment or primary treatment.
- R – rest = When you feel muscle pain doctor is advice to you rest for sometimes form activities for release to muscle pain.
- I- ice = You are Applied to ice on the area of the pan for 20 minutes, release to swellings & muscle pain but always applied to the ice with the help of a towel between the skin & ice to prevent ice burn, you can also be used to ice pack & frozen peas for ice therapy.
- C- compression = You can also apply compression bandage release to muscle pain and swelling.
- E- elevation = You must be elevated to the back with the help of a pillow under the foot for the release of muscle pain & swelling.
Back braces:
- In Some conditions, you wear to back brace which is used to provide comfort & reduce pain.
- In the back, braces use an inelastic corset-style brace.
- This back brace is also helpful after back surgery.
Mindful meditation:
- Meditation helps reduce the perception of pain & reduce depression, anxiety & sleep problems which commonly occur with chronic pain.
- The meditative techniques for pain reduction include everything from deep breathing exercises to an altered focus approach.
Acupuncture:
- This acupuncture also helps to relieve lower back pain.
- It is applied to the stimulating points on the body thought to correct the body & life force.
- It helps to decrease pain & discomfort in the body.
- During a session of Acupuncture apply thin needles which are placed on the skin for an hour.
- It must be provided for pain relief for some people.
What is the medical treatment for lower back pain?
Muscle relaxants durg:
- The medication acts as a depressant of the central nervous system & increases the mobility of tense muscles which helps you relieve pain from muscle tightness & spasms.
- But this muscle relaxants durg have no role in chronic pain management.
Over-the-counter pain medications:
- The most common over-the-counter (OTC) medications include aspirin (e.g. Bayer), ibuprofen (e.g. Advil), naproxen (e.g. Aleve) & acetaminophen (e.g. Tylenol).
- Aspirin, ibuprofen & naproxen are anti-inflammatory medicines, which alleviate your low back pain which is due to swollen nerves or muscles.
- Acetaminophen drug works by interfering with the pain signals sent to the brain.
Narcotic pain medications:
- This narcotic medication which is also known as opioids & painkillers is given to weak signals sent into the brain.
- These all medications are most often used for treating intense & short-term pain such as acute pain after an operation.
- This Narcotics medication is rarely used to treat long-term pain because it is many side effects & easily become too addictive.
Epidural steroid injections:
- This Epidural steroid injection involves a steroid administered which is applied directly into the outer part of the dural sac which is located surrounding the spinal cord.
- A live x-ray which is known as fluoroscopy which is help to doctor guide the needle to the correct area.
- The goal of this injection is to temporarily relieve pain by reducing the inflammation around a compressed nerve root.
What is Physiotherapy treatment for back muscle pain?
When the muscle pain is not relieved after the home treatment & pain medication then the doctor has advised physiotherapy treatment to release muscle pain.
Physiotherapy treatment is help you relieve pain, swelling, spam & tightness of the muscle pain.
The physiotherapy treatment includes massage, electrotherapy treatment, Manual manipulation, and exercise therapy.
Massage therapy:
- In the low back muscle, massage therapy also helps to relieve the muscle spasms which usually lead to low back pain.
- This massage therapy also increases blood flow to the low back, which is applied to speed up healing by starting the nutrients & oxygen to damaged muscles.
- Massage is applied after 2 – 3 days of following the RICE principle when you feel to release of the pain.
- Massage is applied with the help of the oil & applied for 5 -10 minutes.
- Massage is applied 3 times per day at home.
Electrotherapy treatment :
After the RICE principle, pain medication & massage if the muscle pain is not relieved then used Electrotherapy treatment for the release of muscle pain.
To relieve the swellings, spasms & pain therapist is advised you to electrotherapy treatment.
In electrotherapy, the treatment therapist is used to many machines.
- When the trigger & tender points are present therapists are advised & to apply US = ultrasound therapy for the release of muscle pain.
- This treatment is applied with the help of gel & applies for 5 to 10 minutes on the area of pain.
- This therapy helps you release pain & swelling.
- Reduce to pain therapist is applied to SWD = short wave diathermy, IFT = Interferential Therapy, TENS = Transcutaneous Electrical Nerve Stimulation on the area of pain.
- SWD = Short wave diathermy is hot therapy for release to spams on the area of pain.
- IFT = Interferential Therapy & TENS = Transcutaneous Electrical Nerve Stimulation is applied with the help of gel & electrodes on the area of pain.
- This therapy is applied for 10 minutes to the area of pain.
- Traction:
- This traction is known as lumbar traction.
- It is applied by the therapist in the clinic.
- Pulleys & weights are used to stretch the back.
- This traction is applied to half your weight of you.
- It is given to result in a herniated disk moving back into position.
- Traction is used to relieve pain, but only while traction is applied.
Manual manipulation:
- A chiropractor & another healthcare provider makes the physical adjustments to the spine with the goals of improving your mobility & reducing the stiffness & discomfort with pain.
- In this technique apply hand thrusts of varying speed & force are applied to adjust the spinal structures.
Exercise therapy for lower back muscles pain :
After following the RICE principle for the 2- 3 days at home & primary treatment & the help of pain medication, you feel released from the pain.
When you feel too comfortable & release from your Back pain then the physiotherapist is advised to you exercise therapy reduce to muscle weakness & tightness.
The exercise therapy for muscle pain includes Stretching & strengthening Exercises.
Stretching exercise helps to relieve muscle tightness as well as strengthening Exercise is help you relieve muscle weakness.
Stretching exercise:
After the follow of Electrotherapy for 2-3 days for release to muscle pain by the physiotherapist then the therapist is advised to stretch for release to muscle tightness.
This stretching is applied when your pain is released & when you feel comfortable.
- Piriformis stretches
- Knee-to-chest stretch
- Seated spinal twist stretch
- Sphinx stretch
- Knee-to-chest stretches
- Kneeling back stretch
- Modified seated side straddle
- Lower Back Rotation Stretch
Piriformis stretches:

- This stretch is applied to a strong stretch for the backside.
- The starting position of the stretching is supine.
- Then must be placed on the leg cross over onto the other thigh into the figure four of shape.
- Try to gently lower the buttock to the ground.
- Hold this stretching position for 30 seconds.
- Do the 3 times in 1 session & perform 3 sessions per day.
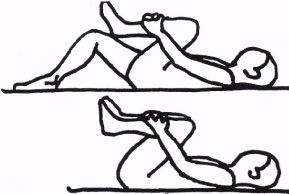
Knee-to-chest stretch:
- You are lying on your back with both knee joints bent & your feet flat on the floor.
- Must keep your left knee joint bent & extend it straight out along the floor.
- Try to draw your right knee joint into your chest.
- Then clasp your hands behind your thigh at the top of your shinbone.
- Lengthen your spine down to your tailbone & avoid lifting your hip joint.
- Hold this stretching for 30 seconds to 1 minute.
- Modifications:
- First, place a cushion under your head for extra padding.
- You also wrap a towel around your leg when it is hard for your arms to reach.
- To deepen the stretch, tuck your chin into your chest & lift your head toward your knee joint.
Seated spinal twist stretch:

- The starting position of this stretching is the sitting position.
- You are sitting on the floor with both legs extended out in front.
- Bend o the left knee joint & place the foot on the outside of the right thigh.
- Then Place the right arm on the outside of the left thigh.
- A place to the left hand behind for support.
- Do the 3 times in 1 session & perform 3 sessions per day
Sphinx stretch :
- The starting position of this stretching is prone.
- You are lying on the stomach with the elbows underneath the shoulder joint & hands extended in front & palms facing down.
- Then Gently engage the lower back, buttocks & thighs as to the lift to the head & chest.
- Press the pelvis into the floor.
- Then Gaze straight ahead or gently close to the eyes.
- Hold this stretching position for 30 seconds.
- Do the 3 times in 1 session & perform 3 sessions per day.
Kneeling back stretch:
- Start this exercise on the hands & knees, positioning the knee joint hip-width apart or with the shoulder joint directly over the hands.
- Try to round the back or pull the belly button up toward the spine & tilting the lower back toward the floor.
- Hold this stretching position for 5 seconds.
- Then rock gently backward & lowering the buttocks as close as possible to the heels.
- Must be ensured that the arms are stretched out in front.
- Hold this stretching position for 5 seconds.
- Then rock gently back up to the starting position.
- Do the 3 times in 1 session & perform 3 sessions per day.
Modified seated side straddle:
- You are sitting with both legs flat against the floor & extended out in front of the body.
- Place your feet far enough apart that the legs form a “V” shape.
- Try to bend the left leg or bring the left foot up to touch the right knee joint & letting the left knee joint fall out away from the body.
- Must be keeping the back straight or bending from the hip joint or reaching forward toward the toes of the right foot.
- Then slowly round the spine or bring the hands toward the right ankle & shin while lowering the head as close as possible to the right knee joint.
- Hold this stretching position for 30 seconds, then relax for 30 seconds.
- Do the 3 times in 1 session & perform 3 sessions per day.
Lower Back Rotation Stretch:
- You are lying on your back with your knee joint bent & your feet flat on the floor.
- Must keep your shoulders flat on the floor & your knee joint together as you let them slowly roll to the right side of your body. hold for five seconds, then slowly return your knee joint to the starting position.
- Then slowly let your knee joint roll to the left side of your body.
- Hold for 10 seconds then return to the starting position.
- Do the 3 times in 1 session & perform 3 sessions per day.
Strengthening Exercises:
After the follow of Electrotherapy & massage for 2 -3 days for the release of muscle pain by the physiotherapist then the therapist is advised to you strengthening exercise for release to muscle weakness.
This strengthening exercise is always advised when you feel to release pain & when you feel comfortable.
This all strengthening exercise helps to you muscle weakness & pain.
- Pelvic Tilts
- Cat/cow
- Bridges
- Drawing-in maneuver
- Lying lateral leg raises
- Supermans
- Partial curls
- Bird-dog
- Plank
- Side plank
- Abdominal crunches

Pelvic Tilts :
- The starting position of this exercise is supine.
- You are Laying on the lower back.
- Try to arch to the lower back & flatten it into the ground.
- Do the 10 times in 1 session & perform 3 sessions per day.
Cat / cow:

- The starting position of this exercise is a kneeling position.
- Start with this exercise on to all fours.
- Try to Create the arch into the low back by raising the abdomen toward the sky & do the head up.
- Hold this exercise for 30 seconds.
- Repeat this position on the other leg.
- Do the 10 times in 1 session & perform 3 sessions per day.
Bridges:

- You are lying on the ground with your feet flat on the floor, hip-width apart.
- With your hands by your sides.
- then press your feet to the floor as you slowly lift your buttocks off the ground till your body is in one straight line.
- must keep your shoulder joint on the floor.
- Hold this exercise for 10 to 15 seconds.
- Repeat this exercise 15 times.
- Do the 10 times in 1 session & perform 3 sessions per day.
Drawing-in maneuver:
- You are lying on the ground with your feet flat on the floor & hip-width apart.
- Try to relax your hands by your sides.
- Then take a deep inhale.
- Breathe out & pull your belly button in toward your spine.
- Try to engage your abdominal muscles without tilting your hip joint.
- Hold this exercise for 10 to 15 seconds.
- Do the 10 times in 1 session & perform 3 sessions per day.
Lying lateral leg raises:
- You are lying on one side.
- Must be keeping your lower leg slightly bent on the ground.
- Then engage your core muscle by drawing your belly button in toward your spine.
- Raise your top leg without moving the rest of your body.
- Hold this exercise for 10 seconds at the top.
- Do the 10 times in 1 session & perform 3 sessions per day.
Supermans:
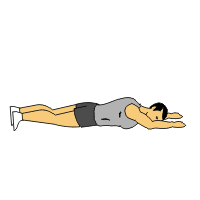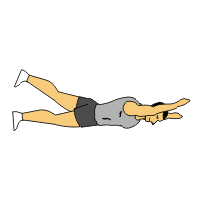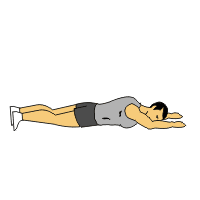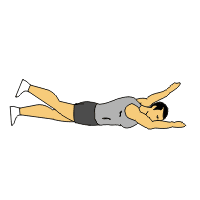
- You are lying on your stomach with your arms extended out in front of you & your legs long.
- Lift your hands & feet off the ground approximately 6 inches till you feel a contraction in your lower back.
- Then engage your core muscles by slightly lifting your belly button off the floor.
- Try to reach away with your hands & feet.
- Must be sure to look at the floor during this exercise to avoid neck strain.
- Hold this exercise for 10 seconds at the top.
- Do the 10 times in 1 session & perform 3 sessions per day.
In partial curls:

- You are lying on the ground with your feet flat on the floor.
- Must be keeping your knee joint bent.
- Then cross your hands over your chest.
- Take a deep breath.
- While you exhale position, brace your abdominals by pulling your belly button in toward your spine.
- Try to slowly lift your shoulder joint off the ground a few inches.
- Try to must keep your neck in line with your spine instead of rounding, to avoid pulling up with your neck.
- Hold this exercise for 10 seconds at the top.
- Do the 10 times in 1 session & perform 3 sessions per day.
Bird-dog:
- Start the exercise on the hands & knees joint with the shoulder joint directly over the hands & the hip joint directly over the knee joint.
- Tense the abdominal muscles & stretch the right arm straight out in front of the body.
- Hold this exercise position while staying balanced.
- Then slowly lift the left leg & extend it straight out behind the body.
- Hold this exercise position for 10 seconds.
- Try to slowly return to the starting position & repeat on the opposite side.
- Do the 10 times in 1 session & perform 3 sessions per day.
Plank:
- You are lying on the stomach with the forearms against the floor & the elbow joint directly in line with the shoulder joint.
- First, tighten the abdominal & gluteal muscles.
- Try to lift the hip joint & both knee joints off the floor.
- Hold this exercise position for 10–30 seconds without allowing the pelvis to sag toward the floor.
- Then slowly return to the start position.
- Do the 10 times in 1 session & perform 3 sessions per day.
- Modification:
- You can make this exercise less challenging by bending the knee joint slightly & keep them on the ground.
- You must focus on maintaining a straight line from the knee joint to the shoulders.
Side plank:
- You are lying on the right side of the body with the right side leg slightly bent & the left side leg straight with the foot on the floor. must be sure that the right arm is directly beneath the right shoulder joint with the forearm extended out in front.
- First tightening the abdominal muscles & lift the right hip off the floor.
- Then try to lift the right knee joint off the floor to straighten the right leg & stack the feet on top of each other.
- Must be keeping the body straight.
- Hold this exercise position for 30 seconds.
- Then slowly return to the starting position & repeat on the other side.
- Do the 10 times in 1 session & perform 3 sessions per day.
- When you find this exercise too difficult then must keep the bottom knee slightly bent & on the ground.
Abdominal crunches:
- You are lying with the back flat against the floor the knee joint bent & the feet flat with hip-width apart.
- Cross the hands over the chest & reach along the sides of the body toward the feet.
- First, tighten the abdominal muscles & lift the head and shoulder blades off the floor while exhaling.
- Then return to the starting position.
- Do the 10 times in 1 session & perform 3 sessions per day.
What is Surgery treatment for lower back muscle pain?
After the medical treatment & physiotherapy treatment pain is not relieved then the doctor is advised surgical treatment.
surgery is advised for you when you feel severe lower back pain which is not become to get better after 6 to12 weeks.
It almost depends on your decision on back surgery & in rare situations need immediate surgery for low back muscle pain.
Some surgery for lower back pain include :
- Decompression Surgeries:
- In this surgery process, a portion of a facet joint is removed to allow them better access to the nerve root & to relieve nerve pressure.
- This surgery removes the pressing on a nerve root from the spinal column including a herniated portion of a disc & a bone spur.
- Microdiscectomy:
- It is a minimally invasive procedure for you with a lumbar herniated disc which is lead to radicular leg pain – sciatica.
- Laminectomy:
- In this surgery, the process removes the part of the layer of the bone & soft tissue which is compressing a nerve & multiple nerve roots. this laminectomy is typically performed for someone with leg pain & weakness from spinal stenosis which is caused by changes in the facet joints, discs & bone spurs.
- This surgery is performed with open & minimally invasive techniques with relatively small incisions & minimal discomfort & recovery before returning to work with other activities.
- Lumbar Spinal Fusion Options:
- In this surgery remove the soft tissues between two & more adjacent vertebral bones which are replaced with bone & metal.
- This procedure enables the bones to grow together over time.
- It is typically 6 to 12 months & fuses into one long bone which is stable & eliminates motion at the spinal segments.
- In the lumbar spine, fusion occurs from the back = posterior approach, the front = anterior approach, and the side = lateral approach& combined.
- The modern techniques include implants, navigation & biologics which is made the surgery more predictable with an easier recovery & return to normal activity with work.
- This lumbar spinal fusion surgery is applied in many conditions like spondylolisthesis, stenosis, deformity, instability, degenerative disc disease & fracture.
- This surgery is also used in sacroiliac joint dysfunction & fusion of the sacroiliac joint.
- Tumors & infections are also treated with this fusion surgery, but it is far less common.
- Lumbar artificial disc:
- This disc replacement is a potential alternative to fusion surgery for symptomatic degenerative disc disease.
- In this procedure potential for a quicker recovery & maintaining more spinal motion than lumbar fusion.
- This long-term data is still being collected.
- Posterior motion device:
- This Coflex inter-laminar device is also an alternative to fusion for stenosis & mild degenerative spondylolisthesis.
- The goals of this approach are give to similar results as fusion but with a smaller surgery & faster recovery.
- Long-term data is still being collected.
What is self-Care for Low Back Pain?
When you feel mild or acute pain you are applied to home remedies that help you relieve the pain.
The self-care methods include:
- Short rest period:
- This lower back pain is improved by briefly avoiding strenuous activity.
- But the doctor is not advised to rest for more than a few days because it is lead to difficulty in healing.
- Activity modification:
- Another variant of resting is to stay active but avoid activities & positions which are aggravating your pain.
- For as long periods of sitting position in a car & at a desk make the pain worse.
- When your standing position makes the pain worse avoid chores that are required to standing position like washing dishes at the sink.
- You must be avoiding or minimizing activities positions which is help you prevent & reduce painful back spasms.
- Heat/ice therapy:
- Heat is produced by an electric heating pad, a hot water bottle, and chemical & adhesive heat wraps which help your muscles & improve the blood flow.
- When increased the blood flow is brought nutrients & oxygen to muscles for healing & stay healthy.
- When this low back is due to inflammation ice & cold packs are used to reduce the swelling.
- But it is important to protect the skin when you apply heat & ice to prevent tissue damage.
- Alternating the heat & ice which is most helpful when you return to activity so that always applying heat before activities helps you relax the muscles to allow better flexibility & mobility.
- Ice is applied after activity which is helpful to you and reduces the chances of an area becoming irritated & swollen from exercise.
- Over-the-counter pain medications:
- The most common over-the-counter (OTC) medications inculde to aspirin (e.g. Bayer), ibuprofen (e.g. Advil), naproxen (e.g. Aleve) & acetaminophen (e.g. Tylenol).
- Aspirin, ibuprofen & naproxen are anti-inflammatory medicines, which alleviate your low back pain which is due to swollen nerves or muscles.
- Acetaminophen drug works by interfering with the pain signals sent to the brain.
- All self-care treatments generally do not need guidance from a doctor but are always used carefully & attentively.
- When you are unsure about talking to a doctor.
How do prevent lower back muscle pain?
- You are maintaining a healthy weight because excess weight puts pressure on vertebrae & disks.
- Always do strengthen your abdominal muscles with Pilates & other exercise programs which are helpful to you in strengthening core muscles & give to support the spine.
- Lift anything in the right way = to avoid injuries, lift with your legs, not your back.
- You must hold heavy items close to your body.

26 Comments